Intro
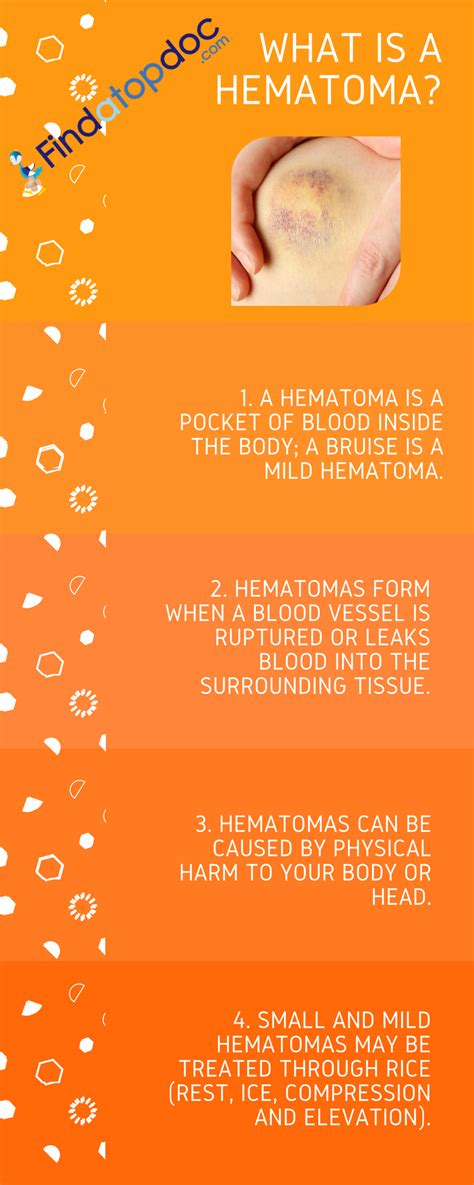
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside of blood vessels, often caused by injury or trauma. It can be painful and may lead to further complications if not treated properly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hematomas is crucial for effective management. Hematomas can occur in various parts of the body, including the brain, muscles, and under the skin, each requiring specific approaches to treatment. The importance of prompt and appropriate treatment cannot be overstated, as it can significantly impact the healing process and prevent long-term damage.
Hematomas are not just a matter of aesthetics; they can be a sign of underlying health issues that need attention. For instance, a hematoma in the brain can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention. Similarly, hematomas in other parts of the body can lead to infection, nerve damage, or chronic pain if not managed correctly. The key to treating a hematoma effectively lies in understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking medical attention when necessary. With the right approach, it is possible to minimize the risk of complications and promote healing.
The treatment of hematomas has evolved over time, with advancements in medical technology and techniques offering new possibilities for effective management. From conservative treatments like rest and ice to more invasive procedures like surgery, the options available depend on the severity and location of the hematoma. Additionally, preventive measures can play a significant role in reducing the risk of hematoma formation, especially in individuals prone to injury or with certain medical conditions. By adopting a proactive approach to health and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can better manage hematomas and prevent their occurrence.
Treatment Options for Hematomas
Treatment options for hematomas vary widely depending on their size, location, and the overall health of the individual. For small, superficial hematomas, conservative management may suffice, including applying ice to reduce swelling, elevating the affected area to minimize blood flow, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers to manage discomfort. However, larger hematomas or those in sensitive areas may require more aggressive interventions, such as drainage or surgical evacuation. The goal of treatment is not only to alleviate symptoms but also to prevent potential complications and promote healing.
Conservative Management
Conservative management is often the first line of treatment for hematomas, especially those that are small and not causing significant symptoms. This approach includes measures to reduce pain and inflammation, such as applying ice packs, using compression bandages, and elevating the affected limb above heart level. Rest is also crucial, as it helps reduce further injury to the affected area. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation. It's essential to follow a healthcare provider's advice on the best course of conservative management, as improper treatment can lead to complications.Surgical Intervention
For larger hematomas or those that are causing significant symptoms, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery involves evacuating the hematoma to relieve pressure and promote healing. This procedure can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the location and size of the hematoma. Surgical intervention is particularly important for intracranial hematomas, as they can be life-threatening and require immediate attention. The decision to proceed with surgery is made on a case-by-case basis, considering the risks and benefits for the individual.Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors for hematomas is crucial for prevention and management. Trauma or injury is the most common cause of hematomas, but they can also occur spontaneously in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Age is another risk factor, as older adults are more prone to developing hematomas due to decreased blood vessel elasticity and other age-related changes. Recognizing these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek medical attention promptly if they suspect a hematoma.
