Intro
Learn 5 ways to check blood sugar levels, including glucose meters, continuous monitoring, and alternative methods, to manage diabetes and maintain healthy blood glucose levels with ease.
Checking blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes. It helps individuals understand how their body responds to different foods, physical activity, and medications, allowing them to make informed decisions about their health. With the advancement of technology, there are now various methods to check blood sugar levels, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. In this article, we will delve into the different ways to check blood sugar levels, providing an in-depth look at the latest techniques and technologies available.
The importance of regular blood sugar monitoring cannot be overstated. By keeping track of their blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can identify patterns and trends, enabling them to adjust their treatment plans accordingly. This, in turn, can help prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Moreover, regular monitoring can also help individuals with diabetes to maintain a healthy weight, improve their overall well-being, and enhance their quality of life.
With the numerous options available, choosing the right method for checking blood sugar levels can be overwhelming. Factors such as accuracy, convenience, and cost play a significant role in determining the most suitable method for an individual. In the following sections, we will explore the different ways to check blood sugar levels, discussing their advantages and disadvantages, as well as providing practical examples and statistical data to support our claims.
Introduction to Blood Sugar Monitoring

Blood sugar monitoring is an essential aspect of diabetes management. It involves tracking blood sugar levels throughout the day, typically before and after meals, as well as before bedtime. This information is then used to adjust the treatment plan, ensuring that blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range. There are several methods for checking blood sugar levels, including fingerstick testing, continuous glucose monitoring, and oral glucose tolerance testing.
Types of Blood Sugar Monitoring
There are two primary types of blood sugar monitoring: self-monitoring and professional monitoring. Self-monitoring involves individuals tracking their own blood sugar levels using a glucometer or other device, while professional monitoring is conducted by a healthcare professional in a clinical setting. Both types of monitoring are essential for effective diabetes management, as they provide valuable insights into an individual's blood sugar levels and help identify potential complications.Fingerstick Testing
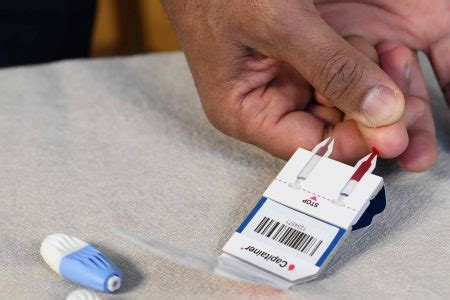
Fingerstick testing is the most common method for checking blood sugar levels. It involves pricking the skin with a lancet to collect a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into a glucometer. The glucometer measures the glucose levels in the blood sample, providing an accurate reading. Fingerstick testing is a relatively simple and inexpensive method, making it a popular choice for individuals with diabetes.
Advantages of Fingerstick Testing
The advantages of fingerstick testing include: * Convenience: Fingerstick testing can be done anywhere, at any time, making it a convenient option for individuals with busy lifestyles. * Affordability: Fingerstick testing is a relatively inexpensive method, with test strips and lancets available at a low cost. * Accuracy: Fingerstick testing provides accurate results, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.Continuous Glucose Monitoring

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a relatively new technology that involves wearing a small sensor under the skin to track blood sugar levels throughout the day. The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, providing real-time data that can be used to adjust the treatment plan. CGM is a valuable tool for individuals with diabetes, as it provides detailed insights into blood sugar levels and helps identify patterns and trends.
Advantages of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The advantages of CGM include: * Detailed insights: CGM provides detailed information about blood sugar levels, enabling individuals to identify patterns and trends. * Real-time data: CGM provides real-time data, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management. * Reduced fingerstick testing: CGM reduces the need for fingerstick testing, making it a convenient option for individuals who prefer not to prick their fingers.Oral Glucose Tolerance Testing

Oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT) is a method used to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes. It involves drinking a sugary drink and then measuring blood sugar levels over a period of time, typically two hours. OGTT is a valuable tool for diagnosing diabetes, as it provides information about the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
Advantages of Oral Glucose Tolerance Testing
The advantages of OGTT include: * Diagnostic accuracy: OGTT provides accurate results, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes. * Simple procedure: OGTT is a relatively simple procedure, involving drinking a sugary drink and then measuring blood sugar levels. * Low cost: OGTT is a low-cost method, making it a convenient option for individuals who require diabetes testing.Other Methods for Checking Blood Sugar Levels
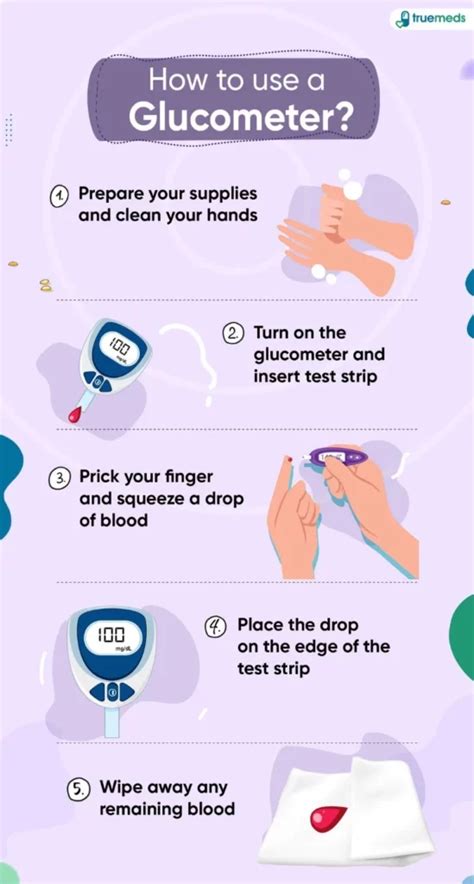
In addition to fingerstick testing, CGM, and OGTT, there are other methods for checking blood sugar levels. These include:
- Urine testing: Urine testing involves measuring the level of glucose in the urine, providing information about blood sugar levels.
- Blood tests: Blood tests involve measuring the level of glucose in the blood, providing information about blood sugar levels.
- Non-invasive testing: Non-invasive testing involves using devices that measure blood sugar levels without requiring a blood sample.
Advantages of Other Methods
The advantages of other methods include: * Convenience: Other methods, such as urine testing and non-invasive testing, are convenient and do not require a blood sample. * Accuracy: Other methods, such as blood tests, provide accurate results, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management. * Low cost: Other methods, such as urine testing, are low-cost and make it a convenient option for individuals who require diabetes testing.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, checking blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. With the various methods available, individuals can choose the one that best suits their needs and lifestyle. Whether it's fingerstick testing, CGM, OGTT, or other methods, regular monitoring is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By understanding the different methods available and their advantages and disadvantages, individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes management and take control of their health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with blood sugar monitoring in the comments section below. Have you tried any of the methods mentioned in this article? What were your results, and how have you incorporated blood sugar monitoring into your diabetes management plan? Your input will help others who are struggling with diabetes management, and we appreciate your participation in this discussion.
What is the best method for checking blood sugar levels?
+The best method for checking blood sugar levels depends on individual needs and preferences. Fingerstick testing is a popular option, while continuous glucose monitoring provides detailed insights into blood sugar levels.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on individual needs and the type of diabetes. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes should check their blood sugar levels 4-6 times a day, while those with type 2 diabetes should check their levels 1-3 times a day.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+The normal range for blood sugar levels is between 70-140 mg/dL. However, this range may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and medication use.
Can I use a glucometer to check my blood sugar levels?
+Yes, a glucometer is a device used to check blood sugar levels. It measures the glucose levels in a blood sample, providing accurate results.
What are the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring?
+The benefits of continuous glucose monitoring include detailed insights into blood sugar levels, real-time data, and reduced fingerstick testing. It is a valuable tool for individuals with diabetes, enabling them to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
