Intro
Discover what an angiogram is, a medical imaging test using X-rays, CT, or MRI to visualize blood vessels, diagnosing conditions like atherosclerosis, aneurysms, and blockages, aiding in angioplasty and stent placement treatments.
An angiogram is a medical imaging test used to visualize the inside of blood vessels and diagnose various conditions affecting the vascular system. It is a crucial diagnostic tool that helps doctors identify blockages, aneurysms, and other vascular problems. The test involves injecting a special dye into the bloodstream, which highlights the blood vessels on X-ray images, allowing doctors to see the inside of the vessels and diagnose any potential problems.
The importance of angiograms cannot be overstated, as they play a critical role in the diagnosis and treatment of various vascular conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. By visualizing the blood vessels, doctors can identify areas of blockage or narrowing, which can help guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes. In addition, angiograms can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments, such as angioplasty and stenting, and to detect any potential complications.
Angiograms are typically performed in a hospital or outpatient imaging center, and the procedure usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour to complete. The test is generally safe, but as with any medical procedure, there are some risks and potential complications, such as allergic reactions to the dye, bleeding, or infection. However, these risks are rare, and the benefits of the test far outweigh the potential risks. With the help of angiograms, doctors can diagnose and treat vascular conditions more effectively, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
How Angiogram Works
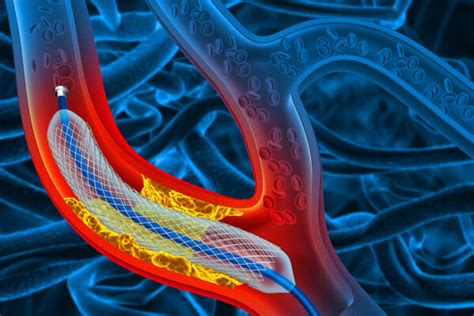
An angiogram works by using a special dye that is injected into the bloodstream, which highlights the blood vessels on X-ray images. The dye is usually injected through a small catheter that is inserted into an artery, typically in the leg or arm. The catheter is then guided through the bloodstream to the area of interest, where the dye is released. The X-ray machine takes pictures of the blood vessels, which are then displayed on a monitor for the doctor to interpret.
The angiogram procedure typically involves the following steps:
- The patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted.
- The catheter is inserted into the artery, and the dye is injected into the bloodstream.
- The X-ray machine takes pictures of the blood vessels, which are then displayed on a monitor.
- The doctor interprets the images, looking for any blockages, aneurysms, or other vascular problems.
- The catheter is removed, and the patient is taken to a recovery area to rest for a few hours.
Types of Angiograms
There are several types of angiograms, including: * Coronary angiogram: This type of angiogram is used to visualize the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. * Cerebral angiogram: This type of angiogram is used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain. * Peripheral angiogram: This type of angiogram is used to visualize the blood vessels in the legs and arms. * Pulmonary angiogram: This type of angiogram is used to visualize the blood vessels in the lungs.Benefits of Angiogram

The benefits of an angiogram are numerous, and the test plays a critical role in the diagnosis and treatment of various vascular conditions. Some of the benefits of an angiogram include:
- Accurate diagnosis: An angiogram provides a detailed picture of the blood vessels, allowing doctors to diagnose vascular conditions more accurately.
- Minimally invasive: The procedure is minimally invasive, and the risk of complications is low.
- Guides treatment: The results of an angiogram can help guide treatment decisions, such as angioplasty and stenting.
- Monitors treatment: An angiogram can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and detect any potential complications.
Risks and Complications
While an angiogram is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks and potential complications, including: * Allergic reactions to the dye * Bleeding or bruising at the site of the catheter insertion * Infection * Damage to the blood vessels * Kidney damagePreparation for Angiogram

