Intro
Lidocaine works quickly as a local anesthetic, providing rapid pain relief and numbing effects, ideal for minor procedures, injections, and topical applications, with fast-acting properties and minimal side effects, making it a popular choice for medical professionals and patients alike.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that has been widely used in the medical field for its rapid and effective pain-relieving properties. It works by blocking the nerve signals in the body, which helps to numb the area where it is applied, thereby reducing pain and discomfort. Lidocaine is commonly used in various medical procedures, including dental fillings, biopsies, and minor surgeries. Its quick action and efficacy have made it a popular choice among medical professionals.
The importance of lidocaine lies in its ability to provide rapid pain relief, which is essential in emergency situations or during medical procedures. It is also used to treat certain medical conditions, such as arrhythmias and epilepsy. Lidocaine's mechanism of action involves blocking the sodium channels in the nerve cells, which prevents the transmission of pain signals to the brain. This results in a rapid reduction of pain and discomfort, making it an ideal choice for various medical applications.
Lidocaine's effectiveness has been extensively studied and documented in various medical research studies. These studies have shown that lidocaine is highly effective in reducing pain and discomfort in patients undergoing medical procedures. Its quick action and minimal side effects have made it a preferred choice among medical professionals. Furthermore, lidocaine is available in various forms, including creams, gels, and injections, which makes it easily accessible and convenient to use.
Lidocaine Mechanism of Action
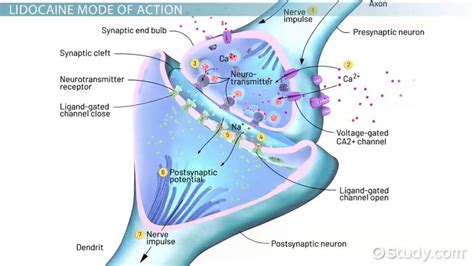
The binding of lidocaine to the sodium channels is a critical step in its mechanism of action. Lidocaine binds to the sodium channels in the nerve cells, which prevents the influx of sodium ions into the cell. This results in a decrease in the excitability of the nerve cell, which ultimately leads to a reduction in pain and discomfort. The blocking of sodium ions is also essential in the mechanism of action of lidocaine, as it prevents the transmission of nerve signals to the brain.
Steps Involved in Lidocaine Mechanism of Action
The steps involved in the mechanism of action of lidocaine include: * Binding of lidocaine to the sodium channels * Blocking of sodium ions * Prevention of nerve signal transmission * Reduction of pain and discomfort These steps are essential in understanding how lidocaine works and its effectiveness in reducing pain and discomfort.Lidocaine Uses and Applications
The uses and applications of lidocaine include:
- Local anesthesia for dental fillings and minor surgeries
- Treatment of arrhythmias and epilepsy
- Pain relief during medical procedures
- Topical anesthesia for skin procedures These uses and applications demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of lidocaine in various medical settings.
Lidocaine Forms and Administration
Lidocaine is available in various forms, including creams, gels, and injections. The form and administration of lidocaine depend on the specific medical application and the patient's needs. The forms of lidocaine include: * Creams and gels for topical anesthesia * Injections for local anesthesia * Oral forms for systemic administration These forms and administration methods make lidocaine easily accessible and convenient to use.Lidocaine Benefits and Advantages

The benefits and advantages of lidocaine include:
- Rapid pain relief
- Minimal side effects
- Easy administration
- Versatility in various medical applications These benefits and advantages demonstrate the effectiveness and convenience of lidocaine in various medical settings.
Lidocaine Side Effects and Precautions
While lidocaine is generally safe and effective, it can cause some side effects and precautions should be taken. The common side effects of lidocaine include: * Numbness or tingling * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Headache or nausea These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but patients should be monitored closely during and after administration.Lidocaine Interactions and Contraindications
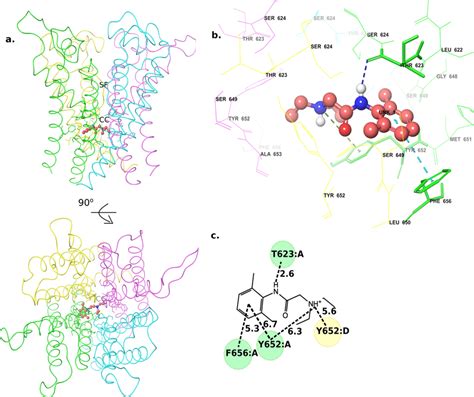
The interactions and contraindications of lidocaine include:
- Interactions with other local anesthetics
- Contraindications in patients with certain medical conditions, such as heart disease or epilepsy
- Interactions with other medications, such as beta blockers or calcium channel blockers These interactions and contraindications should be carefully considered before administering lidocaine.
Lidocaine Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of lidocaine depend on the specific medical application and the patient's needs. The recommended dosage of lidocaine is: * 1-2% solution for local anesthesia * 2-4% solution for topical anesthesia * 5-10mg/kg for systemic administration These dosages and administration methods should be followed carefully to ensure safe and effective use of lidocaine.Lidocaine Alternatives and Comparisons
Lidocaine Future Directions and Research
Lidocaine is a widely used and effective local anesthetic, but there is still ongoing research and development to improve its efficacy and safety. Future directions and research include: * Development of new forms and administration methods * Investigation of new medical applications and uses * Study of lidocaine's mechanism of action and pharmacokinetics These future directions and research will help to improve our understanding of lidocaine and its potential uses in various medical settings.What is lidocaine and how does it work?
+Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that works by blocking the sodium channels in the nerve cells, which prevents the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
What are the benefits and advantages of lidocaine?
+The benefits and advantages of lidocaine include rapid pain relief, minimal side effects, easy administration, and versatility in various medical applications.
What are the side effects and precautions of lidocaine?
+The common side effects of lidocaine include numbness or tingling, dizziness or lightheadedness, and headache or nausea. Precautions should be taken in patients with certain medical conditions or taking other medications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of lidocaine, its mechanism of action, uses, benefits, and precautions. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with lidocaine, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
