Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to get GBS, including Guillain-Barré Syndrome treatment, recovery, and management strategies, to alleviate symptoms and improve neurological health outcomes.
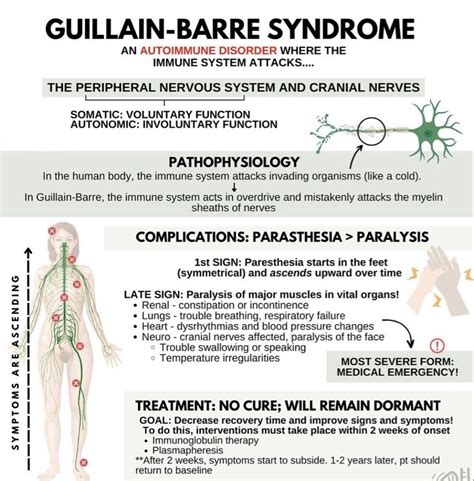
The importance of understanding Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cannot be overstated, as it is a rare but potentially life-threatening neurological disorder. GBS occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous system, which can lead to muscle weakness, numbness, and paralysis. The exact cause of GBS is not fully understood, but it is often triggered by a bacterial or viral infection. As researchers and medical professionals continue to study this complex condition, it is essential for the general public to be aware of the potential risk factors and ways to reduce their likelihood of developing GBS.
GBS is a rare condition, affecting only about 1 in 100,000 people, but its impact can be severe and long-lasting. The recovery process for GBS can be lengthy, and in some cases, patients may experience residual weakness or other neurological symptoms. Given the potential severity of GBS, it is crucial to understand the possible ways to get GBS and take steps to minimize the risk. While some risk factors, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, others can be managed through lifestyle changes and preventive measures.
The medical community has made significant progress in understanding GBS, but more research is needed to uncover the underlying mechanisms of the disease. As scientists continue to investigate the causes and effects of GBS, it is essential for individuals to be proactive in protecting their health. By being aware of the potential risk factors and taking preventive measures, people can reduce their likelihood of developing GBS. In this article, we will explore five possible ways to get GBS, discuss the current understanding of the condition, and provide guidance on reducing the risk of developing this debilitating disorder.
Introduction to GBS

Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of GBS are complex and multifaceted. While some cases may be triggered by a bacterial or viral infection, others may be linked to genetic or environmental factors. Understanding the potential causes and risk factors is crucial in reducing the likelihood of developing GBS. Some of the known risk factors include: * Recent bacterial or viral infection * Genetics * Weakened immune system * Certain vaccinations or medications * Autoimmune disordersViral Infections and GBS
Reducing the Risk of GBS
While some risk factors, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, others can be managed through lifestyle changes and preventive measures. Some ways to reduce the risk of GBS include: * Practicing good hygiene to reduce the risk of viral infections * Getting vaccinated against certain viral infections, such as influenza * Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle to support immune function * Avoiding certain medications or vaccinations that may trigger GBSBacterial Infections and GBS
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for GBS, treatment and management options are available to help alleviate symptoms and support recovery. Some common treatment options include: * Plasma exchange to remove antibodies from the blood * Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to neutralize antibodies * Pain management medications to alleviate discomfort * Physical therapy to support rehabilitation and recoveryGenetic Predisposition and GBS

Current Research and Developments
Researchers are continually working to uncover the underlying mechanisms of GBS and develop new treatments and management options. Some current areas of research include: * Investigating the role of genetic variants in GBS * Developing new treatments, such as immunomodulatory therapies * Improving diagnostic techniques to facilitate early detection and treatmentAutoimmune Disorders and GBS
Managing Autoimmune Disorders
Managing autoimmune disorders is crucial in reducing the risk of GBS. Some ways to manage autoimmune disorders include: * Working with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan * Practicing good self-care, including stress management and exercise * Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle to support immune functionConclusion and Next Steps

We invite readers to share their thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments section below. If you or someone you know has been affected by GBS, we encourage you to reach out to a healthcare provider or support organization for guidance and resources. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote understanding of this important health topic.
What are the symptoms of GBS?
+The symptoms of GBS can include muscle weakness, numbness, and paralysis. In severe cases, GBS can lead to respiratory failure and other life-threatening complications.
How is GBS diagnosed?
+GBS is typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and nerve conduction studies. A healthcare provider may also perform a lumbar puncture to rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for GBS?
+Treatment options for GBS may include plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), pain management medications, and physical therapy. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to support recovery.
