Intro
Recognize Heart Attack Signs Women often miss, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea, to prevent cardiovascular disease and silent heart attacks.
Heart attacks are a leading cause of death worldwide, and they can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. While heart attacks are often associated with men, women are also at risk, and their symptoms can be different from those experienced by men. It's essential to understand the signs of a heart attack in women to provide timely and effective treatment. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing heart attack signs in women and explore the various symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies.
Heart disease is the number one killer of women in the United States, accounting for one in every five deaths. Despite this, many women are unaware of the risks and signs of a heart attack. The American Heart Association reports that women are more likely to die from heart disease than from breast cancer, making it crucial to educate women about the warning signs of a heart attack. By recognizing these signs, women can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and death.
The importance of recognizing heart attack signs in women cannot be overstated. Women often experience different symptoms than men, which can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment. For example, women may experience shortness of breath, nausea, or fatigue, rather than the classic chest pain associated with heart attacks in men. These symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions, such as indigestion or anxiety, leading to delayed treatment. By understanding the unique symptoms of a heart attack in women, healthcare providers and individuals can take prompt action, saving lives and improving outcomes.
Understanding Heart Attack Signs in Women
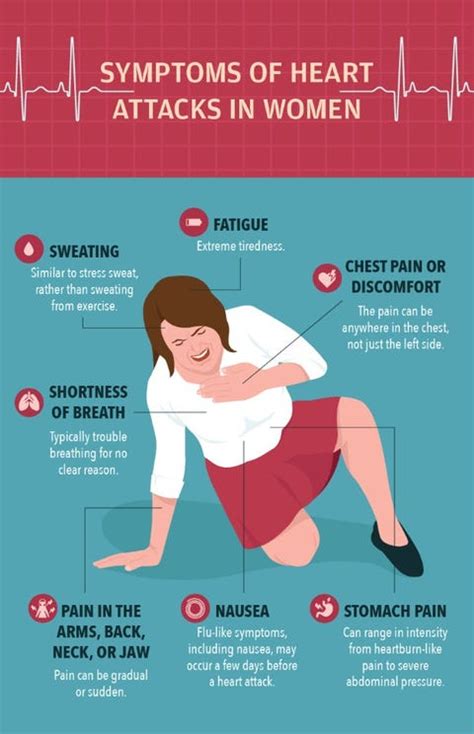
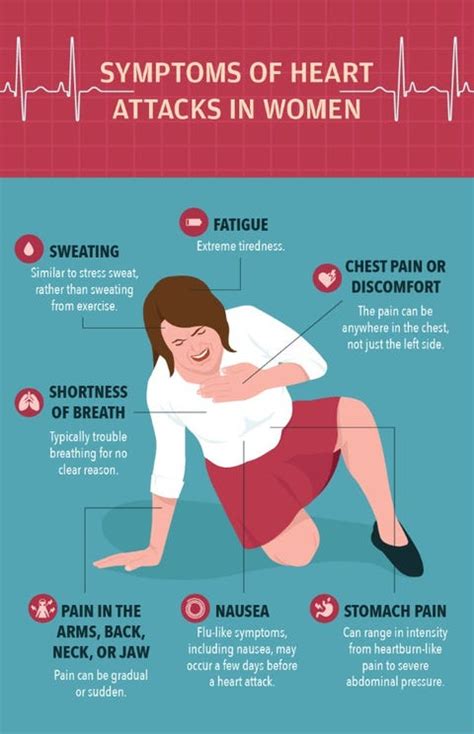
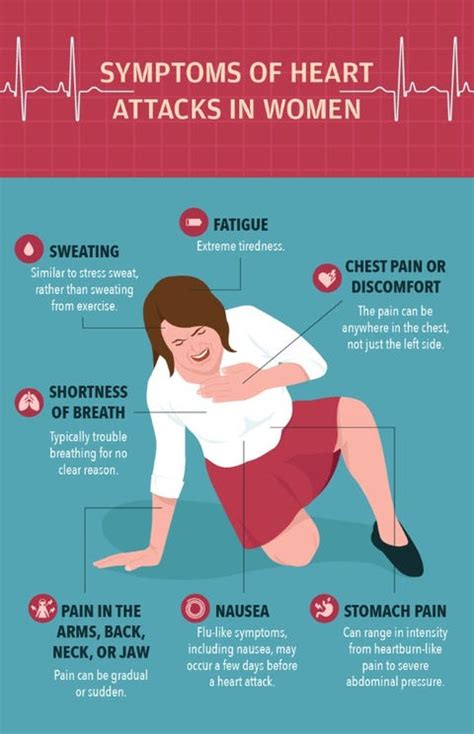
Heart attacks in women can manifest in various ways, making it essential to recognize the different signs and symptoms. Some common symptoms of a heart attack in women include:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This is the most common symptom of a heart attack in women, but it may not always be severe or persistent.
