Intro
Get tested for gonorrhea now with confidential STD testing. Learn symptoms, treatment, and prevention methods to protect against this bacterial infection and related sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia and syphilis.
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and can infect both men and women. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious health complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission. Therefore, it is essential to get tested for gonorrhea if you are sexually active or have engaged in high-risk behaviors.
The importance of gonorrhea testing cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can help prevent long-term health consequences and reduce the risk of transmission to others. Furthermore, gonorrhea testing is a crucial step in maintaining good reproductive health and preventing the spread of STIs. With the rise of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea strains, it is more important than ever to get tested and seek medical attention if you suspect you have been infected.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in gonorrhea cases, particularly among young adults and men who have sex with men. This trend highlights the need for increased awareness and education about gonorrhea prevention, testing, and treatment. By understanding the risks and consequences of gonorrhea, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their partners. In this article, we will delve into the world of gonorrhea testing, exploring the benefits, methods, and importance of getting tested.
Gonorrhea Testing Methods

There are several methods available for gonorrhea testing, including nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), Gram stains, and cultures. NAATs are the most commonly used method, as they are highly sensitive and can detect the presence of gonorrhea DNA in urine, blood, or tissue samples. Gram stains involve examining a sample under a microscope to detect the presence of gonorrhea bacteria, while cultures involve growing the bacteria in a laboratory to confirm the diagnosis.
Types of Gonorrhea Tests
The type of gonorrhea test used depends on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and risk factors. Some common types of gonorrhea tests include: * Urine tests: These are the most common type of gonorrhea test and involve collecting a urine sample to detect the presence of gonorrhea DNA. * Swab tests: These involve collecting a sample from the affected area, such as the cervix, urethra, or rectum, to detect the presence of gonorrhea bacteria. * Blood tests: These are used to detect the presence of gonorrhea antibodies in the blood, which can indicate a current or past infection.Benefits of Gonorrhea Testing
Gonorrhea testing offers several benefits, including:
- Early detection and treatment: Gonorrhea testing can help detect the infection early, reducing the risk of long-term health complications and transmission to others.
- Prevention of health complications: Untreated gonorrhea can lead to serious health complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission.
- Reduced risk of transmission: Gonorrhea testing can help reduce the risk of transmission to others, particularly in high-risk groups such as men who have sex with men.
- Peace of mind: Gonorrhea testing can provide peace of mind for individuals who are concerned about their reproductive health or have engaged in high-risk behaviors.
Who Should Get Tested for Gonorrhea
Anyone who is sexually active or has engaged in high-risk behaviors should get tested for gonorrhea. This includes: * Sexually active women under the age of 25 * Men who have sex with men * Individuals with multiple sex partners * Individuals with a history of STIs * Individuals who have engaged in high-risk behaviors, such as unprotected sex or sharing needlesGonorrhea Treatment and Prevention

Gonorrhea treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can cure the infection. However, it is essential to complete the full course of treatment to ensure that the infection is fully cleared. In addition to treatment, there are several steps that can be taken to prevent gonorrhea, including:
- Practicing safe sex: Using condoms or other barrier methods can reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
- Getting vaccinated: Vaccines are available to protect against other STIs, such as HPV and hepatitis B.
- Getting tested regularly: Regular gonorrhea testing can help detect the infection early and reduce the risk of transmission to others.
Gonorrhea Prevention Methods
Some common gonorrhea prevention methods include: * Condoms: Using condoms can reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission by up to 90%. * Dental dams: Using dental dams can reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission during oral sex. * Vaccines: Vaccines are available to protect against other STIs, such as HPV and hepatitis B.Gonorrhea Statistics and Trends
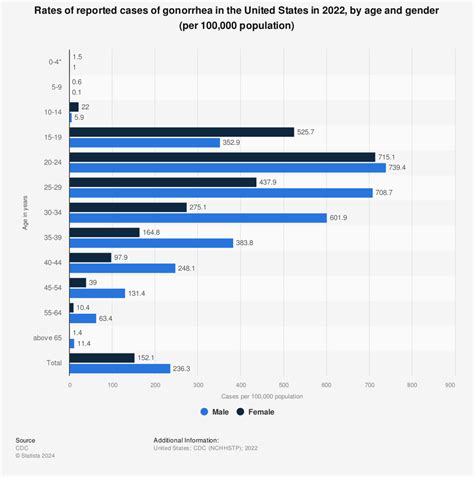
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), gonorrhea is one of the most common STIs in the United States, with over 550,000 reported cases in 2020. The CDC also reports that gonorrhea rates have increased by over 50% since 2014, with the highest rates found among young adults and men who have sex with men.
