Intro
Learn 5 ways to diagnose UTI symptoms, causes, and treatments, including urine tests, physical exams, and medical history, to effectively manage urinary tract infections and prevent recurrence with natural remedies and antibiotics.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. UTIs occur when bacteria, viruses, or fungi infect the urinary tract, causing symptoms such as burning sensations while urinating, frequent urination, and abdominal pain. Diagnosing UTIs is crucial to provide effective treatment and prevent complications. In this article, we will explore the importance of diagnosing UTIs and the various methods used to diagnose this condition.
UTIs can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex. However, women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to easily enter the bladder. If left untreated, UTIs can lead to severe complications, such as kidney damage, sepsis, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to diagnose UTIs promptly and accurately. The diagnosis of UTIs involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests.
The symptoms of UTIs can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include dysuria (painful urination), frequent urination, urgency to urinate, and abdominal pain. In some cases, UTIs can cause more severe symptoms, such as fever, chills, and flank pain. To diagnose UTIs, healthcare providers use various methods, including physical examination, urinalysis, and imaging tests. In the following sections, we will discuss the different methods used to diagnose UTIs.
Understanding UTI Diagnosis
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
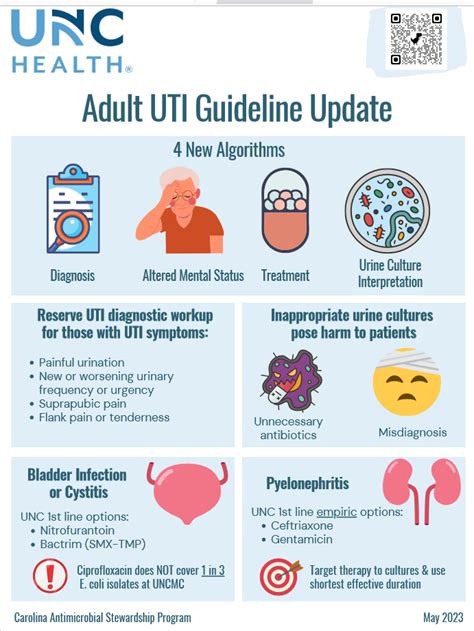
Accurate diagnosis of UTIs is crucial to provide effective treatment and prevent complications. Untreated UTIs can lead to severe consequences, such as kidney damage, sepsis, and even death. Therefore, healthcare providers must use a combination of diagnostic methods to confirm the presence of UTIs and rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.5 Ways to Diagnose UTI
Urinalysis and Urine Culture
Urinalysis and urine culture are the most common methods used to diagnose UTIs. Urinalysis involves analyzing a urine sample to check for the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities. Urine culture involves growing bacteria from a urine sample to confirm the presence of UTI and identify the type of bacteria causing the infection. These tests are essential to diagnose UTIs and provide effective treatment.Benefits of Early Diagnosis
Challenges in Diagnosing UTIs
Diagnosing UTIs can be challenging, especially in patients with underlying health conditions or those who are asymptomatic. The challenges in diagnosing UTIs include: * Asymptomatic patients: Some patients may not exhibit symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose UTIs. * Underlying health conditions: Patients with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease, may be more prone to UTIs and require careful diagnosis and treatment. * Antibiotic resistance: The overuse of antibiotics has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, making it challenging to treat UTIs.Prevention and Treatment

Home Remedies for UTIs
There are several home remedies that can help alleviate UTI symptoms and prevent complications. These include: * Drinking cranberry juice: Cranberry juice may help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the bladder and urinary tract walls. * Taking probiotics: Probiotics may help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract and reduce the risk of UTIs. * Applying heat: Applying heat to the abdomen may help alleviate UTI symptoms, such as pain and discomfort.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
UTIs are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Diagnosing UTIs is crucial to provide effective treatment and prevent complications. By understanding the importance of UTI diagnosis and the various methods used to diagnose this condition, patients can take an active role in their healthcare and reduce the risk of complications. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.What are the common symptoms of UTIs?
+The common symptoms of UTIs include dysuria (painful urination), frequent urination, urgency to urinate, and abdominal pain.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
+UTIs are diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including urinalysis, urine culture, and imaging tests.
Can UTIs be prevented?
+Yes, UTIs can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, avoiding certain foods, and taking antibiotics as prescribed.
What are the complications of untreated UTIs?
+The complications of untreated UTIs include kidney damage, sepsis, and even death.
How can I reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs?
+You can reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs by practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, avoiding certain foods, and taking antibiotics as prescribed.
