Intro
Discover 5 ways diabetes management lowers blood sugar levels, including diet, exercise, and medication, to help regulate glucose and prevent complications like hyperglycemia and insulin resistance.
Managing diabetes is a delicate balance of lifestyle choices, medication, and monitoring. One of the most critical aspects of diabetes management is maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are too high, it can lead to a range of complications, from mild symptoms like fatigue and blurred vision to severe conditions such as kidney damage and nerve damage. Therefore, understanding how to lower blood sugar levels is essential for individuals living with diabetes.
The importance of managing blood sugar cannot be overstated. High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can lead to serious health issues if left unchecked. It can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision problems. On the other hand, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can cause confusion, shakiness, and even loss of consciousness. The goal for individuals with diabetes is to keep their blood sugar levels within a target range, which may vary depending on the individual, their diabetes type, and other health factors.
Living with diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By making informed choices about what to eat, how much to exercise, and when to take medication, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and prevent complications. Moreover, understanding the mechanisms by which different interventions lower blood sugar can empower individuals to take control of their health. Whether through dietary changes, increased physical activity, or the use of medications, there are several ways to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Understanding Blood Sugar Regulation
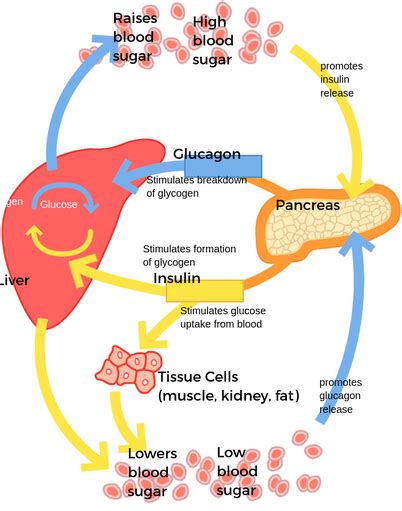
Blood sugar regulation is a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thus lowering blood sugar levels. In individuals with diabetes, either the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). Understanding how insulin works and how other factors influence blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes.
Role of Insulin in Blood Sugar Lowering
Insulin plays a pivotal role in lowering blood sugar levels. After eating, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, which facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. For individuals with diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to mimic this natural process and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.Dietary Changes to Lower Blood Sugar

Dietary changes are among the most effective ways to lower blood sugar levels. A diet rich in whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar. These foods are typically rich in fiber, which can slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, choosing foods with a low glycemic index (GI) can help regulate blood sugar levels. The GI is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are digested more slowly, resulting in a more gradual and lower peak of blood sugar.
Practical Dietary Tips
- **Eat Regular Meals:** Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar, and then overeating can cause high blood sugar. Regular meals help maintain stable blood sugar levels. - **Choose Whole Foods:** Whole, unprocessed foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats are rich in nutrients and fiber, which can help lower blood sugar levels. - **Limit Sugary Drinks and Foods:** Sugary drinks and foods can cause blood sugar to spike. Limiting these can help prevent high blood sugar levels.Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity are crucial components of diabetes management. Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, thereby facilitating the entry of glucose into cells. Physical activity can also reduce the risk of heart disease, improve blood flow, and help with weight management, all of which are important for individuals with diabetes.
Types of Exercise for Diabetes Management
- **Aerobic Exercise:** Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent for improving cardiovascular health and lowering blood sugar levels. - **Resistance Training:** Building muscle through resistance exercises can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively lower blood sugar levels. - **High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):** This type of exercise has been shown to be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels.Medications for Lowering Blood Sugar

For many individuals with diabetes, medication is a necessary part of their treatment plan. There are several types of diabetes medications, each working in a different way to lower blood sugar levels. Some medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, while others improve the body's use of insulin or slow the absorption of sugar from the gut.
Common Diabetes Medications
- **Metformin:** Often the first medication prescribed for Type 2 diabetes, metformin works by improving the body's sensitivity to insulin and reducing glucose production in the liver. - **Sulfonylureas:** These medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. - **GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:** These drugs help the body release more insulin when needed and decrease the amount of sugar made by the liver.Monitoring and Adjusting

Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for understanding how different factors, such as diet, exercise, and medication, affect blood sugar. By tracking blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can identify patterns and make informed decisions about their care. This might involve adjusting the timing or dosage of medication, changing eating habits, or increasing physical activity.
Tools for Monitoring Blood Sugar
- **Blood Glucose Meters:** These devices measure the current level of glucose in the blood. - **Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs):** CGMs provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering a more detailed picture of blood sugar levels and trends. - **Mobile Apps and Online Platforms:** Many apps and platforms allow individuals to track their blood sugar levels, medication, physical activity, and diet, providing valuable insights into their diabetes management.Stress Management and Blood Sugar

Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. When the body is under stress, it releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep can help keep blood sugar levels under control.
Techniques for Managing Stress
- **Meditation and Mindfulness:** Practices like meditation and mindfulness can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being. - **Yoga:** Combining physical movement with deep breathing and meditation, yoga can help lower stress levels and improve insulin sensitivity. - **Getting Enough Sleep:** Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and can help regulate blood sugar levels. Most adults need 7-8 hours of sleep per night.What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. Generally, individuals with diabetes should check their blood sugar levels at least four times a day, but this can vary based on individual needs and healthcare provider recommendations.
Can diet and exercise alone manage diabetes?
+For some individuals with Type 2 diabetes, diet and exercise may be enough to manage the condition, especially if caught early. However, many people will require medication or insulin therapy in addition to lifestyle changes to effectively manage their diabetes.
As individuals navigate the complexities of diabetes management, it's essential to remember that everyone's journey is unique. What works for one person may not work for another, and it's crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to find the right balance of diet, exercise, and medication. By staying informed, proactive, and committed to their health, individuals with diabetes can lead full and active lives, managing their condition effectively and preventing long-term complications. If you have diabetes or are concerned about developing it, take the first step today by talking to your healthcare provider about creating a personalized plan to manage your blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. Share your experiences and tips for managing diabetes in the comments below, and consider sharing this article with someone who might find it helpful. Together, we can support each other in the journey towards better health and wellness.
