Intro
Oxandrolone, commonly known by its brand name Oxandrin, is a synthetic anabolic steroid that has been used for various medical and non-medical purposes. Its mechanism of action and effects on the body are of significant interest to athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking to enhance their physical performance or appearance. Understanding how oxandrolone works is crucial for appreciating its benefits and risks.
The importance of oxandrolone stems from its ability to promote muscle growth, increase strength, and enhance recovery after workouts or injuries. It is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance in the United States due to its potential for abuse and dependence. Despite this, oxandrolone has legitimate medical applications, including the treatment of conditions like Turner syndrome, osteoporosis, and HIV/AIDS-related wasting syndrome.
Oxandrolone's popularity can be attributed to its relatively mild side effects compared to other anabolic steroids, making it a preferred choice among users. However, its use without medical supervision or in doses exceeding therapeutic recommendations can lead to adverse effects. The drug's impact on liver function, cholesterol levels, and hormonal balance is particularly noteworthy. As such, it is essential to delve into the specifics of how oxandrolone works, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks to ensure informed decision-making.
Introduction to Oxandrolone

Oxandrolone is an orally active anabolic steroid derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT), with modifications that enhance its anabolic properties while minimizing its androgenic effects. This alteration allows oxandrolone to promote protein synthesis and muscle growth with less virilization compared to testosterone and other anabolic steroids. Its chemical structure and pharmacological profile make it suitable for treating conditions where muscle wasting or growth retardation is a concern.
Pharmacodynamics of Oxandrolone
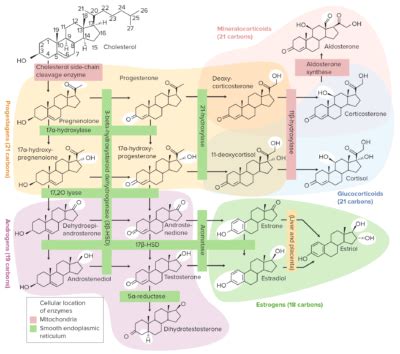
The pharmacodynamics of oxandrolone involve its interaction with androgen receptors, which are found in various tissues throughout the body, including muscle and bone. By binding to these receptors, oxandrolone triggers a series of cellular reactions that lead to increased protein synthesis and muscle cell growth. This anabolic effect is beneficial for individuals seeking to enhance their athletic performance or recover from muscle-wasting diseases.
Benefits of Oxandrolone
The benefits of oxandrolone include: - Enhanced muscle growth and strength - Improved bone density - Increased appetite - Faster recovery from workouts or injuries - Treatment of conditions like Turner syndrome and HIV/AIDS-related wastingWorking Mechanism of Oxandrolone
The working mechanism of oxandrolone involves several key steps:
- Absorption: Oxandrolone is orally administered and undergoes rapid absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Distribution: It is distributed throughout the body, with a high affinity for androgen receptors in muscle and bone tissues.
- Binding to Androgen Receptors: Oxandrolone binds to androgen receptors, initiating a cascade of intracellular signaling pathways that promote protein synthesis and muscle growth.
- Increased Protein Synthesis: The activation of androgen receptors leads to an increase in protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Muscle Growth and Strength: Over time, the increased protein synthesis and muscle cell growth result in enhanced muscle strength and endurance.
Risks and Side Effects of Oxandrolone
While oxandrolone is considered to have a favorable safety profile compared to other anabolic steroids, its use can still lead to several risks and side effects, including:
- Liver toxicity
- Changes in cholesterol levels
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Virilization in women
- Suppression of natural testosterone production
Precautions and Contraindications
Oxandrolone is contraindicated in individuals with: - Known or suspected prostate cancer - Breast cancer - Hypercalcemia - Pregnancy and breastfeeding - Severe liver or kidney diseaseMedical Uses of Oxandrolone

Oxandrolone has several legitimate medical uses, including:
- Treatment of Turner syndrome to promote growth in girls
- Treatment of osteoporosis to improve bone density
- Treatment of HIV/AIDS-related wasting syndrome to prevent muscle loss
- Recovery from severe burns or injuries
Therapeutic Dosages
Therapeutic dosages of oxandrolone vary depending on the condition being treated: - For Turner syndrome: 0.05 mg/kg/day - For osteoporosis: 2.5-10 mg/day - For HIV/AIDS-related wasting: 2.5-20 mg/dayNon-Medical Use of Oxandrolone

The non-medical use of oxandrolone, particularly among athletes and bodybuilders, is a significant concern due to the potential for abuse and adverse effects. Non-medical users often exceed therapeutic dosages, which can lead to severe side effects and long-term health consequences.
Risks of Non-Medical Use
The risks associated with the non-medical use of oxandrolone include: - Dependence and withdrawal symptoms - Aggressive behavior - Cardiovascular problems - Liver damage - Testicular atrophyRegulations and Legal Status
Oxandrolone is a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States, where it is classified as a Schedule III drug. Its possession, sale, and distribution without a valid prescription are illegal and can result in severe penalties.
International Regulations
Internationally, the legal status of oxandrolone varies, with some countries imposing stricter controls than others. It is essential for individuals to be aware of the laws and regulations regarding oxandrolone in their jurisdiction to avoid legal repercussions.What is oxandrolone used for medically?
+Oxandrolone is used medically to treat conditions such as Turner syndrome, osteoporosis, and HIV/AIDS-related wasting syndrome.
Is oxandrolone safe for women?
+Oxandrolone can cause virilization in women, leading to symptoms such as deepening of the voice, acne, and excessive hair growth. Its use in women should be carefully considered and monitored.
Can oxandrolone be used for bodybuilding?
+Oxandrolone is sometimes used by bodybuilders due to its anabolic properties. However, its use without medical supervision can lead to serious health consequences and is illegal in many jurisdictions.
In conclusion, oxandrolone is a complex drug with both medical and non-medical applications. Understanding its working mechanism, benefits, and risks is crucial for making informed decisions about its use. Whether for therapeutic purposes or otherwise, it is essential to approach oxandrolone with caution and be aware of the legal and health implications associated with its use. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with oxandrolone, and we encourage discussion on the responsible use of anabolic steroids in medical and athletic contexts.
