Intro
Learn how to maintain healthy blood glucose levels through balanced diets, regular exercise, and stress management, reducing diabetes risk with optimal blood sugar control and insulin regulation.
Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke is reduced. On the other hand, high or low blood glucose levels can lead to a range of health problems, from mild symptoms like fatigue and dizziness to life-threatening conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis and hypoglycemic coma.
The importance of maintaining healthy blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 422 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels. Furthermore, an estimated 1.5 million people die each year from diabetes-related complications. In addition to diabetes, high blood glucose levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and certain types of cancer. Therefore, it is essential to understand the factors that influence blood glucose levels and to take steps to maintain healthy levels throughout life.
Understanding how blood glucose levels are regulated is vital for maintaining healthy levels. The body's primary source of glucose is the diet, which includes carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. When carbohydrates are digested, they are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. In individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to high blood glucose levels.
Maintaining Healthy Blood Glucose Levels through Diet

In addition to choosing low-GI foods, it is essential to be mindful of portion sizes and to eat regular, balanced meals throughout the day. Skipping meals or going for long periods without eating can lead to low blood glucose levels, while consuming large amounts of high-GI foods can cause a rapid spike in blood glucose. Drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks can also help regulate blood glucose levels. Furthermore, incorporating healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and olive oil into the diet can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and reduce the impact on blood glucose levels.
Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another crucial component of maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, which allows the body to more effectively use insulin and regulate blood glucose levels. Physical activity also helps to reduce stress, which can raise blood glucose levels, and can improve overall cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Additionally, incorporate strength-training exercises, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and other forms of physical activity to improve overall fitness and help regulate blood glucose levels.Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
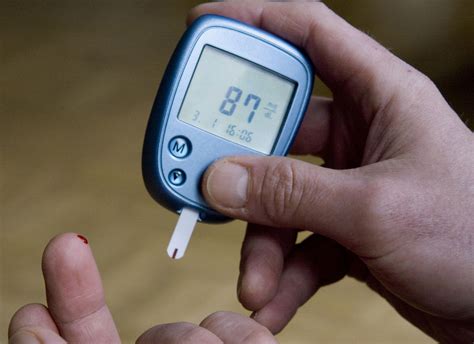
- Fasting blood glucose test: This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Postprandial blood glucose test: This test measures blood glucose levels after eating a meal.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): This test measures blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This test involves wearing a small device that tracks blood glucose levels throughout the day.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can help identify patterns and trends, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule and to develop a personalized plan for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
Managing Stress and Getting Enough Sleep
Managing stress and getting enough sleep are also crucial for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Stress can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate the impact of stress on blood glucose levels. Additionally, aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night can help regulate blood glucose levels and improve overall health.Medications and Supplements for Blood Glucose Control

However, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment and to monitor blood glucose levels regularly. Medications and supplements can have side effects and interact with other medications, so it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and to report any changes or concerns to a healthcare provider.
Natural Remedies for Blood Glucose Control
In addition to medications and supplements, there are several natural remedies that may help regulate blood glucose levels. These include:- Cinnamon: Cinnamon has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce blood glucose levels.
- Ginger: Ginger has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
- Berries: Berries like blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are rich in antioxidants and may help reduce blood glucose levels.
While these natural remedies may be beneficial, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using them, especially if you are taking medications or have a medical condition.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Blood Glucose Control

- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is rich in whole, unprocessed foods.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Managing stress through techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Getting enough sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours per night.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Limiting sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars.
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, and improve their overall health and well-being.
Support Systems for Blood Glucose Control
Having a support system in place can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. This can include:- Working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for blood glucose control.
- Joining a support group for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Sharing goals and progress with friends and family members.
- Using mobile apps or online tools to track blood glucose levels and monitor progress.
By having a support system in place, individuals can stay motivated and accountable, and make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. What lifestyle changes have you made to improve your blood glucose control? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? By sharing your story, you can help inspire and motivate others to take control of their health and well-being.
What are the symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+Symptoms of high blood glucose levels include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood glucose levels depends on the individual's health status and treatment plan. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule.
What are the benefits of regular physical activity for blood glucose control?
+Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
