Intro
Discover key Bupropion facts, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this antidepressant medication and its role in treating depression, anxiety, and smoking cessation, with insights into its benefits and risks.
Bupropion, a medication primarily known for its application in managing depression and smoking cessation, has been a subject of interest for its multifaceted benefits and side effects. Understanding the intricacies of bupropion is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals considering its use. The importance of bupropion lies in its unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other antidepressants and cessation aids, making it a valuable option for those who have not found relief with other treatments.
The mechanism through which bupropion operates is distinct, acting as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI), which means it increases the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby improving mood and reducing the urge to smoke. This dual action on both norepinephrine and dopamine sets bupropion apart, as most antidepressants primarily affect serotonin levels. The unique profile of bupropion contributes to its efficacy in treating major depressive disorder and seasonal affective disorder, as well as aiding in smoking cessation.
As with any medication, it's essential to delve into the specifics of bupropion, including its benefits, potential side effects, and the process of how it works, to make informed decisions about its use. This exploration will not only shed light on the pharmacological aspects of bupropion but also provide insights into its practical applications, helping individuals to understand whether bupropion could be a suitable option for their specific needs.
Introduction to Bupropion
Benefits of Bupropion
How Bupropion Works
The working mechanism of bupropion involves the inhibition of the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters that play key roles in mood regulation and reward pathways. By preventing the reabsorption of these neurotransmitters, bupropion effectively increases their concentration in the synaptic cleft, enhancing neurotransmission. This action is believed to contribute to its antidepressant and smoking cessation effects.Side Effects of Bupropion
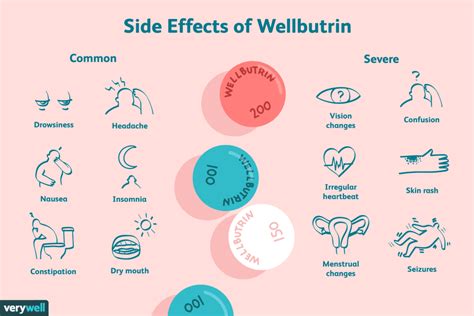
Precautions and Contraindications
It's crucial to approach the use of bupropion with caution, especially in certain populations. Bupropion is contraindicated in individuals with a seizure disorder, as it can lower the seizure threshold. Additionally, it should be used with caution in patients with a history of eating disorders, due to the potential risk of seizures. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking bupropion, as its safety in these populations has not been fully established.Practical Applications of Bupropion
Steps to Initiate Bupropion Therapy
For individuals considering bupropion, the following steps can guide the initiation of therapy: 1. **Consult a Healthcare Provider:** Discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider to determine if bupropion is suitable. 2. **Start with a Low Dose:** Typically, therapy begins with a low dose to assess tolerance and minimize side effects. 3. **Gradually Increase the Dose:** As needed and under medical supervision, the dose can be increased to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. 4. **Monitor Progress:** Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and manage any side effects.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts and Recommendations

Engaging with the Content

What is bupropion primarily used for?
+Bupropion is primarily used for the treatment of major depressive disorder and as an aid for smoking cessation.
How does bupropion work?
+Bupropion works by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, increasing their levels in the brain and improving mood and reducing the urge to smoke.
Can bupropion be used for conditions other than depression and smoking cessation?
+Yes, bupropion is sometimes prescribed off-label for conditions such as ADHD, bipolar depression, and sexual dysfunction, highlighting its potential beyond its approved uses.
