Intro
Discover Neurontin uses and benefits, including nerve pain relief, epilepsy treatment, and anxiety management, with its anticonvulsant and analgesic properties.
The world of pharmaceuticals is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of conditions. One such medication is Neurontin, also known as gabapentin, which has been widely used for various purposes. Understanding the uses and benefits of Neurontin is crucial for both medical professionals and patients, as it can significantly impact treatment outcomes and quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the details of Neurontin, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and advantages.
Neurontin has been on the market for several decades, initially approved for the treatment of epilepsy. Over time, its uses have expanded to include other conditions, such as nerve pain, anxiety disorders, and even mood stabilization. The medication's versatility stems from its unique mechanism of action, which involves modulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain. By influencing the way neurons communicate, Neurontin can help alleviate symptoms associated with various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The importance of Neurontin lies in its ability to provide relief for individuals suffering from debilitating conditions. For instance, patients with epilepsy often experience seizures that can be unpredictable and disruptive to daily life. Neurontin helps reduce the frequency and severity of these seizures, allowing patients to regain control over their lives. Similarly, individuals with nerve pain, such as those with diabetes or shingles, can benefit from Neurontin's analgesic properties, which can significantly reduce discomfort and improve overall well-being.
What is Neurontin?

History of Neurontin
The development of Neurontin dates back to the 1980s, when scientists were searching for new treatments for epilepsy. Initially, the medication was designed to mimic the structure of GABA, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal activity. After several years of research and clinical trials, Neurontin was approved by the FDA in 1993 for the treatment of partial seizures in adults. Since then, its indications have expanded to include other conditions, such as postherpetic neuralgia and restless legs syndrome.Neurontin Uses
Benefits of Neurontin
The benefits of Neurontin are numerous and can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with various conditions. Some of the advantages of using Neurontin include: * Effective seizure control: Neurontin can reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in individuals with epilepsy. * Pain relief: The medication can provide significant relief from nerve pain, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities with greater ease. * Anxiolytic effects: Neurontin may help reduce anxiety symptoms, improving overall mental well-being. * Mood stabilization: The medication may help stabilize mood in individuals with bipolar disorder, reducing the risk of manic or depressive episodes.How Neurontin Works

Neurontin and GABA
Neurontin is often referred to as a GABA analog, as it was designed to mimic the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA. However, its exact relationship with GABA is still unclear. Some studies suggest that Neurontin may increase GABA levels in the brain, while others propose that it may bind to GABA receptors, modulating their activity.Side Effects of Neurontin

Severe Side Effects
In rare cases, Neurontin can cause severe side effects, such as: * Suicidal thoughts or behaviors * Angioedema * Stevens-Johnson syndrome * Toxic epidermal necrolysis * Seizure exacerbationNeurontin Dosage
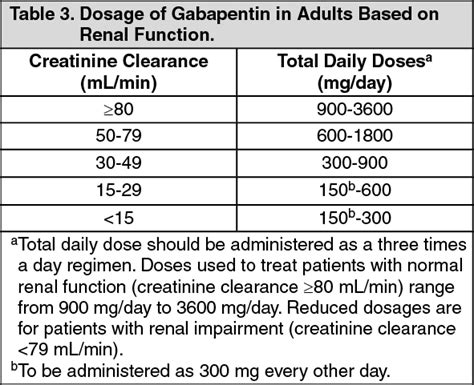
Neurontin Administration
Neurontin is available in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and oral solutions. The medication can be taken with or without food, but it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions to ensure optimal efficacy and minimize side effects.Neurontin Interactions
Neurontin and Pregnancy
Neurontin is classified as a Category C medication, meaning that it may pose a risk to the fetus during pregnancy. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should consult their healthcare provider before taking Neurontin.Neurontin Alternatives
Neurontin and Other Conditions
Neurontin has been used off-label to treat various conditions, including: * Fibromyalgia * Migraines * Hot flashes * Irritable bowel syndrome * Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)What is Neurontin used for?
+Neurontin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, anxiety disorders, and mood stabilization.
How does Neurontin work?
+Neurontin binds to voltage-gated calcium channels in the brain, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters.
What are the common side effects of Neurontin?
+Common side effects of Neurontin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, nausea, and headache.
Can Neurontin be used during pregnancy?
+Neurontin is classified as a Category C medication, meaning that it may pose a risk to the fetus during pregnancy. Women should consult their healthcare provider before taking Neurontin.
What are the alternatives to Neurontin?
+Alternatives to Neurontin include pregabalin, topiramate, carbamazepine, valproate, and lamotrigine.
As we conclude our exploration of Neurontin, it is essential to remember that this medication can significantly impact the lives of individuals with various conditions. By understanding its uses, benefits, and potential side effects, patients and healthcare providers can work together to optimize treatment outcomes. If you have any questions or concerns about Neurontin, we encourage you to share your thoughts and engage in a discussion. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
