Intro
Learn about Hydrocodones classification as an opioid analgesic, its uses, side effects, and interactions, within the Hydrocodone Drug Class, including narcotic pain relievers and controlled substances, to understand its risks and benefits.
Hydrocodone is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various health conditions, including pain and cough. However, its classification and usage have been subject to controversy and changes in recent years. Understanding the hydrocodone drug class is essential for patients, healthcare professionals, and regulatory agencies to ensure safe and effective use.
The importance of knowing the hydrocodone drug class cannot be overstated. With the ongoing opioid crisis, it is crucial to recognize the potential risks and benefits associated with this medication. Hydrocodone is a powerful opioid that can be habit-forming, leading to dependence and addiction. Moreover, its misuse can have severe consequences, including overdose and death. Therefore, it is vital to approach the use of hydrocodone with caution and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
The hydrocodone drug class is also relevant to healthcare professionals, as it helps them make informed decisions about prescribing and monitoring patients. By understanding the pharmacology, benefits, and risks of hydrocodone, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment plans and minimize the potential for adverse effects. Additionally, regulatory agencies rely on the hydrocodone drug class to establish guidelines and regulations for its use, ensuring public safety and preventing misuse.
What is Hydrocodone?
Types of Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is available in various formulations, including: * Immediate-release (IR) tablets and capsules * Extended-release (ER) tablets and capsules * Combination products with other medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen * Liquid formulations for oral administrationHydrocodone Drug Class
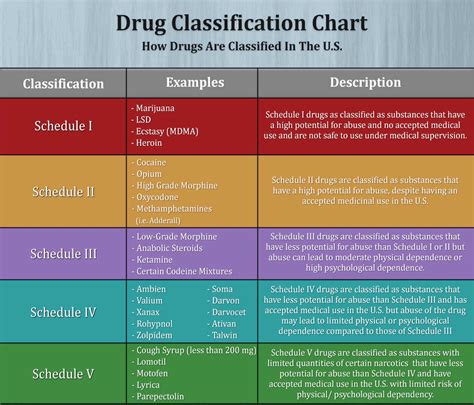
Controlled Substance Status
The controlled substance status of hydrocodone is based on its potential for abuse, dependence, and addiction. The DEA has established the following criteria for scheduling controlled substances: * Schedule I: High potential for abuse and no accepted medical use * Schedule II: High potential for abuse, but has accepted medical use * Schedule III: Moderate to low potential for physical dependence and psychological dependence * Schedule IV: Low potential for abuse and dependence * Schedule V: Very low potential for abuse and dependenceBenefits and Risks of Hydrocodone
Side Effects and Interactions
Hydrocodone can cause several side effects, including: * Drowsiness * Dizziness * Nausea and vomiting * Constipation * Headache * Dry mouth Hydrocodone can also interact with other medications, such as: * Benzodiazepines * Muscle relaxants * Antidepressants * AntihistaminesPrescribing and Monitoring Hydrocodone
Patient Education and Counseling
Patient education and counseling are essential components of hydrocodone therapy. Patients should be informed about: * The potential risks and benefits of hydrocodone * The importance of following the prescribed dosage and treatment plan * The dangers of misuse and addiction * The signs and symptoms of overdose and respiratory depression * The importance of seeking medical attention if adverse effects occurRegulatory Framework and Guidelines
DEA Guidelines
The DEA has established guidelines for the handling and disposal of controlled substances, including hydrocodone. These guidelines include: * Secure storage and disposal of hydrocodone * Use of tamper-evident and tamper-resistant packaging * Monitoring of patient prescriptions and refills * Reporting of suspicious activity and diversionConclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with hydrocodone in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help us better understand the complexities of hydrocodone therapy and provide valuable information for patients and healthcare professionals.
What is hydrocodone used for?
+Hydrocodone is used to treat moderate to severe pain, as well as cough and respiratory issues.
Is hydrocodone a controlled substance?
+Yes, hydrocodone is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance by the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
What are the risks associated with hydrocodone?
+The risks associated with hydrocodone include addiction and dependence, overdose and death, respiratory depression, and interactions with other medications.
