Intro
Discover how HbA1c matters in diabetes management, affecting blood sugar control, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risk, with 5 key ways to monitor and improve your HbA1c levels for better health outcomes.
The importance of HbA1c cannot be overstated, especially for individuals living with diabetes. HbA1c, or glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a crucial indicator of how well diabetes is being managed, and its significance extends beyond just monitoring blood sugar levels. Understanding the implications of HbA1c is vital for maintaining good health, preventing complications, and improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
For people without diabetes, HbA1c levels can also provide valuable insights into their risk of developing the condition. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and physical activity, can significantly impact HbA1c levels, making it an essential marker for overall health. Moreover, research has shown that HbA1c levels are associated with various health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and even cognitive function. As such, it's essential to grasp the concept of HbA1c and its far-reaching implications for health and wellbeing.
The impact of HbA1c on health is multifaceted, and its relevance extends to various aspects of healthcare. From diagnosing and managing diabetes to predicting the risk of complications, HbA1c plays a critical role. Furthermore, HbA1c levels can influence treatment decisions, such as the need for medication or lifestyle interventions. By understanding the importance of HbA1c, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life.
Understanding HbA1c
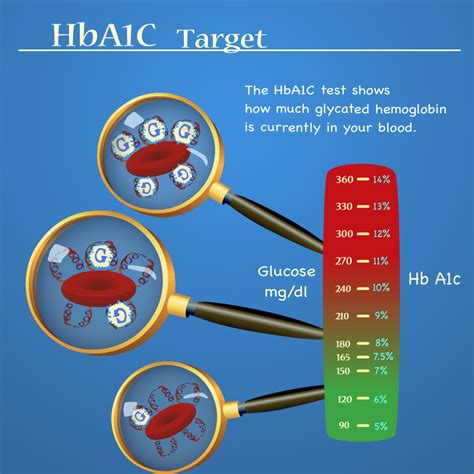
How HbA1c is Measured
HbA1c is typically measured using a blood test, which can be performed at a healthcare provider's office or at a laboratory. The test involves taking a small sample of blood from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually reported as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating higher average blood glucose levels.Diagnosing and Monitoring Diabetes

Treatment Goals
The goal of diabetes treatment is to achieve and maintain HbA1c levels as close to normal as possible. For most adults, the target HbA1c level is less than 7%. However, this goal may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, comorbidities, and the risk of hypoglycemia. By regularly monitoring HbA1c levels, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans to help individuals with diabetes achieve their target levels and reduce the risk of complications.Predicting the Risk of Complications

Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in individuals with diabetes. HbA1c levels are a strong predictor of cardiovascular risk, with higher levels associated with an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. By maintaining good control of blood glucose levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease and improve their overall health outcomes.Lifestyle Interventions
Dietary Recommendations
The American Diabetes Association recommends a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Individuals with diabetes should aim to limit their intake of added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates, which can raise HbA1c levels. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks can help manage blood glucose levels.Medications and Therapies

Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is often necessary for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may be required for those with type 2 diabetes who are unable to achieve target HbA1c levels with oral medications. Insulin works by replacing the body's natural insulin, which is either absent or insufficient. There are several types of insulin, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, each with a different duration of action.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with HbA1c in the comments below. How do you manage your HbA1c levels, and what strategies have been most effective for you? Share this article with friends and family who may benefit from learning more about HbA1c and its significance for health and wellbeing.
What is HbA1c, and why is it important for diabetes management?
+HbA1c, or glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a crucial indicator of how well diabetes is being managed and is used to diagnose and monitor diabetes.
How often should I check my HbA1c levels, and what is the target range?
+For most adults, HbA1c levels should be checked at least twice a year, and the target range is less than 7%. However, this goal may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, comorbidities, and the risk of hypoglycemia.
Can lifestyle interventions, such as diet and physical activity, help lower HbA1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle interventions, such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity, can help lower HbA1c levels and improve insulin sensitivity. A balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help reduce HbA1c levels.
