Intro
Discover 5 ways to test for herpes, including blood tests and swab tests, to diagnose genital herpes, herpes simplex, and other herpes infections, and learn about herpes symptoms, treatment, and prevention methods.
Herpes, a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), is a common and highly contagious condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is essential to understand the various methods of testing for herpes to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment. There are several ways to test for herpes, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this article, we will delve into the different methods of testing for herpes, their accuracy, and what to expect during the testing process.
The importance of testing for herpes cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications and the transmission of the virus to others. Moreover, testing for herpes can also help alleviate the emotional and psychological distress associated with the condition. With the advancements in medical technology, testing for herpes has become more accessible and convenient than ever before.
Testing for herpes is a crucial step in managing the condition and preventing its spread. The various methods of testing for herpes include viral culture, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) testing, serological tests, and physical examinations. Each of these methods has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding the differences between them is essential for making informed decisions about testing and treatment.
Understanding Herpes Testing

Herpes testing is a critical component of diagnosing and managing the condition. The different methods of testing for herpes are designed to detect the presence of the virus, identify the type of virus, and determine the severity of the infection. Understanding the various testing methods and their accuracy is essential for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Types of Herpes Tests
There are several types of herpes tests, including: * Viral culture: This test involves collecting a sample of cells or fluid from the affected area and culturing it in a laboratory to detect the presence of the virus. * PCR (polymerase chain reaction) testing: This test uses a DNA amplification technique to detect the genetic material of the virus. * Serological tests: These tests measure the levels of antibodies against the herpes virus in the blood. * Physical examinations: A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to look for signs and symptoms of herpes, such as blisters or sores.Viral Culture Testing
Viral culture testing is a common method of testing for herpes. This test involves collecting a sample of cells or fluid from the affected area and culturing it in a laboratory to detect the presence of the virus. The sample is typically collected using a swab or a scraping tool, and the results are usually available within 2-14 days. Viral culture testing is most accurate when the sample is collected during the early stages of the infection, when the virus is most active.
Advantages and Limitations of Viral Culture Testing
The advantages of viral culture testing include: * High specificity: Viral culture testing is highly specific, meaning that it can accurately identify the presence of the virus. * Ability to detect the virus during the early stages of infection: Viral culture testing can detect the virus during the early stages of infection, when the symptoms are most severe. The limitations of viral culture testing include: * Limited sensitivity: Viral culture testing may not detect the virus in all cases, especially during the later stages of infection. * Time-consuming: The results of viral culture testing may take several days to become available.PCR Testing

PCR (polymerase chain reaction) testing is a highly sensitive and specific method of testing for herpes. This test uses a DNA amplification technique to detect the genetic material of the virus. PCR testing can detect the virus in a variety of samples, including blood, tissue, and bodily fluids. The results of PCR testing are usually available within 1-3 days, making it a faster and more convenient option than viral culture testing.
Advantages and Limitations of PCR Testing
The advantages of PCR testing include: * High sensitivity: PCR testing is highly sensitive, meaning that it can detect even small amounts of the virus. * Fast results: The results of PCR testing are usually available within 1-3 days, making it a faster option than viral culture testing. The limitations of PCR testing include: * Requires specialized equipment: PCR testing requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, which may not be available in all laboratories. * May detect inactive virus: PCR testing may detect the genetic material of the virus even when it is inactive, which can lead to false-positive results.Serological Tests
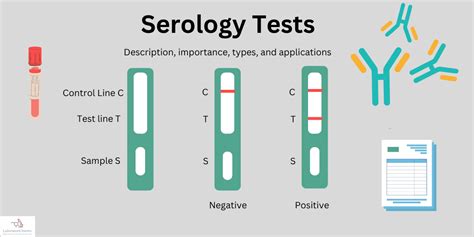
Serological tests measure the levels of antibodies against the herpes virus in the blood. These tests can detect the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies, which are produced by the immune system in response to the infection. Serological tests are commonly used to diagnose herpes in people who have no symptoms or who have had the infection for a long time.
Advantages and Limitations of Serological Tests
The advantages of serological tests include: * Can detect the presence of antibodies: Serological tests can detect the presence of antibodies against the herpes virus, which can indicate a current or past infection. * Non-invasive: Serological tests are non-invasive, meaning that they do not require a sample of cells or tissue from the affected area. The limitations of serological tests include: * May not detect the virus during the early stages of infection: Serological tests may not detect the presence of antibodies during the early stages of infection, when the symptoms are most severe. * May detect false-positive results: Serological tests may detect false-positive results, especially in people who have been vaccinated against herpes.Physical Examinations

Physical examinations are an essential component of diagnosing herpes. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to look for signs and symptoms of herpes, such as blisters or sores. The physical examination may also include a visual inspection of the affected area, as well as a review of the patient's medical history.
Advantages and Limitations of Physical Examinations
The advantages of physical examinations include: * Can detect visible signs and symptoms: Physical examinations can detect visible signs and symptoms of herpes, such as blisters or sores. * Non-invasive: Physical examinations are non-invasive, meaning that they do not require a sample of cells or tissue from the affected area. The limitations of physical examinations include: * May not detect the virus during the early stages of infection: Physical examinations may not detect the presence of the virus during the early stages of infection, when the symptoms are most severe. * May not detect the virus in people with no symptoms: Physical examinations may not detect the presence of the virus in people who have no symptoms or who have had the infection for a long time.What are the symptoms of herpes?
+The symptoms of herpes may include blisters or sores, itching, burning, or tingling sensations, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and headache.
How is herpes diagnosed?
+Herpes is diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as viral culture, PCR testing, and serological tests.
Can herpes be cured?
+Herpes cannot be cured, but it can be managed using antiviral medications, which can reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.
How can herpes be prevented?
+Herpes can be prevented by practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding close contact with people who have the virus.
What are the complications of herpes?
+The complications of herpes may include recurrent infections, transmission of the virus to others, and increased risk of other infections, such as HIV.
In conclusion, testing for herpes is a critical component of diagnosing and managing the condition. The various methods of testing for herpes, including viral culture, PCR testing, serological tests, and physical examinations, each have their own advantages and limitations. Understanding the different testing methods and their accuracy is essential for making informed decisions about treatment and care. If you suspect that you may have herpes, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. By taking the necessary steps to prevent and manage herpes, you can reduce the risk of complications and improve your overall health and well-being. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have.