Gonorrhea Trends and Risk Factors
Some common trends and risk factors associated with gonorrhea include: * Age: Gonorrhea rates are highest among young adults, particularly those under the age of 25. * Sex: Men who have sex with men are at higher risk of gonorrhea transmission. * Multiple sex partners: Having multiple sex partners increases the risk of gonorrhea transmission. * History of STIs: Individuals with a history of STIs are at higher risk of gonorrhea transmission.Gonorrhea Diagnosis and Symptoms
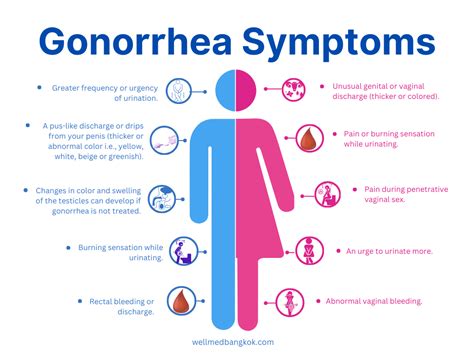
Gonorrhea symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Painful urination
- Discharge or bleeding from the genitals
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Sore throat
Gonorrhea Diagnosis Methods
Gonorrhea diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests. Some common diagnosis methods include: * Urine tests: These are the most common type of gonorrhea test and involve collecting a urine sample to detect the presence of gonorrhea DNA. * Swab tests: These involve collecting a sample from the affected area, such as the cervix, urethra, or rectum, to detect the presence of gonorrhea bacteria. * Blood tests: These are used to detect the presence of gonorrhea antibodies in the blood, which can indicate a current or past infection.Gonorrhea Treatment Options
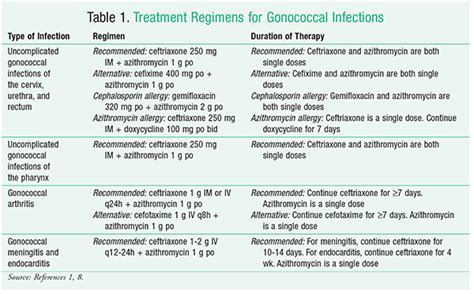
Gonorrhea treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can cure the infection. However, it is essential to complete the full course of treatment to ensure that the infection is fully cleared. Some common treatment options include:
- Ceftriaxone: This is a common antibiotic used to treat gonorrhea and is typically administered via injection.
- Azithromycin: This is an oral antibiotic that is often used in combination with ceftriaxone to treat gonorrhea.
- Doxycycline: This is an oral antibiotic that is often used to treat gonorrhea, particularly in individuals who are allergic to ceftriaxone or azithromycin.
Gonorrhea Treatment Side Effects
Some common side effects associated with gonorrhea treatment include: * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Headache * DizzinessWhat are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
+Gonorrhea symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include painful urination, discharge or bleeding from the genitals, abdominal pain, fever, and sore throat.
How is gonorrhea diagnosed?
+Gonorrhea diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests. Some common diagnosis methods include urine tests, swab tests, and blood tests.
What are the treatment options for gonorrhea?
+Gonorrhea treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can cure the infection. Some common treatment options include ceftriaxone, azithromycin, and doxycycline.
How can I prevent gonorrhea?
+Some common gonorrhea prevention methods include practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, and getting tested regularly. Using condoms or other barrier methods can reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission by up to 90%.
What are the risks of untreated gonorrhea?
+Untreated gonorrhea can lead to serious health complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission. It is essential to get tested and seek medical attention if you suspect you have been infected.
In summary, gonorrhea is a common STI that can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Getting tested for gonorrhea is essential for early detection and treatment, and can help prevent long-term health complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others. By understanding the benefits, methods, and importance of gonorrhea testing, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their partners. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to take action by getting tested for gonorrhea today. Your health and well-being depend on it.
