Intro
Identify Gerd symptoms in babies, including reflux, spit-up, and colic. Learn about infant acid reflux, digestive issues, and treatment options for newborns and toddlers with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, commonly referred to as GERD, is a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting the mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing discomfort. While GERD is often associated with adults, it can also affect infants and babies. In fact, it's estimated that more than 50% of infants experience some degree of reflux, with the majority outgrowing it by 12 to 18 months of age. Understanding the symptoms of GERD in babies is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide the necessary care and seek medical attention when needed.
Babies with GERD may exhibit a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. One of the most common signs is spitting up or vomiting after feeding. This can be a normal occurrence in many infants, but when it happens frequently or in large amounts, it may indicate an underlying issue like GERD. Other symptoms include fussiness or irritability during or after feeding, arching of the back, and refusal to feed due to discomfort. In some cases, babies might experience difficulty gaining weight or show signs of dehydration due to persistent vomiting.
The importance of recognizing these symptoms lies in the potential complications associated with untreated GERD in infants. For instance, frequent exposure to stomach acid can lead to esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus, which can cause pain and discomfort. Furthermore, GERD can increase the risk of respiratory problems, as stomach contents can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially leading to conditions like pneumonia. Therefore, it's vital for parents to be vigilant about their baby's health and consult a pediatrician if they suspect their child is experiencing symptoms of GERD.
Understanding GERD in Babies

Understanding the mechanisms behind GERD in babies is essential for managing the condition. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which acts as a valve between the esophagus and stomach, plays a crucial role. In infants, this sphincter may not be fully developed, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus more easily. Additionally, factors such as overfeeding, lying down after feeding, and food allergies or intolerances can exacerbate the condition. Recognizing these factors can help in implementing strategies to reduce the frequency and severity of reflux episodes.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes and risk factors associated with GERD in babies are multifaceted. Premature infants are at a higher risk due to their underdeveloped digestive systems. Similarly, babies with certain health conditions, such as esophageal atresia or tracheoesophageal fistula, may be more prone to GERD. Other factors include family history, where infants with a family history of GERD or allergies may be more likely to experience reflux. Furthermore, the type of feeding—breastfed versus formula-fed—can influence the risk, although both breastfed and formula-fed infants can develop GERD.Diagnosing GERD in Babies
Diagnosing GERD in babies involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. A pediatrician will typically start by reviewing the baby's symptoms and feeding habits. They may also perform a physical exam to check for any signs of complications such as poor weight gain or dehydration. In some cases, further testing may be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. These tests can include an upper GI series, which involves swallowing a barium solution to visualize the upper digestive system, or a pH probe study to measure the acidity in the esophagus.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for GERD in babies usually involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Lifestyle modifications can include feeding the baby smaller, more frequent meals, keeping the baby upright after feeding, and avoiding overfeeding. For breastfed babies, mothers may be advised to eliminate certain foods from their diet that could be exacerbating the reflux. In formula-fed babies, switching to a hypoallergenic formula may help. When these measures are not sufficient, medication such as antacids or acid reducers may be prescribed to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach.Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes

