Intro
Discover how insulin works simply, regulating blood sugar levels, glucose metabolism, and diabetes management, through a straightforward explanation of insulins role in the body.
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, playing a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels in the body. The importance of insulin cannot be overstated, as it helps to facilitate the entry of glucose into cells, providing them with the necessary energy to function properly. Without insulin, the body's cells would be unable to absorb glucose, leading to a range of serious health problems. In this article, we will delve into the world of insulin, exploring its functions, benefits, and the mechanisms by which it works.
The discovery of insulin in the early 20th century revolutionized the treatment of diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Prior to the discovery of insulin, diabetes was often a fatal disease, with patients facing a significantly reduced life expectancy. However, with the introduction of insulin therapy, people with diabetes were able to manage their condition effectively, leading to a significant improvement in their quality of life. Today, insulin remains a cornerstone of diabetes treatment, with millions of people around the world relying on it to control their blood sugar levels.
The role of insulin in the body is multifaceted, and its functions extend far beyond the regulation of blood sugar levels. Insulin also plays a crucial role in the storage of glucose in the liver, muscles, and fat cells, helping to maintain a stable energy supply. Additionally, insulin helps to regulate the metabolism of protein and fat, ensuring that the body's cells receive the necessary nutrients to function properly. With its wide-ranging functions, insulin is a truly essential hormone, and its importance cannot be overstated.
How Insulin Works
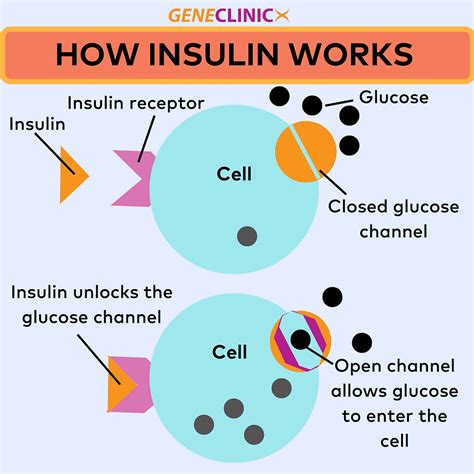
Insulin works by binding to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the uptake of glucose. This process is highly complex, involving a range of molecular interactions and cellular responses. When insulin binds to its receptor, it activates a tyrosine kinase enzyme, which in turn phosphorylates and activates a range of downstream signaling molecules. These signaling molecules then trigger a range of cellular responses, including the translocation of glucose transporter proteins to the cell surface, allowing glucose to enter the cell.
The benefits of insulin are numerous, and its importance extends far beyond the treatment of diabetes. Insulin also plays a crucial role in the regulation of cellular growth and division, helping to ensure that cells grow and divide at a healthy rate. Additionally, insulin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing in the body. With its wide-ranging functions and benefits, insulin is a truly remarkable hormone, and its importance cannot be overstated.
