Intro
Identify dehydration signs and symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and dark urine, to prevent severe dehydration and heat exhaustion, and learn how to stay hydrated with essential fluids and electrolytes.
Dehydration is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, and not drinking enough water. Dehydration can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and it's essential to recognize the signs and symptoms to take prompt action. In this article, we'll delve into the importance of hydration, the causes of dehydration, and the signs and symptoms to look out for.
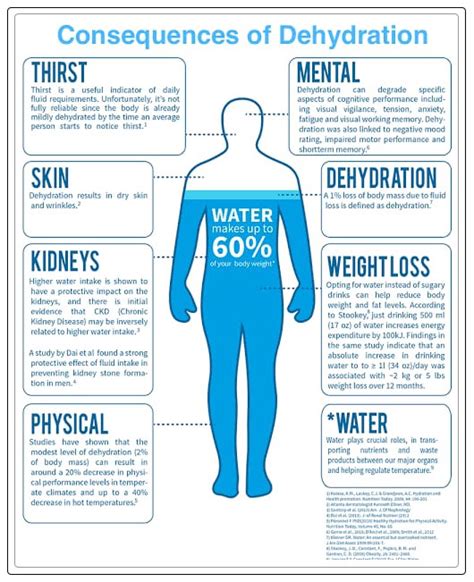
Dehydration can have severe consequences if left untreated, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Even mild dehydration can cause significant impairment in physical and cognitive performance, making it essential to address the issue promptly. Furthermore, dehydration can exacerbate underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, and diabetes, making it crucial for individuals with these conditions to be aware of the signs and symptoms.
The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, which plays a vital role in maintaining various bodily functions, such as regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells, and removing waste products. When the body loses fluids, it disrupts the delicate balance of electrolytes, leading to a range of symptoms. Understanding the causes of dehydration is crucial in preventing and treating the condition. Common causes of dehydration include excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and not drinking enough water.
Understanding Dehydration

Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration can be caused by a variety of factors, including: * Excessive sweating due to hot weather, exercise, or fever * Vomiting and diarrhea, which can lead to a significant loss of fluids and electrolytes * Not drinking enough water, which can be due to a lack of access to clean drinking water, a lack of thirst, or a medical condition that affects the body's ability to regulate fluids * Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, which can increase the risk of dehydration * Medications, such as diuretics, which can increase urine production and lead to dehydrationSigns and Symptoms of Dehydration

Mild Dehydration Symptoms
Mild dehydration symptoms can be easily treated by drinking plenty of water and electrolyte-rich fluids. Common symptoms of mild dehydration include: * Dry mouth and throat * Fatigue and weakness * Headaches and dizziness * Dark yellow or brown urine * Decreased urine outputTreating Dehydration

Preventing Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is crucial, especially for individuals who are at risk of dehydration, such as athletes, individuals with underlying medical conditions, and older adults. Common strategies for preventing dehydration include: * Drinking plenty of water and electrolyte-rich fluids * Avoiding excessive sweating by staying in cool environments and taking regular breaks * Eating foods rich in electrolytes, such as bananas, avocados, and nuts * Monitoring urine output and color to ensure adequate hydrationComplications of Dehydration
Dehydration in Vulnerable Populations
Dehydration can affect anyone, but certain populations are more vulnerable to dehydration, including: * Older adults, who may have a decreased sense of thirst and impaired ability to regulate fluids * Young children, who may be unable to communicate their needs and may have a higher surface area to volume ratio, making them more susceptible to dehydration * Athletes, who may lose excessive amounts of fluids and electrolytes during intense physical activity * Individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure, which can increase the risk of dehydrationConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with dehydration in the comments below. Have you or a loved one experienced dehydration? What steps do you take to stay hydrated? Share your tips and advice with our community.
What are the common causes of dehydration?
+Common causes of dehydration include excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and not drinking enough water.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+Preventing dehydration involves drinking plenty of water and electrolyte-rich fluids, avoiding excessive sweating, eating foods rich in electrolytes, and monitoring urine output and color.
What are the signs and symptoms of severe dehydration?
+Signs and symptoms of severe dehydration include rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, sunken eyes, decreased skin elasticity, and decreased urine output.
