Intro
Discover 5 crucial RSV facts, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, to protect against Respiratory Syncytial Virus infections, particularly in high-risk infants and young children, and understand prevention methods to reduce RSV transmission and complications.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. RSV is a major cause of respiratory illness, and it's essential to understand the facts about this virus to protect yourself and your loved ones. In this article, we'll delve into the world of RSV, exploring its symptoms, transmission, prevention, and treatment options.
RSV is a significant public health concern, and its impact is felt worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), RSV is responsible for approximately 33 million cases of acute lower respiratory infections in children under the age of five, resulting in around 200,000 hospitalizations and 100,000 deaths each year. In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that RSV leads to over 57,000 hospitalizations and 300 deaths in children under the age of five annually.
The importance of understanding RSV cannot be overstated. By educating ourselves about this virus, we can take steps to prevent its spread, recognize its symptoms, and seek medical attention when necessary. In the following sections, we'll explore the key aspects of RSV, including its symptoms, transmission, prevention, and treatment options. Whether you're a parent, caregiver, or simply someone interested in learning more about this virus, this article aims to provide you with the information you need to stay informed and protected.
What is RSV?

Types of RSV
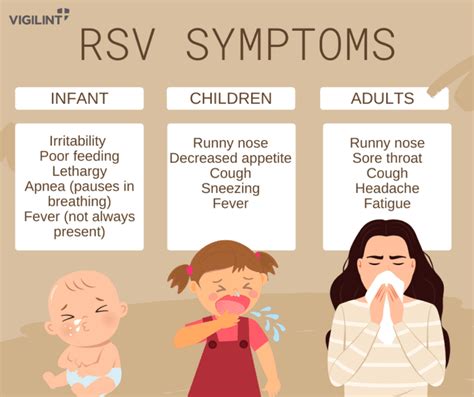
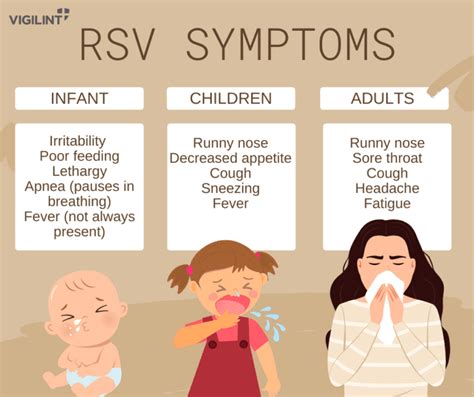
There are two main types of RSV: RSV-A and RSV-B. Both types can cause severe illness, but RSV-A is more commonly associated with severe disease in young children. RSV-A and RSV-B can co-circulate during the same season, making it essential to take preventive measures to avoid infection.RSV Symptoms
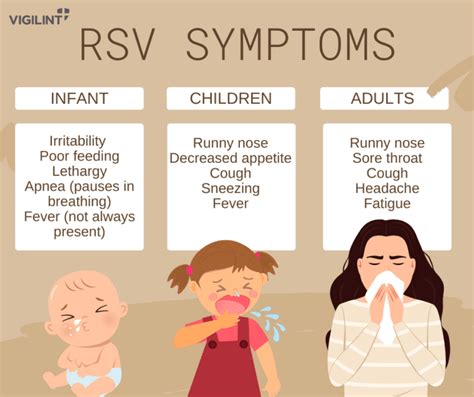
RSV Diagnosis
Diagnosing RSV can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to those of other respiratory viruses. Healthcare providers may use various tests to diagnose RSV, including: * Rapid antigen detection tests * Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests * Viral culture testsRSV Transmission
RSV Prevention
Preventing the spread of RSV is crucial, especially in high-risk groups, such as young children and older adults. Some effective ways to prevent RSV include: * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently * Avoiding close contact with people who are sick * Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects * Avoiding sharing utensils, toys, or other objects * Staying home when sick to avoid spreading the virusRSV Treatment
RSV Complications
RSV can lead to various complications, especially in high-risk groups. Some potential complications include: * Respiratory failure * Sepsis * Pneumonia * Bronchiolitis * Apnea * Cardiac complications, such as heart failure or cardiac arrestRSV Vaccination
RSV Prognosis
The prognosis for RSV depends on various factors, including the individual's age, health status, and the severity of symptoms. In general, most people with RSV recover on their own within a week or two. However, in high-risk groups, such as young children and older adults, RSV can lead to severe illness and even death.RSV in High-Risk Groups
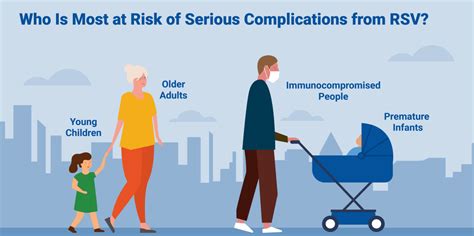
RSV in Pregnancy
RSV can also affect pregnant women, particularly those in their third trimester. RSV infection during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm labor, low birth weight, and other complications. Pregnant women should take precautions to avoid RSV, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.RSV Outbreaks
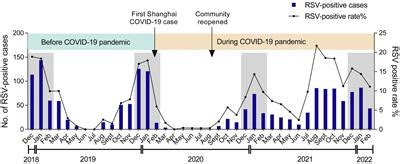
RSV Surveillance
RSV surveillance is essential to monitor the spread of the virus and identify high-risk areas. Healthcare providers and public health officials use various methods to track RSV, including: * Reporting cases and outbreaks * Conducting laboratory tests to confirm RSV infection * Analyzing data to identify trends and patternsWhat is the most common way to get RSV?
+RSV is highly contagious and can spread through close contact with an infected person, touching contaminated surfaces, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Who is most at risk for severe RSV illness?
+Young children, especially those under the age of two, and older adults, especially those over the age of 65, are most at risk for severe RSV illness.
Is there a vaccine available to protect against RSV?
+Currently, there is no vaccine available to protect against RSV. However, researchers are working to develop effective vaccines, and several candidates are in various stages of clinical trials.
How can I prevent the spread of RSV?
+Preventing the spread of RSV is crucial, especially in high-risk groups. Some effective ways to prevent RSV include practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects, and avoiding sharing utensils, toys, or other objects.
What are the symptoms of RSV?
+The symptoms of RSV can vary depending on the age and health status of the individual. In young children, RSV can cause mild to severe symptoms, including runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, wheezing, and apnea. In older adults and people with weakened immune systems, RSV can cause more severe symptoms, such as pneumonia, bronchiolitis, respiratory failure, and sepsis.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of RSV, its symptoms, transmission, prevention, and treatment options. By educating ourselves about this virus, we can take steps to protect ourselves and our loved ones. If you have any questions or concerns about RSV, please don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about RSV, and let's work together to prevent the spread of this highly contagious virus.
