Intro
Monitor your health with our guide on how to test your sugar levels, including blood glucose monitoring, diabetes management, and healthy lifestyle tips to regulate blood sugar and prevent hyperglycemia.
Monitoring and managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When an individual consumes food, their body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells.
The importance of testing sugar levels cannot be overstated. Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes understand how their body responds to different foods, physical activity, and medications. This information enables them to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise routine, and medication regimen, ultimately helping them maintain healthy blood sugar levels. For individuals without diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels can help identify potential issues before they become serious. Factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and a family history of diabetes can increase an individual's risk of developing insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
Testing blood sugar levels is a relatively simple process that can be performed at home using a glucometer, a small device that measures the glucose levels in a blood sample. The process involves pricking the skin with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip inserted into the glucometer. The device provides a reading of the blood glucose level, usually in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Regular testing, combined with a healthy diet and regular physical activity, can help individuals manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing complications related to diabetes.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. Carbohydrates, in particular, have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as white bread and sugary snacks, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, have a more gradual effect.Testing Blood Sugar Levels
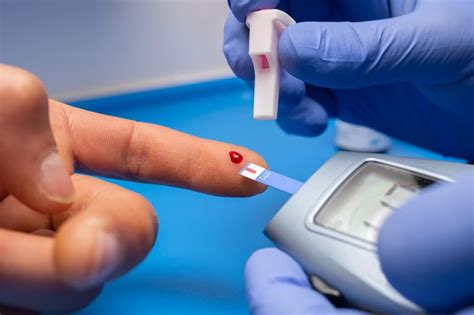
Types of Blood Sugar Tests
* Fasting blood sugar tests: These tests measure blood sugar levels after an overnight fast and are usually performed in the morning. * Postprandial tests: These tests measure blood sugar levels after eating and are usually performed one to two hours after a meal. * Random tests: These tests measure blood sugar levels at any time of day and can be used to monitor blood sugar levels throughout the day.Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
* Eat a healthy, balanced diet that is low in added sugars and saturated fats. * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming. * Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and adjust diet and medication as needed. * Get enough sleep and manage stress levels.Complications of Unmanaged Blood Sugar Levels
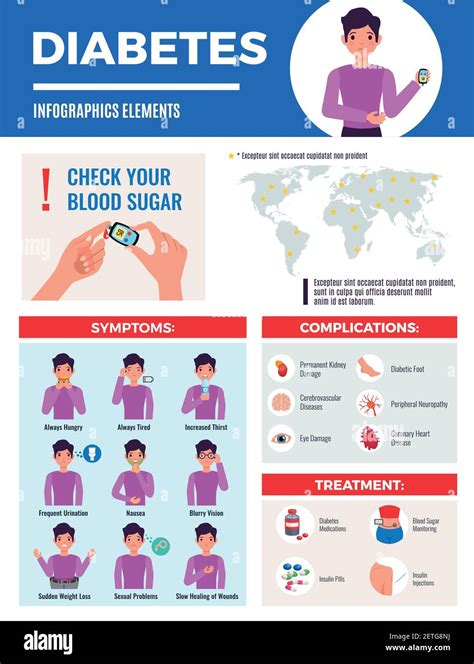
Long-Term Complications of Unmanaged Blood Sugar Levels
* Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. * Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys' filters, leading to kidney failure. * Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.Preventing Blood Sugar-Related Complications

Strategies for Preventing Blood Sugar-Related Complications
* Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and adjust diet and medication as needed. * Eat a healthy, balanced diet that is low in added sugars and saturated fats. * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming. * Get enough sleep and manage stress levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. Your feedback and insights can help others who may be struggling with similar issues. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the information.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+A normal blood sugar level is typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL, although this can vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day.
How often should I test my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of testing blood sugar levels depends on the individual's specific needs and treatment plan, but most people with diabetes test their blood sugar levels at least once a day.
What are the potential complications of unmanaged blood sugar levels?
+Unmanaged blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
