Intro
Ketorolac is a medication that has been widely used for its potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and is primarily used to manage moderate to severe pain. The importance of understanding how ketorolac works cannot be overstated, as it has become a crucial component in the treatment of various conditions, including acute pain, inflammation, and even migraine headaches. By grasping the mechanism of action of ketorolac, healthcare professionals and patients alike can better appreciate its benefits and limitations, leading to more effective and safe use.
The discovery of ketorolac and its subsequent development marked a significant milestone in pain management. Unlike opioids, which can lead to dependence and addiction, ketorolac offers an alternative approach to pain relief without the risk of opioid-related side effects. This aspect is particularly important given the current opioid crisis, making ketorolac a valuable tool in the arsenal against pain. Moreover, its efficacy in reducing inflammation makes it useful in treating conditions where inflammation is a significant component, such as arthritis and post-surgical pain.
The mechanism through which ketorolac exerts its effects is multifaceted. At its core, ketorolac works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are substances in the body that mediate pain and inflammation. Prostaglandins are produced through the action of enzymes known as cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2). By blocking these enzymes, ketorolac reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins, thereby decreasing pain and inflammation. This action is not only beneficial for treating acute conditions but also for managing chronic pain, where ongoing inflammation can lead to significant morbidity.
Pharmacology of Ketorolac
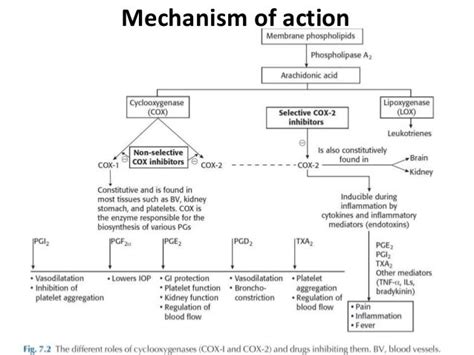
The pharmacology of ketorolac is complex and involves various pathways. Its ability to inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes contributes to its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects. However, this dual inhibition also accounts for some of the gastrointestinal side effects associated with NSAIDs, as COX-1 plays a protective role in the stomach lining. The pharmacokinetics of ketorolac, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, are crucial in understanding how it achieves therapeutic levels in the body and how it is eventually cleared.
Metabolism and Excretion
Ketorolac is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily through the kidneys. Its metabolism involves conjugation reactions, which result in metabolites that are then excreted in the urine. Understanding the metabolic pathway of ketorolac is essential for predicting potential drug interactions and for guiding dosage adjustments in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.Benefits of Ketorolac
The benefits of ketorolac are numerous and well-documented. Its potent analgesic effect makes it an excellent choice for managing acute pain, especially in postoperative settings. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in reducing swelling and pain associated with injuries and inflammatory conditions. The fact that ketorolac can be administered via various routes, including oral, intramuscular, and intravenous, adds to its versatility and convenience.
Advantages Over Other NSAIDs
Compared to other NSAIDs, ketorolac has several advantages. Its high potency means that lower doses can be effective, potentially reducing the risk of side effects. Furthermore, its rapid onset of action makes it particularly useful in situations where quick pain relief is necessary. However, like all NSAIDs, ketorolac is not without its limitations and potential side effects, which must be carefully considered when deciding on its use.Side Effects and Precautions
While ketorolac is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, some of which can be serious. Gastrointestinal complications, such as ulcers and bleeding, are among the most significant risks, particularly with long-term use. Other potential side effects include renal impairment, increased blood pressure, and allergic reactions. It is crucial for patients to be aware of these risks and to use the medication under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Contraindications and Warnings
There are certain conditions under which ketorolac should be used with caution or avoided altogether. Patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding, severe renal impairment, or heart failure should exercise caution. Additionally, ketorolac is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or other NSAIDs. Pregnant women, especially those in the third trimester, should avoid ketorolac due to the risk of premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.Practical Applications and Dosage

The practical applications of ketorolac are diverse, ranging from the management of postoperative pain to the treatment of migraine headaches. The dosage of ketorolac can vary depending on the condition being treated, the route of administration, and the patient's response. Generally, the goal is to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to minimize the risk of side effects.
