Intro
Doxycycline works in 5 ways, treating infections, acne, and Lyme disease with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects, showcasing its broad-spectrum antibiotic properties.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications serving different purposes. Among these, doxycycline stands out as a versatile and widely used antibiotic. Its applications range from treating bacterial infections to being used as a preventive measure against certain diseases. Understanding how doxycycline works is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can help in making informed decisions about its use. In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms and applications of doxycycline, exploring its benefits, side effects, and the conditions it treats.
Doxycycline is a type of tetracycline antibiotic that has been in use for several decades. It is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. One of the key reasons doxycycline is preferred over other antibiotics is its ability to penetrate into the tissues of the body, ensuring that the infection site receives an adequate concentration of the drug. This characteristic makes doxycycline particularly useful in treating infections that are deep-seated or widespread.
The importance of understanding how doxycycline works cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary. Doxycycline, like other antibiotics, should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure that it is used effectively and safely. Moreover, being informed about the potential side effects and interactions of doxycycline can help individuals take necessary precautions and monitor their health while undergoing treatment.
Introduction to Doxycycline Mechanism
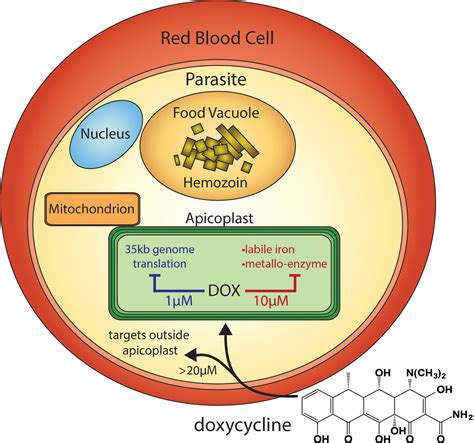
Doxycycline works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. It does so by binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis. This binding action prevents the amino acids from being added to the growing protein chain, thereby stopping the production of essential proteins needed for bacterial growth and survival. Without these proteins, the bacteria cannot multiply, and the infection is controlled. This mechanism is specific to bacteria and does not affect human cells, making doxycycline a safe and effective treatment option for bacterial infections.
Benefits of Doxycycline

The benefits of doxycycline are numerous. It is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. Doxycycline is also used in the treatment of certain sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia. Additionally, it has anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in treating conditions like acne. Its ability to penetrate into tissues makes it particularly useful for treating infections that are difficult to reach with other antibiotics.
Applications of Doxycycline
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Doxycycline is commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: It is effective against skin infections like acne, rosacea, and dermatitis, as well as soft tissue infections.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Doxycycline can be used to treat infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: It is used in the treatment of certain sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and syphilis.
Working Mechanisms of Doxycycline
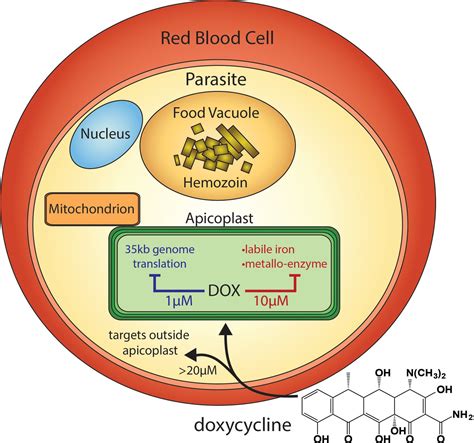
The working mechanisms of doxycycline involve several key steps:
- Absorption: Doxycycline is absorbed into the bloodstream after oral administration.
- Distribution: It is distributed throughout the body, penetrating into various tissues and fluids.
- Binding to Ribosomes: Doxycycline binds to the bacterial ribosomes, inhibiting protein synthesis.
- Inhibition of Bacterial Growth: By preventing protein synthesis, doxycycline inhibits the growth and multiplication of bacteria, thereby controlling the infection.
Steps for Effective Use
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting doxycycline, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it is the right treatment for your condition.
- Follow the Prescribed Dosage: Adhere to the prescribed dosage and treatment duration to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Keep an eye out for potential side effects and report them to your healthcare provider if they occur.
Side Effects and Interactions of Doxycycline
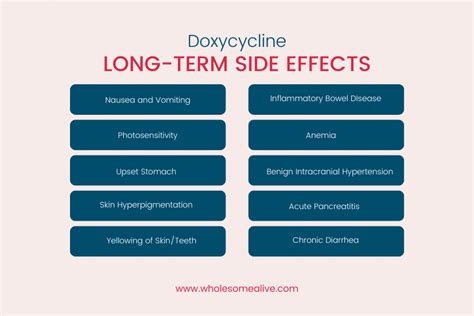
Like all medications, doxycycline can cause side effects and interact with other drugs. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sensitivity to sunlight. It can also cause more serious side effects, such as an allergic reaction or increased risk of yeast infections. Doxycycline can interact with other medications, including antacids, blood thinners, and certain vitamins, which can affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects.
Precautions and Warnings
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Doxycycline should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it can affect the fetus or baby.
- Allergic Reactions: Individuals who are allergic to tetracycline antibiotics should avoid doxycycline.
- Sun Sensitivity: Patients taking doxycycline should avoid excessive sun exposure to prevent sunburn.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives

In conclusion, doxycycline is a versatile and effective antibiotic that offers numerous benefits in the treatment of bacterial infections. Its broad spectrum of activity, ability to penetrate into tissues, and anti-inflammatory properties make it a valuable option for various conditions. However, it is crucial to use doxycycline judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of side effects and antibiotic resistance. As research continues to uncover new applications and mechanisms of doxycycline, its role in modern medicine is likely to expand, offering new hope for the treatment of infectious diseases.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with doxycycline in the comments below. Have you used doxycycline for a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Your insights can help others understand the benefits and challenges of using doxycycline. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
What is doxycycline used for?
+Doxycycline is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections.
How does doxycycline work?
+Doxycycline works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, preventing them from growing and multiplying. It binds to the bacterial ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis, and stops the production of essential proteins needed for bacterial survival.
What are the common side effects of doxycycline?
+Common side effects of doxycycline include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sensitivity to sunlight. More serious side effects can include allergic reactions and increased risk of yeast infections.