- Shortness of breath: Women may experience shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, even when sitting still or engaging in light physical activity.
- Pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach: Women may experience pain or discomfort in these areas, which can be a sign of a heart attack.
- Nausea or vomiting: Women may feel nauseous or vomit, which can be mistaken for other conditions, such as food poisoning or a stomach virus.
- Fatigue: Women may feel extremely tired or weak, even after resting or engaging in light physical activity.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Women may feel lightheaded or dizzy, which can increase the risk of falls and other accidents.
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks in Women
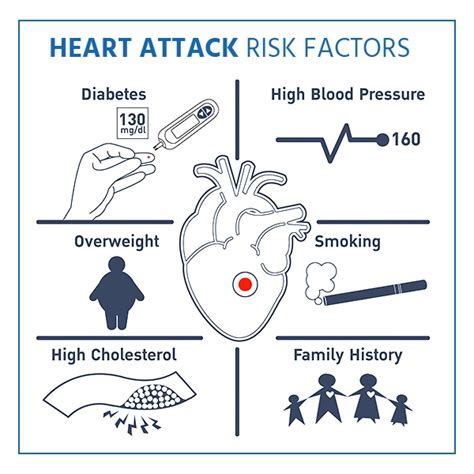
Several risk factors can increase a woman's likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. These include:
- Age: Women over 55 are at higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Family history: Women with a family history of heart disease are more likely to experience a heart attack.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- High cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes are at higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Preventing Heart Attacks in Women
Preventing heart attacks in women requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some strategies for preventing heart attacks in women include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Getting enough sleep: Adequate sleep can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Treatment Options for Heart Attacks in Women
Treatment options for heart attacks in women depend on the severity of the attack and the individual's overall health. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Medications such as aspirin, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors can help reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes.
- Angioplasty: Angioplasty involves inserting a catheter into the blocked artery to restore blood flow.
- Stenting: Stenting involves inserting a small mesh tube into the blocked artery to keep it open.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): CABG involves surgically bypassing the blocked artery to restore blood flow.
Recovering from a Heart Attack

Recovering from a heart attack requires a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. Some strategies for recovering from a heart attack include:
- Following a rehabilitation program: A rehabilitation program can help women regain strength, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
- Making lifestyle changes: Women can reduce their risk of future heart attacks by making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a healthy diet.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart disease and heart attacks, making it essential to manage stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Getting enough sleep: Adequate sleep can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Supporting Loved Ones

Supporting loved ones who have experienced a heart attack is crucial for their recovery and well-being. Some ways to support loved ones include:
- Encouraging lifestyle changes: Encourage loved ones to make lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a healthy diet.
- Providing emotional support: Provide emotional support by listening, offering words of encouragement, and helping with daily tasks.
- Helping with medication management: Help loved ones manage their medications by reminding them to take their medications, filling prescriptions, and monitoring side effects.
- Encouraging rehabilitation: Encourage loved ones to participate in a rehabilitation program to regain strength, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, recognizing heart attack signs in women is crucial for providing timely and effective treatment. By understanding the unique symptoms of a heart attack in women, healthcare providers and individuals can take prompt action, saving lives and improving outcomes. Preventing heart attacks in women requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, and recovering from a heart attack requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and emotional support.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with heart attacks in women. Have you or a loved one experienced a heart attack? What symptoms did you experience, and how did you receive treatment? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to raise awareness about heart attack signs in women.
What are the most common symptoms of a heart attack in women?
+The most common symptoms of a heart attack in women include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, nausea or vomiting, fatigue, and lightheadedness or dizziness.
How can women reduce their risk of heart attacks?
+Women can reduce their risk of heart attacks by maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a healthy diet, managing stress, getting enough sleep, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
What are the treatment options for heart attacks in women?
+Treatment options for heart attacks in women depend on the severity of the attack and the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include medications, angioplasty, stenting, and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
