Intro
Discover the Fodmap diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) relief, reducing symptoms with low Fodmap foods, gut-friendly recipes, and personalized meal planning for digestive health and wellness.
The FODMAP diet has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential to alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by recurring abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements. The FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that involves limiting or avoiding certain types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest. In this article, we will delve into the world of FODMAPs, exploring what they are, how they affect the body, and how the FODMAP diet can help manage IBS symptoms.
The term FODMAP is an acronym that stands for Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Mono-saccharides, and Polyols. These are types of carbohydrates that are found in a wide range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products. FODMAPs are not necessarily "bad" carbohydrates, but rather ones that can be problematic for individuals with sensitive digestive systems. When FODMAPs are not properly absorbed in the small intestine, they can be fermented by bacteria in the large intestine, leading to the production of gas and other symptoms.
FODMAPs and Their Effects on the Body
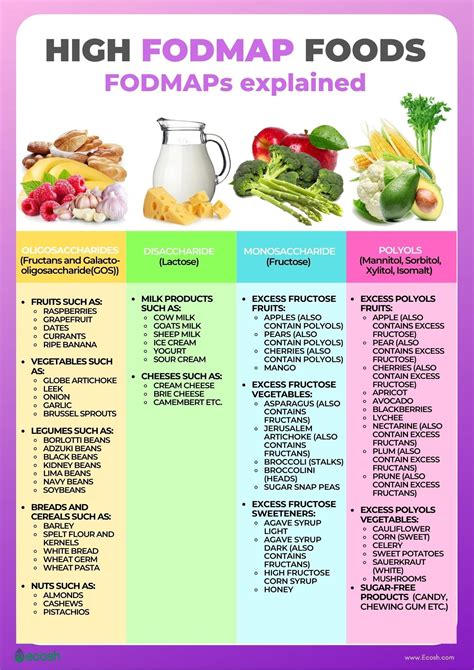
FODMAPs can have a significant impact on the body, particularly for individuals with IBS. When FODMAPs are fermented by bacteria in the large intestine, they can produce gas, leading to bloating, discomfort, and pain. Additionally, FODMAPs can also affect the movement of food through the digestive system, leading to changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation. Some common symptoms of FODMAP intolerance include:
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Bloating and gas
- Changes in bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and lethargy
Types of FODMAPs
There are several types of FODMAPs, each with its own unique characteristics and effects on the body. The main types of FODMAPs include:- Fructans: found in wheat, barley, rye, and some fruits and vegetables
- Galactans: found in legumes, such as beans and lentils
- Polyols: found in some fruits, such as apples and pears, and in sugar substitutes, such as sorbitol and xylitol
- Fructose: found in many fruits, such as apples and bananas, and in some sweeteners, such as high-fructose corn syrup
- Lactose: found in milk and other dairy products
The FODMAP Diet
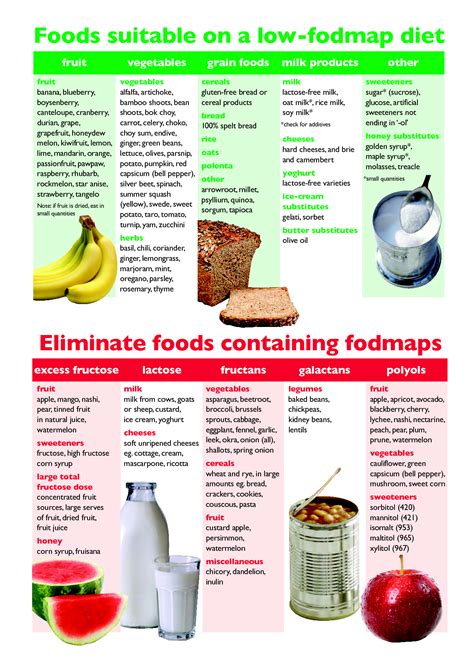
The FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that involves limiting or avoiding foods that are high in FODMAPs. The diet is typically divided into three phases:
- Elimination phase: This phase involves removing all high-FODMAP foods from the diet for a period of 2-6 weeks. This allows the body to adjust and reduces symptoms.
- Reintroduction phase: This phase involves gradually reintroducing high-FODMAP foods into the diet, one at a time, to assess tolerance.
- Modification phase: This phase involves making long-term changes to the diet, based on the results of the reintroduction phase, to minimize symptoms and optimize digestive health.
Foods to Avoid on the FODMAP Diet
Some common foods that are high in FODMAPs and should be avoided on the FODMAP diet include:- Wheat, barley, and rye
- Onions, garlic, and shallots
- Beans and legumes
- Apples, pears, and watermelon
- Dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and ice cream
- High-fructose corn syrup and other sweeteners
Benefits of the FODMAP Diet

The FODMAP diet has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of IBS and improving overall digestive health. Some of the benefits of the FODMAP diet include:
- Reduced abdominal pain and discomfort
- Improved bowel habits
- Reduced bloating and gas
- Improved energy levels
- Enhanced overall quality of life
Challenges of the FODMAP Diet
While the FODMAP diet can be effective in managing IBS symptoms, it can also be challenging to follow. Some of the challenges of the FODMAP diet include:- Restrictive nature of the diet
- Difficulty in identifying high-FODMAP foods
- Social and emotional challenges of changing eating habits
- Potential for nutrient deficiencies if not planned properly
Practical Tips for Following the FODMAP Diet

Here are some practical tips for following the FODMAP diet:
- Keep a food diary to track symptoms and identify trigger foods
- Read food labels carefully to identify high-FODMAP ingredients
- Plan meals in advance to ensure a balanced and varied diet
- Seek support from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian
- Be patient and persistent, as it may take time to notice improvements in symptoms
Common Mistakes to Avoid on the FODMAP Diet
Some common mistakes to avoid on the FODMAP diet include:- Not fully eliminating high-FODMAP foods during the elimination phase
- Reintroducing high-FODMAP foods too quickly or in large quantities
- Not seeking support from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian
- Not planning meals carefully to ensure a balanced and varied diet
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, the FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that can be effective in managing symptoms of IBS and improving overall digestive health. By understanding what FODMAPs are, how they affect the body, and how to follow the FODMAP diet, individuals can take control of their digestive health and improve their overall quality of life. If you are considering trying the FODMAP diet, be sure to seek support from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian and be patient and persistent as you work through the different phases of the diet.
We invite you to share your experiences with the FODMAP diet in the comments below. Have you tried the FODMAP diet? What were your results? Do you have any questions or concerns about the diet? Share your thoughts and let's start a conversation.
What are FODMAPs and how do they affect the body?
+FODMAPs are types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest. When FODMAPs are not properly absorbed in the small intestine, they can be fermented by bacteria in the large intestine, leading to the production of gas and other symptoms.
What are the benefits of the FODMAP diet?
+The FODMAP diet has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of IBS and improving overall digestive health. Some of the benefits of the FODMAP diet include reduced abdominal pain and discomfort, improved bowel habits, and enhanced overall quality of life.
How do I get started with the FODMAP diet?
+To get started with the FODMAP diet, it's recommended that you seek support from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They can help you understand the diet and create a personalized plan to meet your needs.
