Intro
Discover foods rich in calcium, including dairy, leafy greens, and fortified options, to support strong bones and overall health, with essential minerals like vitamin D and phosphorus.
Calcium is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting various bodily functions. Adequate calcium intake is essential for people of all ages, and a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of calcium-rich foods can help meet daily calcium needs. In this article, we will explore the importance of calcium, its benefits, and provide a comprehensive list of foods rich in calcium.
Adequate calcium intake is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting muscle and nerve function. Calcium deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, osteopenia, and increased risk of fractures. Additionally, calcium plays a role in maintaining healthy blood pressure, supporting weight management, and reducing the risk of certain diseases, such as colon cancer and kidney stones.
Calcium is an essential nutrient that is often overlooked, but it is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being. With so many delicious and calcium-rich foods available, it is easy to incorporate more calcium into your diet. From dairy products to leafy greens, and from fortified foods to fish, there are many ways to boost your calcium intake and support strong bones and teeth.
Benefits of Calcium-Rich Foods

Calcium-rich foods offer numerous health benefits, including supporting strong bones and teeth, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, and maintaining healthy blood pressure. Additionally, calcium-rich foods can help support weight management, reduce the risk of certain diseases, and promote overall health and well-being. Some of the key benefits of calcium-rich foods include:
- Supporting strong bones and teeth
- Reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure
- Supporting weight management
- Reducing the risk of certain diseases, such as colon cancer and kidney stones
Types of Calcium-Rich Foods
Calcium-rich foods can be broadly categorized into several groups, including dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, and fish. Each of these groups offers a range of delicious and nutritious options that can help boost calcium intake.Dairy Products

Dairy products are some of the richest sources of calcium, and they include milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. These foods are not only high in calcium but also rich in other essential nutrients, such as protein, vitamin D, and potassium. Some of the best dairy products for calcium include:
- Milk: 1 cup of milk contains approximately 300 mg of calcium
- Cheese: 1 ounce of cheese contains approximately 200-300 mg of calcium
- Yogurt: 1 cup of yogurt contains approximately 300-400 mg of calcium
- Butter: 1 tablespoon of butter contains approximately 20-30 mg of calcium
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are another excellent source of calcium, and they include foods such as kale, broccoli, spinach, and collard greens. These foods are not only rich in calcium but also high in other essential nutrients, such as vitamin K, vitamin A, and fiber. Some of the best leafy greens for calcium include:- Kale: 1 cup of cooked kale contains approximately 200-250 mg of calcium
- Broccoli: 1 cup of cooked broccoli contains approximately 200-250 mg of calcium
- Spinach: 1 cup of cooked spinach contains approximately 200-250 mg of calcium
- Collard greens: 1 cup of cooked collard greens contains approximately 250-300 mg of calcium
Fortified Foods

Fortified foods are foods that have been enriched with calcium and other essential nutrients. These foods can be an excellent way to boost calcium intake, especially for those who have difficulty consuming enough calcium-rich foods. Some of the best fortified foods for calcium include:
- Fortified orange juice: 1 cup of fortified orange juice contains approximately 300-400 mg of calcium
- Fortified cereals: 1 serving of fortified cereal contains approximately 100-300 mg of calcium
- Fortified plant-based milk: 1 cup of fortified plant-based milk contains approximately 300-400 mg of calcium
Fish and Seafood
Fish and seafood are excellent sources of calcium, and they include foods such as salmon, sardines, and shrimp. These foods are not only rich in calcium but also high in other essential nutrients, such as protein, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. Some of the best fish and seafood for calcium include:- Salmon: 3 ounces of cooked salmon contains approximately 180-200 mg of calcium
- Sardines: 3 ounces of canned sardines contains approximately 350-400 mg of calcium
- Shrimp: 3 ounces of cooked shrimp contains approximately 100-150 mg of calcium
Other Calcium-Rich Foods

In addition to dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, and fish, there are many other foods that are rich in calcium. Some of these foods include:
- Tofu: 3 ounces of cooked tofu contains approximately 200-250 mg of calcium
- Edamame: 1 cup of cooked edamame contains approximately 200-250 mg of calcium
- Almonds: 1 ounce of almonds contains approximately 80-100 mg of calcium
- Sesame seeds: 1 tablespoon of sesame seeds contains approximately 80-100 mg of calcium
Calcium-Rich Food Combinations
Combining different calcium-rich foods can help boost calcium intake and support strong bones and teeth. Some examples of calcium-rich food combinations include:- Greek yogurt with spinach and almonds
- Fortified orange juice with fortified cereal
- Grilled salmon with roasted broccoli and brown rice
- Smoothie bowl with fortified plant-based milk, banana, and sesame seeds
Calcium Intake Recommendations
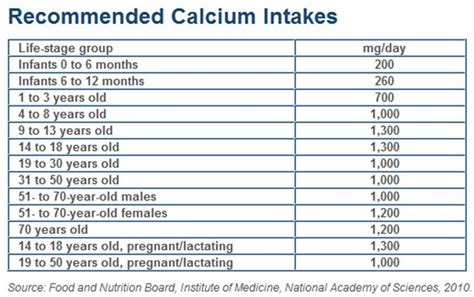
The recommended daily intake of calcium varies by age and sex, but most adults need approximately 1,000 mg of calcium per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as older adults, may need more calcium to support their health. Some examples of calcium intake recommendations include:
- Adults 19-50 years: 1,000 mg per day
- Adults 51-70 years: 1,000 mg per day
- Adults 71 years and older: 1,200 mg per day
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 1,300 mg per day
Calcium Deficiency and Toxicity
Calcium deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, osteopenia, and increased risk of fractures. On the other hand, excessive calcium intake can lead to toxicity and increase the risk of kidney stones and other health problems. Some examples of calcium deficiency and toxicity include:- Calcium deficiency: osteoporosis, osteopenia, increased risk of fractures
- Calcium toxicity: kidney stones, constipation, nausea and vomiting
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, calcium is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting various bodily functions. Incorporating a variety of calcium-rich foods into your diet can help meet daily calcium needs and support overall health and well-being. By following the calcium intake recommendations and combining different calcium-rich foods, you can boost your calcium intake and reduce the risk of calcium deficiency and toxicity.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with calcium-rich foods in the comments below. Have you found any creative ways to incorporate more calcium into your diet? Do you have any favorite calcium-rich foods or recipes? Share your stories and tips with us, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and family who may benefit from learning more about the importance of calcium.
What are the best sources of calcium?
+The best sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, and fish. Some examples of calcium-rich foods include milk, cheese, yogurt, kale, broccoli, spinach, fortified orange juice, and salmon.
How much calcium do I need per day?
+The recommended daily intake of calcium varies by age and sex, but most adults need approximately 1,000 mg of calcium per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as older adults, may need more calcium to support their health.
What happens if I don't get enough calcium?
+Calcium deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including osteoporosis, osteopenia, and increased risk of fractures. On the other hand, excessive calcium intake can lead to toxicity and increase the risk of kidney stones and other health problems.
