Intro
Learn to give subcutaneous injections easily with step-by-step guides, injection techniques, and safety precautions, mastering subcutaneous injection methods and medication administration.
Subcutaneous injections are a crucial aspect of medical treatment for various conditions, including diabetes, hormone replacement therapy, and vaccinations. These injections involve inserting a needle into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin, delivering medication directly to the site of action. Understanding the proper technique for administering subcutaneous injections is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals who self-administer these injections. In this article, we will delve into the world of subcutaneous injections, exploring their importance, benefits, and the step-by-step process of administering them safely and effectively.
The significance of subcutaneous injections cannot be overstated. They offer a convenient and relatively painless method of drug delivery, allowing for the administration of a wide range of medications. For individuals with conditions such as diabetes, subcutaneous injections of insulin are a lifeline, enabling them to manage their blood glucose levels and lead active lives. Moreover, subcutaneous injections are used in vaccination programs, providing immunity against infectious diseases and contributing to public health.
As we navigate the realm of subcutaneous injections, it becomes clear that their benefits extend beyond the medical sphere. They also play a critical role in improving the quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions. By providing a simple and effective means of drug administration, subcutaneous injections empower patients to take control of their health, reducing the need for hospital visits and minimizing the risk of complications. Furthermore, advancements in injection technology have led to the development of user-friendly devices, such as auto-injectors and prefilled syringes, which simplify the injection process and enhance patient comfort.
Understanding Subcutaneous Injections
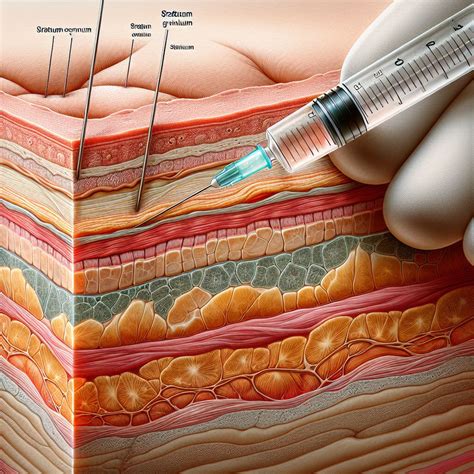
To administer a subcutaneous injection, it is essential to understand the anatomy of the skin and the underlying tissue. The skin is composed of several layers, with the epidermis being the outermost layer, followed by the dermis, and finally, the subcutaneous tissue, which is the target area for these injections. The subcutaneous tissue is rich in blood vessels and contains a significant amount of fatty tissue, making it an ideal site for drug absorption.
Preparation and Planning
Before administering a subcutaneous injection, several steps must be taken to ensure a safe and successful procedure. Firstly, the injection site must be selected, taking into account factors such as the presence of scar tissue, tattoos, or other skin lesions that may interfere with the injection. Common sites for subcutaneous injections include the abdomen, thigh, and upper arm. It is crucial to rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy, a condition characterized by the abnormal distribution of body fat.Step-by-Step Guide to Administering Subcutaneous Injections
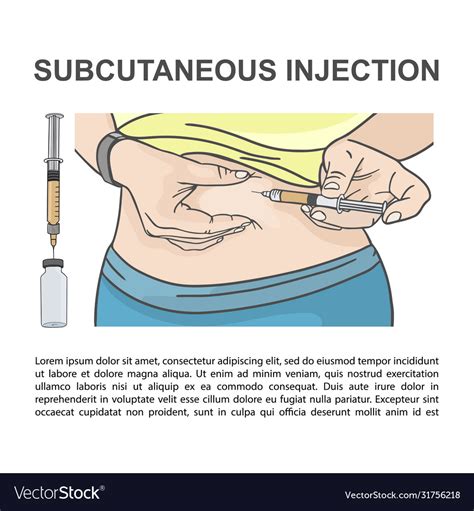
Administering a subcutaneous injection involves several key steps:
- Step 1: Prepare the injection site by cleaning the area with an antiseptic wipe and allowing it to dry.
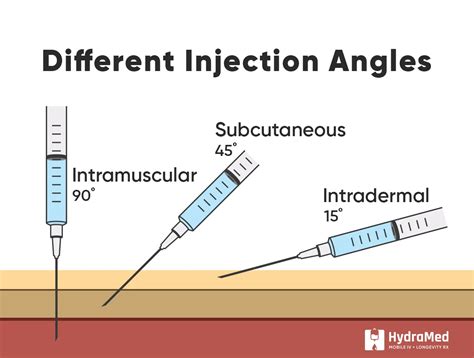
- Step 2: Remove the needle cap and hold the syringe at a 45-degree angle, with the needle bevel facing up.
- Step 3: Pinch the skin at the injection site, creating a fold of skin between the thumb and index finger.
- Step 4: Insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45-degree angle, using a smooth, steady motion.
- Step 5: Release the skin and slowly inject the medication over 5-10 seconds.
- Step 6: Withdraw the needle at the same angle it was inserted and apply gentle pressure to the injection site with a cotton ball or gauze.
Tips and Tricks for a Successful Injection
To ensure a successful subcutaneous injection, several tips and tricks can be employed: * **Use the correct needle size** to minimize discomfort and ensure proper drug delivery. * **Inject at the correct angle** to avoid injecting into the muscle or other tissues. * **Use a steady hand** and inject slowly to reduce pain and discomfort. * **Apply a cold compress** or topical anesthetic cream to the injection site before administering the injection to reduce pain.Potential Complications and Side Effects

While subcutaneous injections are generally safe, potential complications and side effects can occur. These may include:
- Pain and discomfort at the injection site
- Redness and swelling due to inflammation or allergic reactions
- Infection if the injection site is not properly cleaned and disinfected
- Nerve damage if the needle is inserted too deeply or at the wrong angle
Managing Complications and Side Effects
To manage complications and side effects, it is essential to: * **Monitor the injection site** for signs of infection or other adverse reactions * **Apply a cold compress** or topical cream to reduce pain and inflammation * **Seek medical attention** if symptoms persist or worsen over timeBest Practices for Subcutaneous Injections
To ensure safe and effective subcutaneous injections, several best practices should be followed:
- Use sterile equipment and follow proper infection control procedures
- Select the correct injection site and rotate sites to prevent lipodystrophy
- Inject at the correct angle and use the correct needle size
- Monitor the injection site for signs of complications or side effects
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, subcutaneous injections are a vital component of medical treatment, offering a convenient and effective means of drug delivery. By understanding the proper technique for administering these injections and following best practices, healthcare professionals and individuals can ensure safe and successful procedures. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see advancements in injection devices and techniques, further improving the administration of subcutaneous injections.What is the most common site for subcutaneous injections?
+The most common site for subcutaneous injections is the abdomen, followed by the thigh and upper arm.
How often should injection sites be rotated?
+Injection sites should be rotated regularly to prevent lipodystrophy, with the exact frequency depending on the individual's treatment plan and medical condition.
What are the potential complications of subcutaneous injections?
+Potential complications of subcutaneous injections include pain and discomfort, redness and swelling, infection, and nerve damage.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of subcutaneous injections and their importance in medical treatment. Whether you are a healthcare professional or an individual administering injections, it is essential to follow proper techniques and best practices to ensure safe and effective procedures. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to share them with us. We invite you to engage with our content, share your experiences, and join the conversation on subcutaneous injections. Together, we can work towards improving healthcare outcomes and enhancing the lives of individuals around the world.
