Intro
Discover the 7 common Indomethacin side effects, including stomach issues, dizziness, and headaches, and learn how to manage them with proper dosage and medication management to minimize risks and ensure safe treatment.
Indomethacin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used to treat pain, inflammation, and fever. It is often prescribed for conditions such as arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory diseases. While indomethacin can be effective in managing pain and inflammation, it can also cause a range of side effects. In this article, we will explore 7 common indomethacin side effects, their mechanisms, and what you can do to minimize their impact.
Indomethacin works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that cause pain and inflammation in the body. However, prostaglandins also play a role in protecting the stomach lining and maintaining kidney function, which is why indomethacin can cause gastrointestinal and renal side effects. Understanding the benefits and risks of indomethacin is crucial for patients who are considering taking this medication.
The importance of being aware of indomethacin side effects cannot be overstated. By knowing what to expect, patients can take steps to minimize their risk of experiencing adverse effects and maximize the benefits of treatment. In the following sections, we will delve into the 7 common indomethacin side effects, exploring their causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
Introduction to Indomethacin Side Effects

Types of Indomethacin Side Effects
Indomethacin side effects can be categorized into several types, including: * Gastrointestinal side effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach ulcers, and bleeding * Renal side effects: kidney damage, increased risk of kidney stones, and decreased urine output * Cardiovascular side effects: increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure * Hepatic side effects: liver damage and increased risk of liver failure * Allergic reactions: hives, itching, and difficulty breathingGastrointestinal Side Effects of Indomethacin

To minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, patients can take indomethacin with food, avoid taking the medication on an empty stomach, and consider taking a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or other medication to reduce stomach acid.
Managing Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Some strategies for managing gastrointestinal side effects include: * Taking indomethacin with food * Avoiding taking the medication on an empty stomach * Considering taking a PPI or other medication to reduce stomach acid * Monitoring for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, such as black stools or vomiting bloodRenal Side Effects of Indomethacin
To minimize the risk of renal side effects, patients can stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, monitor their urine output, and consider taking a medication to reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Managing Renal Side Effects
Some strategies for managing renal side effects include: * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Monitoring urine output * Considering taking a medication to reduce the risk of kidney stones * Avoiding taking other medications that can increase the risk of kidney damageCardiovascular Side Effects of Indomethacin
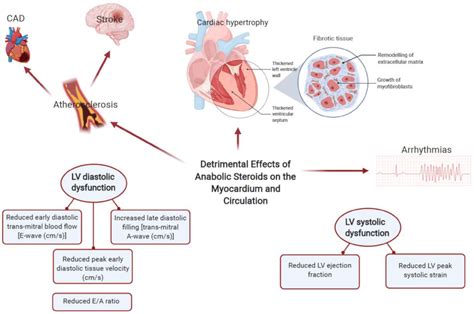
To minimize the risk of cardiovascular side effects, patients can monitor their blood pressure, consider taking a medication to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, and maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Managing Cardiovascular Side Effects
Some strategies for managing cardiovascular side effects include: * Monitoring blood pressure * Considering taking a medication to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise * Avoiding taking other medications that can increase the risk of cardiovascular problemsHepatic Side Effects of Indomethacin

To minimize the risk of hepatic side effects, patients can monitor their liver function, consider taking a medication to reduce the risk of liver damage, and avoid taking other medications that can increase the risk of liver problems.
Managing Hepatic Side Effects
Some strategies for managing hepatic side effects include: * Monitoring liver function * Considering taking a medication to reduce the risk of liver damage * Avoiding taking other medications that can increase the risk of liver problems * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exerciseAllergic Reactions to Indomethacin

To minimize the risk of allergic reactions, patients can monitor for signs of an allergic reaction, consider taking a medication to reduce the risk of allergic reactions, and seek medical attention immediately if symptoms occur.
Managing Allergic Reactions
Some strategies for managing allergic reactions include: * Monitoring for signs of an allergic reaction * Considering taking a medication to reduce the risk of allergic reactions * Seeking medical attention immediately if symptoms occur * Avoiding taking other medications that can increase the risk of allergic reactionsMinimizing the Risk of Indomethacin Side Effects

By following these strategies, patients can reduce their risk of experiencing indomethacin side effects and maximize the benefits of treatment.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with indomethacin in the comments below. Have you taken indomethacin and experienced side effects? What strategies have you used to manage side effects? Your feedback can help others who are considering taking this medication.
What is indomethacin used for?
+Indomethacin is used to treat pain, inflammation, and fever. It is often prescribed for conditions such as arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory diseases.
What are the common side effects of indomethacin?
+The common side effects of indomethacin include gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as renal issues, such as kidney damage and increased risk of kidney stones.
How can I minimize the risk of indomethacin side effects?
+To minimize the risk of indomethacin side effects, patients can take several steps, including taking the medication as directed, monitoring for signs of side effects, considering taking a medication to reduce the risk of side effects, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Can I take indomethacin with other medications?
+It is not recommended to take indomethacin with other medications that can increase the risk of side effects. Patients should consult their doctor before taking any other medications with indomethacin.
How long does it take for indomethacin to start working?
+Indomethacin can start working within a few hours of taking the medication. However, it may take several days to experience the full benefits of treatment.
