Intro
Unlock HSA reimbursement rules, eligibility, and qualified medical expenses, including deductibles, copays, and prescriptions, to maximize tax-free healthcare savings and minimize penalties.
The Health Savings Account (HSA) reimbursement rules are a crucial aspect of managing healthcare expenses for individuals and families. Understanding these rules is essential to maximize the benefits of an HSA and avoid any potential penalties. In this article, we will delve into the details of HSA reimbursement rules, exploring the eligibility criteria, qualified medical expenses, and the process of reimbursing oneself from an HSA.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) have become increasingly popular as a means to save for medical expenses on a tax-free basis. These accounts are designed to work in conjunction with High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs), allowing individuals to set aside pre-tax dollars for qualified medical expenses. The HSA reimbursement rules are designed to ensure that these accounts are used for their intended purpose, which is to cover legitimate healthcare costs.
The importance of understanding HSA reimbursement rules cannot be overstated. Misuse of an HSA or failure to comply with the rules can result in penalties, including taxes on the distributions and potential fines. Moreover, the rules governing HSAs are subject to change, making it essential for account holders to stay informed about any updates or modifications. By grasping the fundamentals of HSA reimbursement, individuals can optimize their healthcare savings strategy and make the most of their HSA benefits.
HSA Eligibility and Contribution Limits

To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be covered under a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) and not be covered under any other health plan that is not an HDHP. This includes not being enrolled in Medicare or having coverage under a general purpose health flexible spending account (FSA) or health reimbursement arrangement (HRA). Additionally, individuals cannot be claimed as a dependent on someone else's tax return. The annual contribution limits to an HSA are set by the IRS and are adjusted for inflation. For 2023, the contribution limit for individuals is $3,850, and for families, it is $7,750. There is also a catch-up contribution of $1,000 for individuals aged 55 or older.
Qualified Medical Expenses
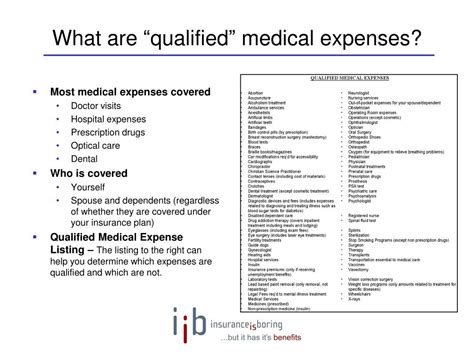
One of the critical aspects of HSA reimbursement rules is understanding what constitutes qualified medical expenses. These are expenses that are eligible for reimbursement from an HSA. Qualified medical expenses include a wide range of healthcare costs, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, prescriptions, and medical equipment. The IRS provides a detailed list of qualified medical expenses in Publication 502. It's essential to note that expenses for non-medical purposes, such as cosmetic procedures not required for medical reasons, are not qualified expenses. Additionally, expenses paid for by another health plan or reimbursed under another arrangement cannot be reimbursed from an HSA.
Examples of Qualified Medical Expenses
- Doctor visits and consultations
- Hospital stays and surgeries
- Prescription medications
- Medical equipment, such as wheelchairs and walkers
- Vision and dental care, including glasses, contacts, and dental procedures
- Transportation costs related to medical care, such as mileage for trips to the doctor
The Reimbursement Process
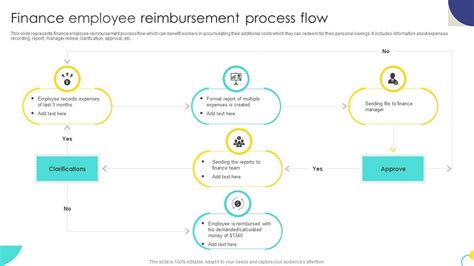
Reimbursing oneself from an HSA for qualified medical expenses is a straightforward process. Individuals should keep receipts and records of their medical expenses, as these will be needed to substantiate the expenses in case of an audit. Most HSA providers offer debit cards or checks that can be used to pay for medical expenses directly from the HSA. Alternatively, individuals can pay out-of-pocket for medical expenses and then reimburse themselves from their HSA. It's crucial to ensure that the reimbursement is made for qualified medical expenses and that the amount does not exceed the expense incurred.
Steps for Reimbursement
- Incur a qualified medical expense.
- Pay for the expense out-of-pocket or use the HSA debit card/check.
- Keep receipts and records of the expense.
- Submit a claim for reimbursement to the HSA provider, if necessary.
- Receive reimbursement from the HSA for the qualified medical expense.
Record Keeping and Substantiation

Proper record keeping and substantiation of medical expenses are vital components of HSA reimbursement rules. Individuals must maintain detailed records of their qualified medical expenses, including receipts, invoices, and statements of medical services. These records should include the date of service, description of the service, and the amount paid. In the event of an audit, these records will be necessary to substantiate the expenses and demonstrate compliance with HSA rules.
Importance of Record Keeping
- Helps in tracking qualified medical expenses.
- Provides evidence of compliance with HSA rules in case of an audit.
- Ensures that reimbursements are made only for legitimate healthcare costs.
Tax Implications and Penalties

The tax implications and potential penalties associated with HSA reimbursement rules are significant considerations. Distributions from an HSA for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. However, distributions for non-qualified expenses before the age of 65 are subject to income tax and a 20% penalty. After the age of 65, distributions for non-qualified expenses are subject to income tax but not the penalty. It's essential to understand these tax implications to avoid any adverse consequences.
Tax Benefits of HSAs
- Contributions are tax-deductible.
- Earnings on the account grow tax-free.
- Distributions for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding HSA reimbursement rules is crucial for maximizing the benefits of a Health Savings Account. By grasping the eligibility criteria, qualified medical expenses, and the reimbursement process, individuals can optimize their healthcare savings strategy. It's also important to stay informed about any updates or changes to the rules governing HSAs. As healthcare costs continue to rise, HSAs will play an increasingly important role in helping individuals and families manage their medical expenses. By leveraging the tax benefits and flexibility of HSAs, individuals can better prepare for future healthcare needs.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations

As we move forward, it's essential to consider the long-term implications of HSA reimbursement rules. Individuals should regularly review their HSA contributions, ensure they are maximizing their annual limits, and explore ways to optimize their healthcare expenses. Moreover, staying updated on any legislative changes or updates to HSA guidelines will be crucial for making informed decisions about healthcare savings. By taking a proactive approach to managing their HSAs, individuals can ensure they are making the most of their healthcare dollars.
What are the primary benefits of having an HSA?
+The primary benefits include tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth of earnings, and tax-free distributions for qualified medical expenses.
Can I use my HSA for expenses related to my family members?
+What happens to my HSA if I leave my job or retire?
+Your HSA is portable, meaning you can take it with you if you leave your job or retire. You can continue to use it for qualified medical expenses, and you may also be able to make contributions if you have an HDHP.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with HSA reimbursement rules in the comments below. Your insights can help others navigate the complexities of managing their healthcare expenses. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding HSA reimbursement rules. Together, we can work towards making healthcare more accessible and affordable for everyone.