Several home remedies and lifestyle changes can help alleviate GERD symptoms in babies. Elevating the head of the baby's bed by about 30 degrees can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Avoiding tight clothing around the baby's abdomen can also reduce pressure on the stomach. Furthermore, burping the baby frequently during and after feeding can help release trapped air and reduce discomfort. For some babies, thickening their feed with a small amount of cereal may help, although this should be done under the guidance of a pediatrician to avoid overthickening, which can lead to other issues.
Natural and Alternative Therapies
While there is limited research on the effectiveness of natural and alternative therapies for GERD in babies, some parents find them helpful. Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria, can aid in digestion and potentially reduce reflux symptoms. Gentle massage techniques may also help soothe the baby and improve digestion. However, it's crucial for parents to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new remedies, especially if their baby is already on medication for GERD.Complications and Long-term Effects
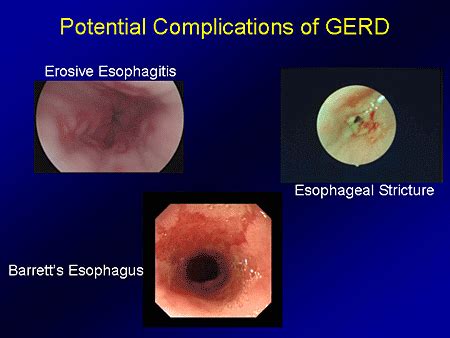
If left untreated, GERD can lead to several complications in babies. Esophagitis, as mentioned earlier, is a common complication where the esophagus becomes inflamed due to constant exposure to stomach acid. This can cause pain and make feeding difficult. Another complication is respiratory problems, such as asthma or pneumonia, which can occur if stomach contents are inhaled into the lungs. In severe cases, GERD can lead to failure to thrive, where the baby does not gain weight at a healthy rate due to persistent vomiting and discomfort during feeding.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing GERD in babies involves a combination of feeding practices, lifestyle adjustments, and awareness of risk factors. For instance, feeding in an upright position and burping frequently can help reduce the risk of reflux. Avoiding overfeeding and ensuring the baby's diet is appropriate for their age can also play a role in prevention. Furthermore, managing the mother's diet during breastfeeding, avoiding smoking, and ensuring the baby is at a healthy weight can contribute to reducing the risk of GERD.Parental Support and Community

Having a baby with GERD can be challenging and stressful for parents. Seeking support from healthcare providers, family, and friends is crucial. Joining a community or support group, either online or in-person, can provide valuable resources, advice, and emotional support. Sharing experiences and learning from others who are going through similar situations can help parents feel less isolated and more empowered to manage their baby's condition effectively.
Coping with the Emotional Impact
The emotional impact of having a baby with GERD should not be underestimated. Parents may feel anxious, worried, or guilty, especially if they are unsure about how to manage their baby's symptoms effectively. It's essential for parents to prioritize their own well-being, take breaks when needed, and seek professional help if they are struggling with their emotions. A strong support system, combined with open communication with healthcare providers, can make a significant difference in coping with the emotional challenges of caring for a baby with GERD.Future Outlook and Research

Research into GERD in babies is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments, diagnostic methods, and preventive strategies. Advances in understanding the role of genetics, diet, and environmental factors in the development of GERD could lead to more targeted and effective interventions. Additionally, the development of new medications and therapies that are safer and more effective for infants could significantly improve the management of GERD in this age group.
Advances in Diagnostic Techniques
Improvements in diagnostic techniques are also on the horizon, which could help in earlier and more accurate diagnosis of GERD in babies. For example, non-invasive tests that can measure esophageal pH and impedance could become more widely available, reducing the need for invasive procedures. Furthermore, advances in imaging technology could provide clearer insights into the anatomical and functional issues contributing to GERD, guiding more personalized treatment plans.What are the common symptoms of GERD in babies?
+Common symptoms include spitting up or vomiting after feeding, fussiness or irritability during or after feeding, arching of the back, and refusal to feed.
How is GERD diagnosed in babies?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination, review of symptoms, and sometimes diagnostic tests like an upper GI series or pH probe study.
What are some home remedies for GERD in babies?
+Home remedies include elevating the head of the baby's bed, avoiding tight clothing, frequent burping, and in some cases, thickening feeds under medical guidance.
Can GERD in babies lead to long-term complications?
+Yes, if left untreated, GERD can lead to complications such as esophagitis, respiratory problems, and failure to thrive.
How can parents cope with the emotional impact of caring for a baby with GERD?
+Parents can cope by seeking support from healthcare providers, family, and friends, joining support groups, and prioritizing their own well-being.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of GERD in babies and understanding the condition's causes, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications are vital for parents and caregivers. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, it's possible to manage GERD effectively, ensuring the best possible outcome for the baby. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and explore the resources provided to deepen their understanding of this important topic. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in creating a supportive community for those affected by GERD in babies.