Types of Insulin
There are several types of insulin, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. These include: * Rapid-acting insulin, which begins to work within 15 minutes of injection and peaks after 1-3 hours * Short-acting insulin, which begins to work within 30 minutes of injection and peaks after 2-4 hours * Intermediate-acting insulin, which begins to work within 1-2 hours of injection and peaks after 4-12 hours * Long-acting insulin, which begins to work after several hours of injection and provides a steady level of insulin throughout the dayInsulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is a highly effective treatment for diabetes, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. There are several types of insulin therapy, including:
- Basal insulin therapy, which involves the use of long-acting insulin to provide a steady background level of insulin throughout the day
- Bolus insulin therapy, which involves the use of rapid-acting or short-acting insulin to provide a quick burst of insulin after meals
- Premixed insulin therapy, which involves the use of a combination of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin to provide both basal and bolus coverage
The steps involved in insulin therapy are relatively straightforward, and involve:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly to determine the optimal dose of insulin
- Injecting insulin using a syringe, pen, or pump
- Adjusting the dose of insulin based on blood sugar levels, diet, and exercise
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting the insulin regimen to ensure optimal blood sugar control
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small, portable devices that deliver a continuous flow of insulin throughout the day. They are highly effective, and offer a range of benefits, including: * Improved blood sugar control * Increased flexibility and convenience * Reduced risk of hypoglycemia * Enhanced quality of lifeInsulin Resistance
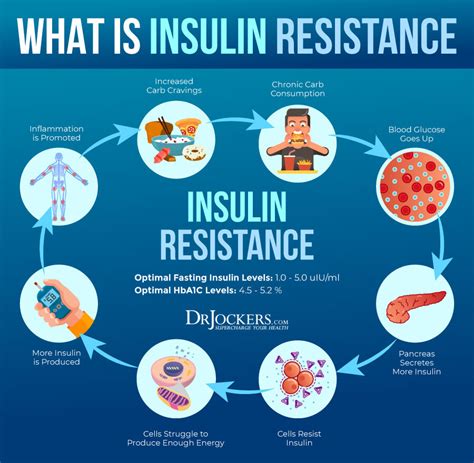
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter the cells. This can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- High blood sugar levels
- Weight gain
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
- Reduced fertility
The causes of insulin resistance are complex, and involve a range of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. These include:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Poor diet
- Stress
- Certain medications
Treating Insulin Resistance
Treating insulin resistance involves a range of lifestyle and medical interventions, including: * Losing weight * Increasing physical activity * Improving diet * Reducing stress * Taking medications to improve insulin sensitivityInsulin and Exercise
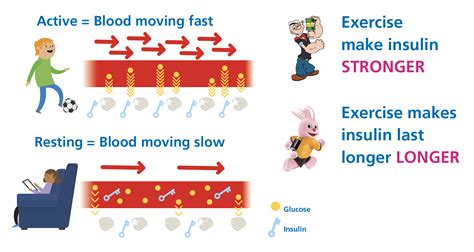
Exercise is a highly effective way to improve insulin sensitivity, and can help to reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The benefits of exercise include:
- Improved blood sugar control
- Increased insulin sensitivity
- Weight loss
- Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke
- Enhanced quality of life
The best types of exercise for improving insulin sensitivity include:
- Aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming
- Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
Insulin and Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing insulin levels, and can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The best foods for improving insulin sensitivity include: * Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale * Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries * Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna * Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa * Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeasInsulin and Stress

Stress can have a significant impact on insulin levels, and can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The effects of stress on insulin include:
- Increased cortisol levels, which can lead to insulin resistance
- Reduced insulin sensitivity
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Weight gain
The best ways to manage stress and improve insulin sensitivity include:
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Yoga and tai chi
- Deep breathing exercises
- Getting enough sleep
- Engaging in regular exercise
Insulin and Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating insulin levels, and can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The benefits of sleep include: * Improved insulin sensitivity * Reduced cortisol levels * Increased human growth hormone (HGH) production * Enhanced weight loss * Improved overall health and well-beingThe best ways to improve sleep quality include:
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine
- Avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime
- Getting regular exercise
- Avoiding heavy meals before bedtime
What is insulin and how does it work?
+Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels in the body. It works by binding to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the uptake of glucose.
What are the benefits of insulin therapy?
+Insulin therapy is a highly effective treatment for diabetes, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. The benefits of insulin therapy include improved blood sugar control, increased flexibility and convenience, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and enhanced quality of life.
How can I improve my insulin sensitivity?
+Improving insulin sensitivity can be achieved through a range of lifestyle and medical interventions, including losing weight, increasing physical activity, improving diet, reducing stress, and taking medications to improve insulin sensitivity.
In conclusion, insulin is a vital hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels in the body. Its importance extends far beyond the treatment of diabetes, and its functions and benefits are numerous. By understanding how insulin works, and by taking steps to improve insulin sensitivity, individuals can reduce their risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, and can improve their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with insulin, and to ask any questions you may have. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of this essential hormone, and can improve the lives of those affected by diabetes and insulin resistance.
