Intro
Identify UTI symptoms with our comprehensive test guide, covering urinary tract infection causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, including cloudy urine, burning sensation, and frequent urination.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing inflammation and infection. The symptoms of a UTI can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs that may indicate the presence of an infection. In this article, we will discuss the importance of testing for UTI symptoms, the different types of tests available, and what to expect during the testing process.
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, and if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis. It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any symptoms of a UTI, such as burning during urination, frequent urination, or abdominal pain. Early detection and treatment can help to prevent long-term damage and alleviate symptoms.
The importance of testing for UTI symptoms cannot be overstated. A prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. There are several types of tests available to diagnose UTIs, including urine tests, imaging tests, and physical exams. Each test has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of test depends on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and other factors.
Understanding UTI Symptoms
Common UTI Symptoms
Some common UTI symptoms include: * Burning during urination * Frequent urination * Abdominal pain * Fever * Chills * Blood in the urine * Cloudy or strong-smelling urine * Pelvic painTypes of UTI Tests

Urine Tests
Urine tests are the most common type of test used to diagnose UTIs. These tests involve analyzing a urine sample for the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities. There are several types of urine tests, including: * Urinalysis: This test involves analyzing a urine sample for the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities. * Urine culture: This test involves growing bacteria from a urine sample to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection.Preparing for UTI Testing

What to Expect During UTI Testing
During UTI testing, a healthcare provider will: * Take a medical history: This involves asking questions about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and other factors. * Perform a physical exam: This involves examining the patient's abdomen, back, and genital area to check for signs of infection or other complications. * Collect a urine sample: This involves collecting a urine sample from the patient to analyze for the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities.Treatment Options for UTIs
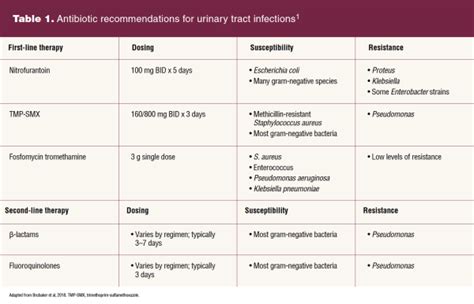
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is the most common type of treatment used to treat UTIs. Antibiotics work by killing the bacteria causing the infection, which can help to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. There are several types of antibiotics available, including: * Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole * Nitrofurantoin * CephalexinPreventing UTIs
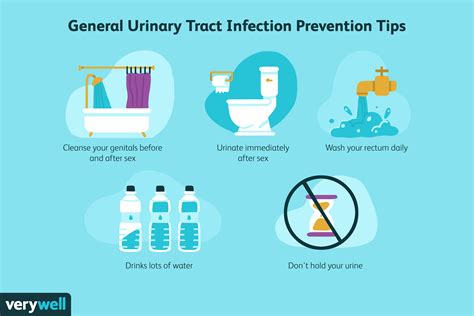
Additional Tips for Preventing UTIs
Some additional tips for preventing UTIs include: * Avoiding tight clothing: Tight clothing can trap moisture and create an environment that is conducive to bacterial growth. * Avoiding spermicides: Spermicides can increase the risk of UTIs, so it is essential to avoid using them. * Getting tested regularly: Regular testing can help to detect UTIs early, which can prevent complications and alleviate symptoms.Complications of UTIs
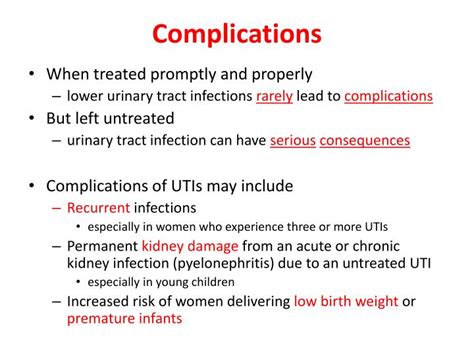
Long-Term Complications of UTIs
Some long-term complications of UTIs include: * Kidney damage: UTIs can cause scarring and damage to the kidneys, which can lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. * Sepsis: UTIs can cause sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection becomes uncontrolled and causes widespread inflammation. * Recurrent UTIs: Some people may experience recurrent UTIs, which can be painful and uncomfortable.What are the symptoms of a UTI?
+The symptoms of a UTI can include burning during urination, frequent urination, abdominal pain, fever, and chills. In some cases, UTIs can also cause blood in the urine, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
+UTIs are typically diagnosed using a combination of physical exams, medical history, and urine tests. Urine tests can help to detect the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine.
How are UTIs treated?
+UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, which can help to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, other treatments may be necessary, such as pain relievers or urinary tract analgesics.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of UTI symptoms, testing, and treatment options. If you are experiencing any symptoms of a UTI, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent complications and alleviate symptoms. Remember to drink plenty of water, urinate when needed, and practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of UTIs. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of UTI testing and treatment. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts and experiences with UTIs.