Administration Routes
Ketorolac can be administered through several routes, each with its advantages. Intravenous administration is often used in hospital settings for rapid pain relief, while oral and intramuscular routes may be preferred in outpatient settings or when intravenous access is not available. The choice of administration route should be based on the patient's condition, the severity of pain, and the potential for side effects.Comparison with Other Pain Management Options
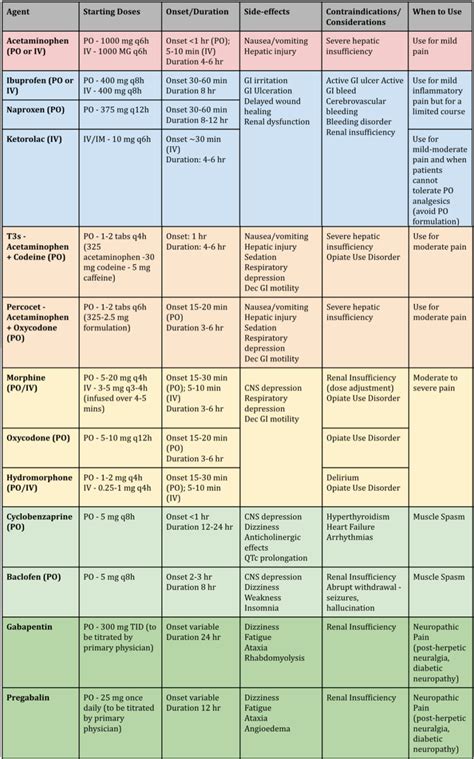
In comparing ketorolac with other pain management options, it is essential to consider the efficacy, safety profile, and potential for abuse. Unlike opioids, ketorolac does not have the potential for dependence, making it a safer alternative for long-term pain management. However, its side effect profile, particularly the risk of gastrointestinal complications, must be weighed against the benefits.
Evidence-Based Practice
Evidence-based practice supports the use of ketorolac in various clinical scenarios. Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation, with a favorable safety profile when used appropriately. Guidelines from professional organizations often recommend ketorolac as a first-line treatment for certain conditions, underscoring its importance in pain management.Future Directions and Research

Research into ketorolac and its analogs continues, with a focus on developing drugs that retain the therapeutic benefits of ketorolac while minimizing its side effects. The development of selective COX-2 inhibitors, for example, aims to reduce the gastrointestinal risks associated with dual COX inhibition. Additionally, studies exploring the use of ketorolac in new clinical settings, such as in the management of cancer pain, may further expand its utility.
Emerging Trends in Pain Management
Emerging trends in pain management emphasize a multimodal approach, combining different classes of drugs and non-pharmacological interventions to achieve optimal pain relief while minimizing side effects. Ketorolac, with its potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, is likely to remain a valuable component of this approach, particularly in scenarios where rapid and effective pain relief is critical.In conclusion, ketorolac is a versatile and potent medication that has found a significant place in the management of pain and inflammation. Its mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects make it a crucial tool for healthcare providers. As research continues to uncover new aspects of ketorolac's pharmacology and clinical applications, its role in pain management is likely to evolve, offering patients more effective and safer options for pain relief.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ketorolac, and to consider the implications of its use in various clinical contexts. Your feedback and questions are invaluable in fostering a deeper understanding of this important medication and its potential to improve patient outcomes.
What is the primary mechanism of action of ketorolac?
+Ketorolac works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, specifically COX-1 and COX-2.
What are the common side effects of ketorolac?
+Common side effects include gastrointestinal complications such as ulcers and bleeding, renal impairment, increased blood pressure, and allergic reactions.
Can ketorolac be used in patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding?
+Ketorolac should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding, as it can increase the risk of recurrence.
