Intro
Discover 8 ibuprofen side effects, including stomach issues, allergic reactions, and increased risk of heart problems, highlighting potential interactions and long-term risks associated with NSAID use and pain relief medications.
Ibuprofen is a widely used over-the-counter medication for relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. It is commonly found in medications such as Advil, Motrin, and Nuprin. While ibuprofen can be effective in managing various types of pain, it can also have side effects, some of which can be serious. Understanding the potential side effects of ibuprofen is crucial for safe usage and to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
The importance of being aware of ibuprofen side effects cannot be overstated. With its widespread use, the potential for side effects to occur is significant. Moreover, certain individuals may be more susceptible to these side effects due to factors such as age, health status, or concurrent use of other medications. By acknowledging and understanding these potential side effects, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and seek medical attention if necessary.
Ibuprofen, like other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are substances in the body that mediate inflammation and pain. While this mechanism of action is beneficial for relieving pain and reducing inflammation, it can also lead to various side effects. The severity and likelihood of these side effects can vary depending on several factors, including the dosage of ibuprofen, the duration of use, and individual susceptibility.
Ibuprofen Side Effects Overview
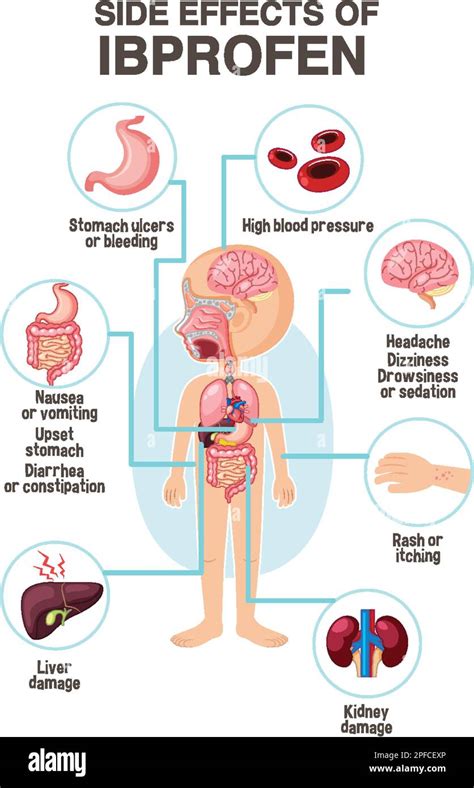
Ibuprofen side effects can range from mild to severe and may affect different systems of the body. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Less common but more serious side effects can involve the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and liver. It is essential to recognize the signs of these side effects to ensure timely medical intervention.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
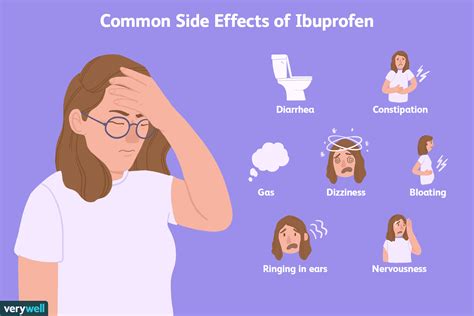
Gastrointestinal side effects are among the most common adverse reactions to ibuprofen. These can include stomach pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The risk of gastrointestinal complications, such as ulcers and bleeding, increases with higher doses and prolonged use of ibuprofen. Individuals with a history of stomach problems or those taking other medications that can irritate the stomach may be at higher risk.Cardiovascular Side Effects
Ibuprofen can also have cardiovascular side effects, particularly with long-term use or in high doses. These can include increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure. The mechanism behind these effects is thought to be related to ibuprofen's impact on blood clotting and its effects on blood vessels. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or risk factors for cardiovascular disease should use ibuprofen with caution and under medical supervision.
Renal Side Effects
The kidneys are another system that can be affected by ibuprofen use. Ibuprofen can reduce blood flow to the kidneys, which may impair their function, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney problems. Long-term use of ibuprofen can lead to kidney damage or exacerbate existing kidney disease. Monitoring kidney function is crucial for individuals taking ibuprofen regularly.Neurological Side Effects

Neurological side effects of ibuprofen, although less common, can include dizziness, headaches, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus). In rare cases, ibuprofen can cause more severe neurological effects, such as seizures or meningitis. These serious side effects are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of neurological disorders or those taking high doses of ibuprofen.
Dermatological Side Effects
Dermatological side effects, including skin rashes, itching, and blistering, can occur with ibuprofen use. These reactions are usually mild but can be severe in rare cases, such as with Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. Individuals experiencing any skin reactions while taking ibuprofen should seek medical attention.Hepatic Side Effects

Ibuprofen can also affect the liver, leading to elevated liver enzymes, which indicate liver damage. In rare cases, ibuprofen can cause severe liver injury, including liver failure. Monitoring liver function is essential for individuals taking ibuprofen, especially those with pre-existing liver conditions.
Respiratory Side Effects
Respiratory side effects of ibuprofen are less common but can include worsening of asthma symptoms in susceptible individuals. Ibuprofen can trigger or exacerbate asthma attacks in some people, particularly those with a history of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD).Minimizing Ibuprofen Side Effects
To minimize the risk of side effects when taking ibuprofen, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare provider before starting treatment, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications. Taking ibuprofen with food can help reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Staying hydrated and monitoring for signs of side effects can also help in early detection and management of adverse reactions.
Alternatives to Ibuprofen
For individuals who experience side effects from ibuprofen or wish to explore alternative pain relief options, several choices are available. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is a common alternative for pain and fever reduction, although it does not have anti-inflammatory properties. Topical pain relievers, such as capsaicin cream or lidocaine patches, can be effective for localized pain without the systemic side effects of oral medications. Natural remedies like turmeric, ginger, and willow bark have anti-inflammatory properties and may provide relief for some individuals.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, while ibuprofen is a valuable medication for managing pain and inflammation, its potential side effects should not be overlooked. By understanding these side effects and taking steps to minimize risks, individuals can safely use ibuprofen when necessary. Future research into safer, more effective pain relief options will be crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden of pain and inflammation on global health.
Final Thoughts
As with any medication, the decision to use ibuprofen should be made with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider when possible. Being informed about the potential side effects and benefits of ibuprofen empowers individuals to make better choices about their health. Whether considering over-the-counter or prescription medications, prioritizing safety and efficacy is paramount.What are the most common side effects of ibuprofen?
+The most common side effects of ibuprofen include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Less common but more serious side effects can involve the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and liver.
Can ibuprofen cause serious health problems?
+Yes, ibuprofen can cause serious health problems, especially with long-term use or in high doses. These can include increased risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and liver injury.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects when taking ibuprofen?
+To minimize the risk of side effects, follow the recommended dosage, take ibuprofen with food, stay hydrated, and monitor for signs of side effects. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting treatment, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ibuprofen side effects. Have you or a loved one encountered any of these side effects? What steps have you taken to manage pain and inflammation safely? Your insights can help others make informed decisions about their health. Please comment below and consider sharing this article with those who might benefit from this information.
