Intro
Discover how Levothyroxine works, a thyroid hormone replacement medication, to treat hypothyroidism, regulating metabolism, energy, and hormone balance, with effects on thyroid function, T4 conversion, and overall health.
The human body is a complex system that relies on various hormones to function properly. One of the most crucial hormones is thyroxine, produced by the thyroid gland. However, some individuals may experience thyroid hormone deficiency, which can lead to a range of health issues. This is where levothyroxine comes in – a synthetic form of thyroxine that helps replace the missing hormone in the body. Understanding how levothyroxine works is essential for individuals who rely on this medication to manage their thyroid hormone levels.
Levothyroxine is a widely prescribed medication for individuals with hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. The medication works by replacing the missing thyroxine in the body, which helps regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and development. When taken as directed, levothyroxine can help alleviate symptoms of hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. It's essential to understand the mechanism of action of levothyroxine to appreciate its importance in managing thyroid hormone deficiency.
The importance of levothyroxine cannot be overstated, as it helps individuals with hypothyroidism lead normal, healthy lives. By replacing the missing thyroxine, levothyroxine enables the body to function properly, regulating various physiological processes. This medication has been widely used for decades, and its effectiveness has been well-documented in numerous clinical trials. As we delve into the world of levothyroxine, it's essential to explore its benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects to provide a comprehensive understanding of this vital medication.
What is Levothyroxine?
How Levothyroxine is Absorbed
Levothyroxine is absorbed into the bloodstream through the digestive system, primarily in the small intestine. The absorption rate can vary depending on factors such as the presence of food, other medications, and individual digestive health. Once absorbed, levothyroxine is transported to the liver, where it's converted into its active form, triiodothyronine (T3). T3 is then released into the bloodstream, where it binds to thyroid hormone receptors, regulating various physiological processes.Benefits of Levothyroxine

Working Mechanism of Levothyroxine
The working mechanism of levothyroxine involves replacing the missing thyroxine in the body, which helps regulate various physiological processes. Levothyroxine binds to thyroid hormone receptors, which triggers a response that regulates metabolism, growth, and development. The medication also helps regulate the production of other hormones, such as triiodothyronine (T3), which plays a crucial role in energy production and metabolism.Side Effects of Levothyroxine

Precautions and Interactions
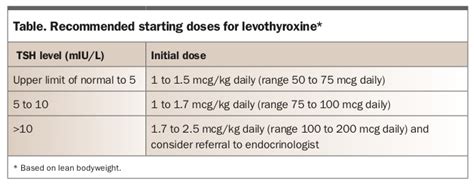
It's essential to take levothyroxine as directed to minimize the risk of side effects and interactions. Individuals taking levothyroxine should be aware of the following precautions and interactions: * Take levothyroxine on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before breakfast. * Avoid taking levothyroxine with other medications, such as antacids, calcium supplements, and iron supplements. * Inform your doctor about any other medications you're taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications. * Monitor your thyroid hormone levels regularly to ensure the medication is working effectively.Levothyroxine Dosage and Administration

Monitoring Thyroid Hormone Levels
Monitoring thyroid hormone levels is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of levothyroxine. Thyroid hormone levels can be measured using blood tests, which help determine the optimal dosage and administration of the medication. Individuals taking levothyroxine should have their thyroid hormone levels checked regularly, typically every 6-12 months, to ensure the medication is working effectively.Levothyroxine and Pregnancy
Levothyroxine and Breastfeeding
Levothyroxine is generally considered safe for breastfeeding women, as it's excreted in small amounts in breast milk. However, breastfeeding women taking levothyroxine should be monitored closely by their healthcare provider to ensure the medication is not affecting the baby's thyroid hormone levels.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What is levothyroxine used for?
+Levothyroxine is used to treat hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
How does levothyroxine work?
+Levothyroxine works by replacing the missing thyroxine in the body, which helps regulate various physiological processes such as metabolism, growth, and development.
What are the common side effects of levothyroxine?
+The common side effects of levothyroxine include nausea, headaches, fatigue, weight loss, and increased appetite.
Can levothyroxine be taken during pregnancy?
+Yes, levothyroxine is essential for pregnant women with hypothyroidism, as it helps regulate thyroid hormone levels and support fetal development.
Is levothyroxine safe for breastfeeding women?
+Yes, levothyroxine is generally considered safe for breastfeeding women, as it's excreted in small amounts in breast milk.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of levothyroxine and its importance in managing thyroid hormone deficiency. If you have any questions or concerns about levothyroxine, please don't hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of thyroid health. Take the first step towards managing your thyroid health today and consult with your healthcare provider about levothyroxine and other treatment options.
