Intro
Discover 5 ways a higher sed rate affects health, including inflammation, infection, and autoimmune disorders, with insights into ESR tests and abnormal results.
Elevated sedimentation rates, often referred to as sed rates, are a common indicator of inflammation within the body. The sed rate test measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle in a test tube containing a blood sample. It's used to detect and monitor various conditions, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancers. Understanding the implications of a higher sed rate can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of underlying conditions.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, aiming to protect against harm, such as infections, injuries, and toxins. However, chronic or excessive inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of various diseases. A higher sed rate suggests the presence of inflammation, which could be indicative of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. It's essential to identify the causes of elevated sed rates to provide appropriate treatment and prevent potential complications.
The sed rate can be influenced by several factors, including age, gender, and the presence of certain medical conditions. For instance, sed rates naturally increase with age and are generally higher in women than in men. However, significantly elevated sed rates, particularly when accompanied by symptoms such as fever, weight loss, or fatigue, warrant further investigation. Healthcare providers use sed rate tests in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as complete blood counts, blood chemistry tests, and imaging studies, to determine the cause of inflammation and develop an effective treatment plan.
Understanding Sed Rate
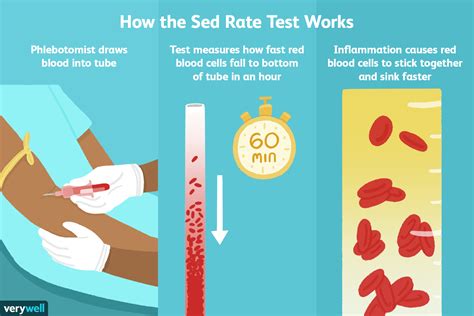
The sed rate is a non-specific test, meaning it does not diagnose a specific disease but rather indicates the presence of inflammation. It's crucial to interpret sed rate results in the context of clinical symptoms, medical history, and other laboratory findings. For example, a mildly elevated sed rate in an otherwise healthy individual might not be as concerning as a significantly elevated sed rate in someone with symptoms of infection or autoimmune disease.
Causes of Elevated Sed Rates
Several conditions can cause an elevated sed rate, including: - Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to inflammation and an increased sed rate. - Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues, can cause chronic inflammation. - Cancers: Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma or multiple myeloma, can lead to elevated sed rates due to the production of abnormal proteins that promote inflammation. - Chronic diseases: Conditions like kidney disease, liver disease, and heart disease can also contribute to increased sed rates.Diagnosing Underlying Conditions

Diagnosing the underlying cause of an elevated sed rate involves a comprehensive approach, including:
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient's medical history to identify any pre-existing conditions that could contribute to inflammation.
- Physical Examination: Performing a thorough physical examination to look for signs of infection, inflammation, or other conditions.
- Laboratory Tests: Conducting additional laboratory tests, such as complete blood counts, blood chemistry tests, and specific tests for autoimmune diseases or infections.
- Imaging Studies: Using imaging studies like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize internal organs and tissues for signs of inflammation or disease.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for an elevated sed rate focuses on addressing the underlying cause of inflammation. This may involve: - **Anti-inflammatory Medications**: Prescribing medications to reduce inflammation, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids. - **Antibiotics or Antivirals**: Administering antibiotics or antivirals to treat underlying infections. - **Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)**: Using DMARDs to manage autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. - **Supportive Care**: Providing supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and nutritional support, to help manage symptoms and promote recovery.Prevention and Lifestyle Changes

While some causes of elevated sed rates cannot be prevented, adopting certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and related conditions:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can contribute to chronic inflammation; maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce this risk.
- Eating an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and low in processed and sugary foods, can help reduce inflammation.
- Staying Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for overall health and can help reduce inflammation.
- Managing Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation; engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are crucial for individuals with elevated sed rates. This allows for: - **Tracking Progress**: Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and adjusting the treatment plan as necessary. - **Early Detection of Complications**: Identifying potential complications or worsening of the underlying condition early, which can improve outcomes. - **Preventing Future Episodes**: Implementing strategies to prevent future episodes of inflammation and related conditions.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, an elevated sed rate is a significant indicator of inflammation that requires thorough investigation to determine the underlying cause. By understanding the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for elevated sed rates, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to manage inflammation and prevent potential complications. It's essential to adopt a proactive approach to health, incorporating lifestyle changes that promote overall well-being and reduce the risk of chronic inflammation.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about elevated sed rates and inflammation in the comments below. If you found this information helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding the importance of sed rate tests and managing inflammation.
What does an elevated sed rate indicate?
+An elevated sed rate indicates the presence of inflammation in the body, which could be due to various conditions such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers.
How is an elevated sed rate diagnosed?
+Diagnosing an elevated sed rate involves a comprehensive approach including medical history review, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to identify the underlying cause of inflammation.
What are the treatment options for an elevated sed rate?
+Treatment for an elevated sed rate focuses on addressing the underlying cause of inflammation and may include anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics or antivirals, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and supportive care.