Preventive Measures
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of hematoma formation. For individuals prone to injury, such as athletes, wearing protective gear and following safety guidelines can minimize the risk of trauma. For those with medical conditions that increase the risk of bleeding, such as hemophilia, adhering to treatment plans and avoiding activities that could lead to injury is crucial. Additionally, individuals on anticoagulant therapy should be aware of the signs of bleeding and seek medical attention immediately if they suspect a hematoma.Complications and Long-Term Effects
While many hematomas resolve without significant complications, some can lead to long-term effects or serious health issues. Infection is a potential complication, especially if the hematoma becomes infected or if the individual has a compromised immune system. Nerve damage is another risk, particularly for hematomas that compress nerves or are located near sensitive areas. Chronic pain and limited mobility can also result from large or improperly managed hematomas. Understanding these potential complications underscores the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Chronic Pain Management
For individuals who experience chronic pain as a result of a hematoma, management strategies are available. These may include physical therapy to improve mobility and strength, pain management medications, and in some cases, interventions like nerve blocks or steroid injections. A multidisciplinary approach, involving healthcare providers from various specialties, can be beneficial in managing chronic pain and improving quality of life.Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing a hematoma typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider will assess the affected area for signs of bruising, swelling, and tenderness, and may perform tests to evaluate nerve function and mobility. Imaging studies like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can provide detailed images of the hematoma and surrounding tissues, helping to determine its size, location, and potential impact on surrounding structures.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are critical for diagnosing and managing hematomas, especially those in deep or sensitive areas. Ultrasound is often used for superficial hematomas, while CT scans and MRI are preferred for deeper or more complex cases. These studies can help identify the hematoma's size, location, and relationship to surrounding structures, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions.Recovery and Rehabilitation

Recovery from a hematoma depends on its size, location, and the effectiveness of treatment. For small, superficial hematomas, recovery may be quick, with symptoms resolving within a few weeks. Larger or more complex hematomas may require a longer recovery period, potentially involving physical therapy to regain strength and mobility. Rehabilitation focuses on promoting healing, preventing complications, and restoring function to the affected area.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process, especially for individuals who have experienced significant trauma or have developed chronic pain. A physical therapist can design a personalized program to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility, and to address any functional limitations resulting from the hematoma. Early intervention with physical therapy can significantly impact the recovery process, reducing the risk of long-term disability and improving overall outcomes.Current Research and Advances
Research into the causes, treatment, and management of hematomas is ongoing, with scientists and clinicians exploring new therapies and technologies to improve outcomes. Advances in imaging and diagnostic techniques are enabling earlier and more accurate diagnoses, while developments in surgical and interventional procedures are expanding treatment options. Additionally, studies on preventive measures and rehabilitation strategies are providing insights into how to reduce the risk of hematoma formation and promote more effective recovery.
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies, including the use of growth factors, platelet-rich plasma, and other biologic agents, are being investigated for their potential to enhance healing and reduce the risk of complications. These therapies aim to promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall healing environment. While more research is needed to fully understand their benefits and risks, these emerging therapies offer promising avenues for the management of hematomas.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, treating a hematoma effectively requires a comprehensive approach that considers its causes, symptoms, and potential complications. From conservative management to surgical intervention, the treatment options available depend on the hematoma's size, location, and the individual's overall health. As research continues to uncover new insights into the management of hematomas, it is essential for healthcare providers and individuals to stay informed about the latest advances and best practices. By working together, we can improve outcomes, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance the quality of life for those affected by hematomas.
We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, or seek advice on managing hematomas. Your engagement can help others understand the importance of prompt and appropriate treatment, and how to navigate the complex process of recovery and rehabilitation. Together, let's promote awareness and support for those affected by hematomas, and look forward to a future where advancements in medical science continue to improve our ability to treat and manage these conditions effectively.
What are the common symptoms of a hematoma?
+Common symptoms of a hematoma include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility in the affected area. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the hematoma.
How are hematomas diagnosed?
+Hematomas are diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. These tests help determine the size, location, and impact of the hematoma on surrounding tissues.
What are the treatment options for hematomas?
+Treatment options for hematomas vary and may include conservative management with rest, ice, and pain relievers, or more invasive procedures like drainage or surgical evacuation, depending on the size, location, and severity of the hematoma.
Can hematomas be prevented?
+While not all hematomas can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk, such as wearing protective gear during sports, following safety guidelines, and managing underlying medical conditions that may increase the risk of bleeding.
What is the recovery time for a hematoma?
+The recovery time for a hematoma depends on its size, location, and the effectiveness of treatment. Small, superficial hematomas may resolve within a few weeks, while larger or more complex cases may require several months for full recovery.
