Intro
Learn 5 ways to measure blood sugar levels, including glucose meters, continuous monitors, and lab tests, to effectively manage diabetes and track blood glucose, insulin, and glycemic control.
Measuring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. With the advancement of technology, there are various methods available to measure blood sugar levels, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. In this article, we will delve into the different ways to measure blood sugar levels, exploring their mechanisms, advantages, and limitations.
The importance of measuring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. It helps individuals with diabetes to monitor their condition, make informed decisions about their diet and exercise, and adjust their medication accordingly. Moreover, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it is essential to understand the different methods of measuring blood sugar levels and their significance in maintaining good health.
Measuring blood sugar levels is not only crucial for individuals with diabetes but also for those who are at risk of developing the condition. Factors such as obesity, family history, and physical inactivity can increase the risk of developing diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can identify potential issues early on and take preventive measures to reduce their risk. Furthermore, measuring blood sugar levels can help individuals understand how different foods, exercises, and medications affect their blood sugar levels, enabling them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle.
Introduction to Blood Sugar Measurement
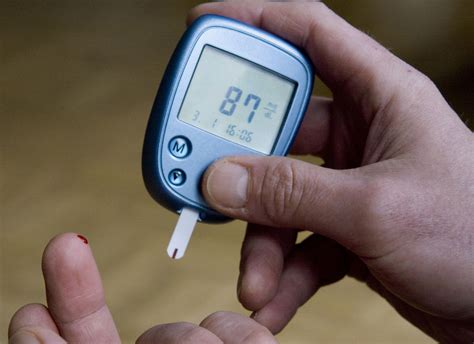
Types of Blood Sugar Measurements
There are several types of blood sugar measurements, including fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar, and random blood sugar. Fasting blood sugar measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast, typically 8-12 hours. Postprandial blood sugar measures the level of glucose in the blood after a meal, usually 1-2 hours after eating. Random blood sugar measures the level of glucose in the blood at any time of the day, regardless of when the last meal was consumed.Method 1: Fingertip Blood Sampling
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fingertip Blood Sampling
The advantages of fingertip blood sampling include its ease of use, quick results, and minimal pain. However, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Fingertip blood sampling can be affected by factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude, which can impact the accuracy of the results. Additionally, some individuals may experience pain or discomfort when pricking their fingertip, especially if they have sensitive skin.Method 2: Continuous Glucose Monitoring

Benefits and Limitations of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The benefits of CGM include its ability to provide real-time glucose data, identify patterns and trends in glucose levels, and alert individuals to potential high or low blood sugar levels. However, there are also some limitations to consider. CGM requires calibration, which can be time-consuming and may require additional fingerstick tests. Additionally, CGM sensors can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance.Method 3: Urine Testing

Advantages and Disadvantages of Urine Testing
The advantages of urine testing include its non-invasive nature and ease of use. However, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Urine testing is not as accurate as other methods, as it can be affected by factors such as hydration levels and kidney function. Additionally, urine testing may not detect high blood sugar levels until they have reached a certain threshold, which can be a concern for individuals with diabetes.Method 4: Oral Glucose Tolerance Test

Benefits and Limitations of Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The benefits of the OGTT include its ability to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes, as well as its ability to assess insulin resistance. However, there are also some limitations to consider. The OGTT can be time-consuming and may require multiple blood samples. Additionally, the test may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as gastroparesis.Method 5: Hemoglobin A1c Test
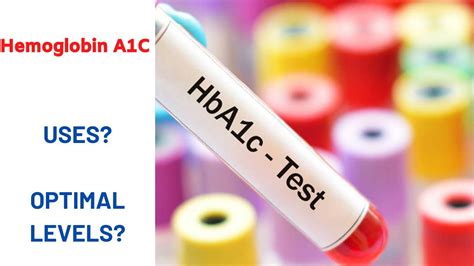
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hemoglobin A1c Test
The advantages of the HbA1c test include its ability to provide a comprehensive picture of blood sugar control over time. However, there are also some limitations to consider. The HbA1c test may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as anemia or kidney disease. Additionally, the test may not reflect recent changes in blood sugar levels.What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+The normal range for blood sugar levels is between 70-140 mg/dL. However, this range may vary depending on the individual and their medical condition.
How often should I measure my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of measuring blood sugar levels depends on the individual and their medical condition. Generally, individuals with diabetes should measure their blood sugar levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the risks of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. It is essential to manage blood sugar levels to prevent these complications.
Can I measure my blood sugar levels at home?
+Yes, you can measure your blood sugar levels at home using a glucose meter. However, it is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns.
What are the different types of glucose meters available?
+There are several types of glucose meters available, including fingertip blood sampling, continuous glucose monitoring, and urine testing. The choice of glucose meter depends on the individual's needs and preferences.
In conclusion, measuring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. There are various methods available to measure blood sugar levels, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. By understanding the different methods and their significance, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to prevent complications associated with diabetes. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips on measuring blood sugar levels, and to consult with a healthcare professional if they have any questions or concerns. Additionally, we invite readers to explore other articles on our website that provide comprehensive information on diabetes management and blood sugar control.
