Intro
Kidney stones are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, hard mineral deposits can cause severe pain, nausea, and vomiting, and if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications. Detecting kidney stones early on is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further problems. In this article, we will discuss the importance of detecting kidney stones, the symptoms to look out for, and the various methods used to diagnose this condition.
Detecting kidney stones is essential because it allows for prompt treatment, which can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Kidney stones can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and certain medical conditions. If you have a family history of kidney stones, are overweight or obese, or have a history of certain medical conditions, such as gout or inflammatory bowel disease, you may be more likely to develop kidney stones.
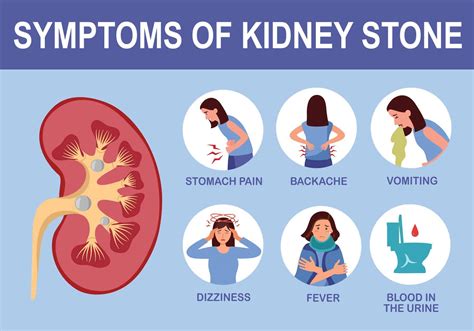
The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on the size and location of the stone. Small stones may not cause any symptoms at all, while larger stones can cause severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. Common symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain in the side or back, below the ribs, pain that radiates to the lower abdomen or groin, nausea and vomiting, frequent or painful urination, and blood in the urine. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Detecting Kidney Stones

Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and ultrasound, can help confirm the diagnosis of kidney stones. These tests can show the size, shape, and location of the stone, as well as any blockages or damage to the kidneys or urinary tract. CT scans are often used to diagnose kidney stones because they can provide detailed images of the kidneys and urinary tract.Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Causes of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and certain medical conditions. If you have a family history of kidney stones, are overweight or obese, or have a history of certain medical conditions, such as gout or inflammatory bowel disease, you may be more likely to develop kidney stones. Other factors that can increase your risk of developing kidney stones include: * Dehydration * Certain medications, such as diuretics and calcium supplements * A diet high in salt, sugar, and animal protein * Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease and urinary tract infectionsTreatment Options

Prevention
Preventing kidney stones is essential to reduce the risk of developing this condition. To prevent kidney stones, you can: * Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated * Limit your intake of salt, sugar, and animal protein * Avoid certain medications, such as diuretics and calcium supplements * Manage any underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease and urinary tract infections * Maintain a healthy weight and dietRisk Factors

Complications
If left untreated, kidney stones can lead to serious complications, such as: * Infection * Blockage of the urinary tract * Damage to the kidneys or urinary tract * Severe pain and nausea * Vomiting and dehydrationDiagnosis
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests can help diagnose kidney stones by checking for: * Blood in the urine * Infection * Other abnormalities, such as high levels of certain minerals or proteinsTreatment
Follow-up Care
After treatment, it is essential to follow up with your doctor to ensure that the stone has passed and to prevent further complications. Your doctor may recommend: * Follow-up imaging studies to check for any remaining stone fragments * Laboratory tests to check for any abnormalities * Lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake and avoiding certain foodsConclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with kidney stones in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with others who may be affected by kidney stones.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
+The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on the size and location of the stone. Common symptoms include severe pain in the side or back, below the ribs, pain that radiates to the lower abdomen or groin, nausea and vomiting, frequent or painful urination, and blood in the urine.
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
+Kidney stones are typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Your doctor will start by asking you questions about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. They will also perform a physical examination to check for signs of kidney stones, such as tenderness in the abdomen or back.
What are the treatment options for kidney stones?
+Treatment options for kidney stones depend on the size and location of the stone, as well as the severity of symptoms. Small stones may pass on their own without treatment, while larger stones may require medical intervention. Treatment options include pain relief medication, fluids, medication to help pass the stone, surgery, and lithotripsy.
Can kidney stones be prevented?
+Yes, kidney stones can be prevented by staying hydrated, limiting intake of salt, sugar, and animal protein, avoiding certain medications, managing underlying medical conditions, and maintaining a healthy weight and diet.
What are the risk factors for kidney stones?
+Certain risk factors can increase your likelihood of developing kidney stones, including family history, obesity or being overweight, certain medical conditions, dehydration, certain medications, and a diet high in salt, sugar, and animal protein.
