Intro
Identify groin muscle strain symptoms, including pain, swelling, and limited mobility, and learn about treatment options for adductor strains, thigh injuries, and inner thigh muscle pulls.
The groin area is a complex region of the body that consists of several muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It plays a crucial role in movements such as walking, running, and kicking. However, this area is also prone to injuries, particularly muscle strains. A groin muscle strain occurs when one of the muscles in the groin area is stretched or torn, leading to pain, discomfort, and limited mobility. Understanding the symptoms of a groin muscle strain is essential for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
Groin muscle strains are common among athletes, especially those who participate in sports that involve sudden changes of direction, such as soccer, football, and basketball. However, anyone can experience a groin muscle strain, regardless of their athletic background. The symptoms of a groin muscle strain can vary in severity, ranging from mild to severe. In some cases, the symptoms may develop suddenly, while in others, they may appear gradually over time.
The severity of a groin muscle strain can be classified into three grades. Grade 1 is the mildest form, characterized by minimal pain and limited loss of function. Grade 2 is moderate, with more significant pain and some loss of function. Grade 3 is the most severe, involving significant pain and substantial loss of function. Recognizing the symptoms of a groin muscle strain is critical for determining the appropriate course of treatment and preventing further complications.
Groin Muscle Strain Symptoms
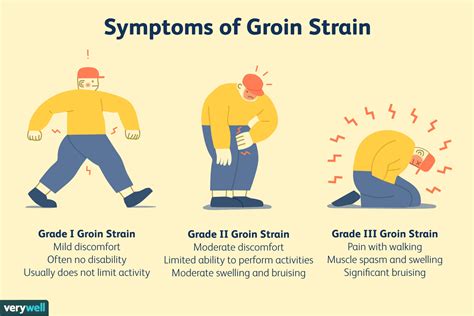
The symptoms of a groin muscle strain can be quite distressing, affecting an individual's daily activities and overall quality of life. Some common symptoms include pain and tenderness in the groin area, swelling and bruising, limited mobility, and weakness in the affected muscle. In some cases, a groin muscle strain can also cause a snapping or popping sensation, especially when the muscle is stretched or contracted.
Causes and Risk Factors

Several factors can contribute to the development of a groin muscle strain. These include overuse or repetitive strain, poor warm-up or cool-down routines, inadequate stretching or flexibility exercises, weak or imbalanced muscles, and poor technique or biomechanics. Additionally, certain sports or activities that involve sudden changes of direction, kicking, or pivoting can increase the risk of a groin muscle strain.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing a groin muscle strain typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. The treatment for a groin muscle strain depends on the severity of the injury and may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, pain management, and in some cases, surgery. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as delayed treatment can lead to further complications and prolonged recovery.
Prevention and Recovery

Preventing a groin muscle strain involves a combination of proper training, warm-up and cool-down routines, stretching and flexibility exercises, and strengthening the muscles in the groin area. Recovery from a groin muscle strain requires patience, as it can take several weeks or even months for the muscle to heal completely. A gradual return to activity, incorporating strengthening and stretching exercises, can help prevent re-injury and promote optimal recovery.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
If left untreated or poorly managed, a groin muscle strain can lead to several complications, including chronic pain, limited mobility, and decreased athletic performance. In some cases, a groin muscle strain can also increase the risk of developing other conditions, such as osteoarthritis or tendinitis. Long-term effects of a groin muscle strain can be significant, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
Returning to Activity

Returning to activity after a groin muscle strain requires a gradual and structured approach. This involves a series of progressive exercises and drills designed to strengthen the affected muscle, improve flexibility, and enhance overall athletic performance. A well-planned return to activity can help prevent re-injury, promote optimal recovery, and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, a groin muscle strain is a common injury that can have significant consequences if left untreated or poorly managed. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for prompt diagnosis and effective management. Future research should focus on developing more effective prevention and treatment strategies, as well as improving our understanding of the long-term effects of groin muscle strains.
Final Thoughts

Groin muscle strains are a significant concern for athletes and non-athletes alike. By recognizing the symptoms, taking preventive measures, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of developing a groin muscle strain and promote optimal recovery. As our understanding of groin muscle strains continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed and adapt to new developments in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
What are the common symptoms of a groin muscle strain?
+Pain and tenderness in the groin area, swelling and bruising, limited mobility, and weakness in the affected muscle are common symptoms of a groin muscle strain.
How can I prevent a groin muscle strain?
+Preventing a groin muscle strain involves a combination of proper training, warm-up and cool-down routines, stretching and flexibility exercises, and strengthening the muscles in the groin area.
What is the typical recovery time for a groin muscle strain?
+The recovery time for a groin muscle strain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but it can take several weeks or even months for the muscle to heal completely.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into groin muscle strain symptoms, causes, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of preventing and managing groin muscle strains. Take the first step towards optimal recovery and reduced risk of injury by incorporating preventive measures into your daily routine.
