Intro
Discover the impact of high INR on health, including increased risk of bleeding, stroke, and cardiovascular events, and learn 5 ways to manage INR levels, preventing complications and ensuring optimal anticoagulation therapy, blood thinner safety, and overall well-being.
The importance of understanding the concept of INR, or Internationalized Normalized Ratio, cannot be overstated. This critical measure is used to assess the time it takes for blood to clot and is essential in evaluating the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin. For individuals taking these medications, monitoring INR levels is crucial to prevent both thrombosis and bleeding complications. High INR levels indicate that blood is taking longer than normal to clot, which can increase the risk of bleeding. On the other hand, low INR levels suggest that blood is clotting too quickly, which can lead to the formation of dangerous blood clots. The delicate balance of INR levels is vital for maintaining good health, especially for those with certain medical conditions or those undergoing specific treatments.
Understanding the implications of high INR levels is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. A high INR reading can signal that the dosage of anticoagulant medication needs adjustment to prevent adverse effects. It is also crucial for individuals to be aware of the factors that can influence INR levels, including dietary changes, other medications, and lifestyle factors. By grasping the significance of INR and how it relates to their health, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications. Moreover, a comprehensive understanding of INR can facilitate better communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to more effective treatment plans and improved outcomes.
The concept of INR and its management is multifaceted, involving not only the monitoring of blood clotting times but also the consideration of various factors that can impact these levels. Dietary factors, for instance, play a significant role in INR management. Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy greens, can affect how the body responds to warfarin, necessitating careful dietary planning for individuals on this medication. Additionally, the presence of other health conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, can influence INR levels, making regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans essential. As the management of INR involves a complex interplay of medication, diet, and health status, a thorough understanding of these dynamics is vital for optimizing patient care.
Introduction to INR and Its Significance
The Internationalized Normalized Ratio (INR) is a test used to measure blood clotting and is primarily used to monitor patients on warfarin therapy. Warfarin is an anticoagulant that helps prevent blood clots from forming or growing. The INR test is crucial because it helps determine if the blood is clotting too quickly or too slowly. An INR range of 2.0 to 3.0 is typically considered the therapeutic range for most indications, though this can vary depending on the individual's condition and the reason for anticoagulation.
Understanding INR Ranges

- Low INR (Below 2.0): Indicates that the blood is clotting too quickly, which may suggest that the dose of anticoagulant medication is too low. This can increase the risk of thrombosis.
- Therapeutic INR (2.0-3.0): This range is generally considered optimal for most patients on warfarin, balancing the risk of clotting and bleeding.
- High INR (Above 3.0): Suggests that the blood is clotting too slowly, which may indicate that the dose of anticoagulant medication is too high. This can increase the risk of bleeding.
Factors Influencing INR Levels
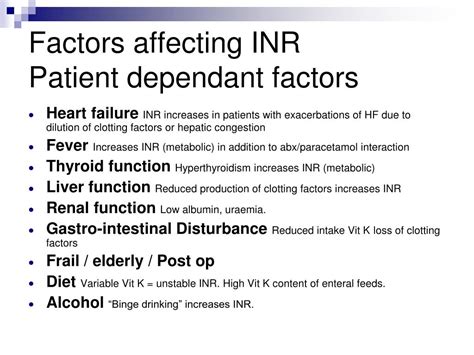
Several factors can influence INR levels, including:
- Diet: Foods high in vitamin K can decrease INR levels, while foods low in vitamin K can increase them.
- Other Medications: Certain medications can interact with warfarin, either increasing or decreasing its effect.
- Health Conditions: Liver or kidney disease can affect how the body metabolizes warfarin.
- Lifestyle Changes: Significant changes in alcohol consumption or physical activity can also impact INR levels.
Managing High INR Levels
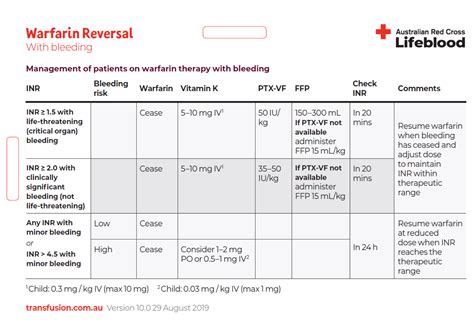
Managing high INR levels involves adjusting the dose of warfarin and addressing any underlying factors that may be contributing to the elevated INR. This can include dietary adjustments, reviewing other medications for potential interactions, and treating any underlying health conditions. In cases of significantly elevated INR levels, especially if associated with bleeding, more urgent interventions may be necessary, including the administration of vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma to rapidly reverse anticoagulation.
Complications of High INR Levels
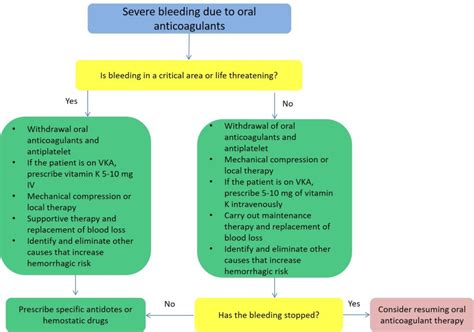
High INR levels can lead to serious complications, primarily related to an increased risk of bleeding. This can range from minor bleeding, such as bruising or nosebleeds, to more severe and potentially life-threatening bleeding, such as intracranial hemorrhage. The risk of bleeding underscores the importance of regular INR monitoring and prompt adjustment of anticoagulant therapy as needed.
Regular Monitoring and Patient Education

Regular monitoring of INR levels and patient education are key components of effective anticoagulation management. Patients should be informed about the importance of adhering to their medication regimen, the need for regular blood tests, and how to recognize signs of bleeding or thrombosis. Additionally, understanding the factors that can influence INR levels empowers patients to take an active role in managing their condition, reducing the risk of complications.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the management of INR levels is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors, including medication, diet, and underlying health conditions. As research continues to advance our understanding of anticoagulation therapy and its effects on the body, new strategies and technologies may emerge to improve the management of INR levels and reduce the risk of complications. For now, a comprehensive approach that includes regular monitoring, patient education, and timely adjustments to treatment plans remains the cornerstone of effective INR management.
What does a high INR level indicate?
+A high INR level indicates that the blood is taking longer than normal to clot, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
How often should INR levels be monitored?
+The frequency of INR monitoring depends on the individual's condition and stability of their INR levels but is typically done weekly or biweekly for patients on warfarin.
What factors can influence INR levels?
+Several factors can influence INR levels, including diet (especially vitamin K intake), other medications, health conditions like liver or kidney disease, and lifestyle changes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences related to managing INR levels and anticoagulation therapy. Your insights can help others better understand the complexities of INR management and the importance of careful monitoring and patient education. By engaging in this discussion, we can work together to improve outcomes for individuals on anticoagulant medications and promote a deeper understanding of the factors that influence INR levels.
