Intro
Understand High Pt Inr, a blood test measuring clotting time, related to prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and blood coagulation, helping diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulant therapy.
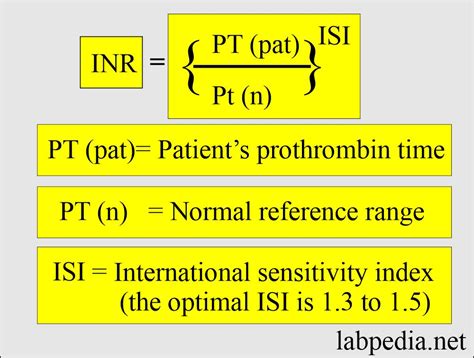
High PT INR is a condition where the Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR) are elevated, indicating a higher risk of bleeding. PT and INR are blood tests used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot and the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. A high PT INR can be a cause for concern, as it may indicate an increased risk of bleeding complications.
The importance of monitoring PT INR levels cannot be overstated, as it helps healthcare professionals to adjust anticoagulant medication dosages and prevent potential bleeding risks. In addition, high PT INR levels can be a sign of underlying health conditions, such as liver disease or vitamin K deficiency, which require prompt medical attention. In this article, we will delve into the world of high PT INR, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
PT INR is a crucial parameter in the management of patients taking anticoagulant medications, as it helps to prevent thrombotic and bleeding complications. Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, work by inhibiting the production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, thereby prolonging the time it takes for blood to clot. By monitoring PT INR levels, healthcare professionals can adjust the dosage of anticoagulant medications to achieve optimal anticoagulation, reducing the risk of bleeding and thrombotic complications.
What is High PT INR?
Causes of High PT INR
High PT INR can be caused by a range of factors, including: * Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin * Liver disease, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis * Vitamin K deficiency * Other medical conditions, such as kidney disease or cancer * Interactions with other medications, such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications * Genetic disorders, such as factor II or factor VII deficiencySymptoms of High PT INR
Diagnosis of High PT INR
The diagnosis of high PT INR typically involves a combination of laboratory tests and physical examination. The following tests may be used to diagnose high PT INR: * Prothrombin Time (PT) test * International Normalized Ratio (INR) test * Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) test * Complete Blood Count (CBC) test * Liver function tests, such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) * Vitamin K level testTreatment Options for High PT INR
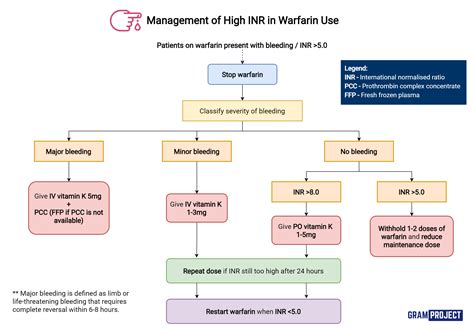
Management Strategies for High PT INR
The management of high PT INR requires a comprehensive approach that includes: * Regular monitoring of PT INR levels * Adjusting anticoagulant medication dosages as needed * Avoiding medications that interact with anticoagulant medications * Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle * Avoiding activities that increase the risk of bleeding, such as contact sportsComplications of High PT INR
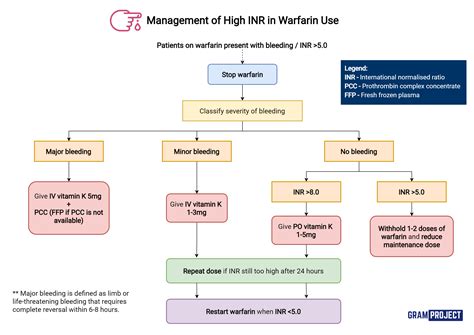
Prevention of High PT INR
The prevention of high PT INR involves: * Regular monitoring of PT INR levels * Adjusting anticoagulant medication dosages as needed * Avoiding medications that interact with anticoagulant medications * Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle * Avoiding activities that increase the risk of bleeding, such as contact sportsConclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high PT INR in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. We also encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about high PT INR.
What is the normal range for PT INR?
+The normal range for PT INR varies depending on the laboratory and the specific test used, but generally, a PT INR of 1.0-1.5 is considered normal.
What are the symptoms of high PT INR?
+The symptoms of high PT INR can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition, but common symptoms include easy bruising or bleeding, nosebleeds or bleeding gums, and heavy menstrual bleeding or prolonged bleeding after childbirth.
How is high PT INR diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of high PT INR typically involves a combination of laboratory tests, including Prothrombin Time (PT) test, International Normalized Ratio (INR) test, and Complete Blood Count (CBC) test, as well as physical examination and medical history.
What are the treatment options for high PT INR?
+The treatment options for high PT INR depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition, but may include adjusting anticoagulant medication dosages, vitamin K supplementation, and fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) transfusions.
How can high PT INR be prevented?
+High PT INR can be prevented by regular monitoring of PT INR levels, adjusting anticoagulant medication dosages as needed, avoiding medications that interact with anticoagulant medications, maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle, and avoiding activities that increase the risk of bleeding, such as contact sports.