To prepare for an angiogram, patients should follow these steps:
- Stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, for a few days before the procedure.
- Avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the procedure.
- Wear comfortable clothing and remove any jewelry or metal objects.
- Bring a list of medications and medical history to the procedure.
- Plan for someone to drive you home after the procedure.
After the Procedure
After the procedure, patients should: * Rest for a few hours to allow the catheter site to heal. * Avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or bending, for a few days. * Monitor the catheter site for any signs of bleeding or infection. * Follow up with the doctor to discuss the results of the procedure and any further treatment.Angiogram Results

The results of an angiogram are usually available immediately after the procedure. The doctor will interpret the images and look for any blockages, aneurysms, or other vascular problems. If any problems are detected, the doctor will discuss the results with the patient and recommend further treatment.
Interpreting the Results
The results of an angiogram can be interpreted in the following ways: * Normal: The blood vessels appear normal, and no blockages or aneurysms are detected. * Abnormal: The blood vessels appear abnormal, and blockages or aneurysms are detected. * Inconclusive: The results are inconclusive, and further testing may be needed to confirm a diagnosis.Angiogram and Other Medical Conditions
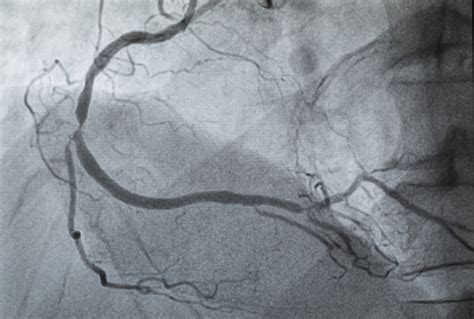
An angiogram can be used to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, including:
- Heart disease: An angiogram can be used to visualize the coronary arteries and diagnose heart disease.
- Stroke: An angiogram can be used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain and diagnose stroke.
- Peripheral artery disease: An angiogram can be used to visualize the blood vessels in the legs and arms and diagnose peripheral artery disease.
- Aneurysms: An angiogram can be used to visualize the blood vessels and diagnose aneurysms.
Angiogram and Pregnancy
An angiogram is generally not recommended during pregnancy, as the dye used in the procedure can harm the fetus. However, in some cases, an angiogram may be necessary to diagnose and treat a life-threatening condition. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should discuss the risks and benefits of an angiogram with their doctor before undergoing the procedure.Future of Angiogram

The future of angiogram is promising, with advancements in technology and imaging techniques. Some of the potential advancements include:
- 3D imaging: The development of 3D imaging techniques could provide more detailed and accurate images of the blood vessels.
- Contrast-free angiogram: The development of contrast-free angiogram techniques could reduce the risk of allergic reactions and kidney damage.
- Minimally invasive procedures: The development of minimally invasive procedures could reduce the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
Current Research
Current research is focused on improving the accuracy and safety of angiogram procedures. Some of the areas of research include: * Developing new imaging techniques, such as 3D imaging and contrast-free angiogram. * Improving the safety of the procedure, such as reducing the risk of allergic reactions and kidney damage. * Developing new treatments, such as minimally invasive procedures and new medications.What is an angiogram?
+An angiogram is a medical imaging test used to visualize the inside of blood vessels and diagnose various conditions affecting the vascular system.
What are the benefits of an angiogram?
+The benefits of an angiogram include accurate diagnosis, minimally invasive procedure, guides treatment, and monitors treatment.
What are the risks and complications of an angiogram?
+The risks and complications of an angiogram include allergic reactions to the dye, bleeding or bruising at the site of the catheter insertion, infection, damage to the blood vessels, and kidney damage.
In conclusion, an angiogram is a valuable diagnostic tool that plays a critical role in the diagnosis and treatment of various vascular conditions. By understanding the benefits, risks, and complications of an angiogram, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare. If you have any questions or concerns about angiograms, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you are experiencing any symptoms of vascular disease, such as chest pain or leg pain, we encourage you to consult with your doctor to discuss the possibility of an angiogram.
