Intro
Discover 8 ibuprofen side effects, including stomach issues, allergic reactions, and increased risk of heart problems, highlighting potential interactions and long-term risks associated with NSAID use and pain relief medications.
The use of ibuprofen, a common over-the-counter pain reliever, has become ubiquitous in modern society. Its effectiveness in treating pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever has made it a staple in many households. However, like any medication, ibuprofen is not without its risks. While generally considered safe when used as directed, ibuprofen can cause a range of side effects, some of which can be severe. Understanding these potential side effects is crucial for individuals who rely on ibuprofen for pain management.
Ibuprofen belongs to a class of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, substances in the body that mediate pain and inflammation. While this mechanism of action is beneficial for relieving pain, it can also lead to adverse effects, particularly when the drug is used excessively or in susceptible individuals. The risk of side effects increases with the dose and duration of treatment, emphasizing the importance of using ibuprofen judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional when necessary.
The prevalence of ibuprofen use, coupled with its potential for side effects, underscores the need for awareness among consumers. By understanding the possible risks associated with ibuprofen, individuals can make informed decisions about their pain management strategies and take steps to minimize the risk of adverse effects. This includes being aware of the most common side effects, recognizing the signs of more severe reactions, and knowing when to seek medical attention.
Ibuprofen Side Effects Overview
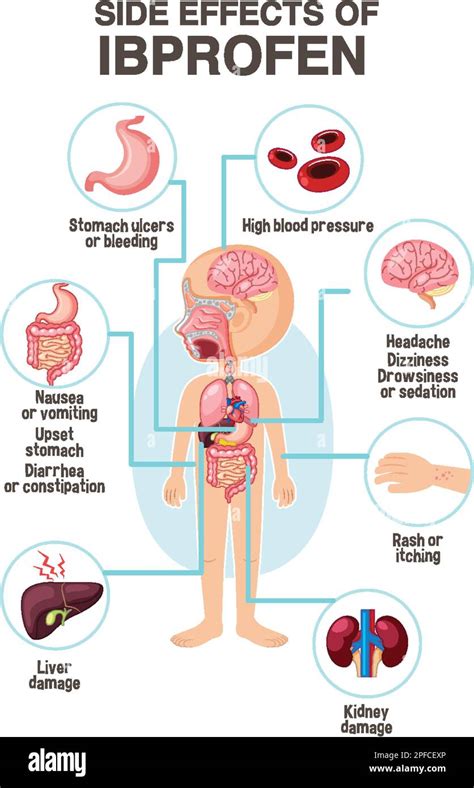
Ibuprofen side effects can range from mild to severe and may affect various systems in the body. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain, as well as dizziness, headache, and fatigue. While these effects are typically transient and resolve on their own, they can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, especially if they occur frequently or are severe.
Common Ibuprofen Side Effects

Some of the most common side effects of ibuprofen include:
- Gastrointestinal upset: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain are among the most frequently reported side effects.
- Dizziness and drowsiness: Ibuprofen can cause feelings of dizziness or drowsiness, which may impair an individual's ability to perform tasks that require alertness.
- Headache: Ironically, ibuprofen, which is often used to treat headaches, can also cause them as a side effect in some individuals.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak is another common side effect, which can be exacerbated by the drug's effect on sleep patterns.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While less frequent, certain side effects of ibuprofen can be serious and require immediate medical attention. These include: - Allergic reactions: Symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing indicate a severe allergic reaction. - Stomach ulcers and bleeding: Long-term use of ibuprofen can increase the risk of developing stomach ulcers and bleeding, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. - Kidney problems: Ibuprofen can affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease, leading to acute kidney injury in severe cases. - Increased risk of heart attack and stroke: The use of ibuprofen, especially at high doses, has been associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke, emphasizing the need for caution in individuals with cardiovascular disease.Long-Term Effects of Ibuprofen

The long-term use of ibuprofen can lead to several complications, including chronic kidney disease, gastrointestinal complications such as ulcers and bleeding, and an increased risk of cardiovascular events. Furthermore, long-term ibuprofen use has been linked to hearing loss and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, although the evidence for these associations is still emerging and requires further investigation.
Minimizing the Risk of Side Effects
To minimize the risk of ibuprofen side effects, it is essential to use the drug responsibly. This includes: - Following the recommended dosage: Do not exceed the recommended dose, as this can significantly increase the risk of side effects. - Using the drug for the shortest duration necessary: Limit the use of ibuprofen to the shortest duration necessary to treat the condition, as prolonged use increases the risk of adverse effects. - Avoiding use in high-risk populations: Individuals with a history of stomach ulcers, kidney disease, or cardiovascular disease should use ibuprofen with caution and under medical supervision. - Monitoring for side effects: Regularly monitoring for signs of side effects and seeking medical attention if they occur can help mitigate the risk of severe complications.Ibuprofen Interactions

Ibuprofen can interact with a variety of medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and certain antidepressants, either by enhancing their effects or increasing the risk of side effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for individuals taking multiple medications, as it can help prevent adverse drug reactions.
Special Considerations
Certain populations, such as the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic medical conditions, may require special consideration when using ibuprofen. For example, pregnant women should avoid using ibuprofen during the third trimester due to the risk of premature closure of the ductus arteriosus, a vital blood vessel in the fetus. Similarly, individuals with chronic kidney disease should use ibuprofen with caution, as it can worsen kidney function.Pregnancy and Ibuprofen

The use of ibuprofen during pregnancy requires careful consideration. While it is generally considered safe during the first and second trimesters, its use during the third trimester is associated with an increased risk of fetal complications. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should discuss the risks and benefits of ibuprofen use with their healthcare provider.
Breastfeeding and Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is excreted in breast milk, but the amounts are generally considered safe for infants. However, breastfeeding mothers should use ibuprofen with caution and under medical guidance, as high doses or prolonged use could potentially affect the infant.Alternatives to Ibuprofen

For individuals who experience side effects from ibuprofen or wish to avoid its use, several alternatives are available. These include other NSAIDs like naproxen, acetaminophen (which has a different mechanism of action and side effect profile), and non-pharmacological approaches such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications. The choice of alternative depends on the individual's specific condition, medical history, and personal preferences.
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management
Non-pharmacological approaches to pain management are gaining recognition for their effectiveness and safety. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals manage chronic pain without the risk of medication side effects. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can contribute to overall well-being and reduce the reliance on pain medications like ibuprofen.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, while ibuprofen is a valuable medication for managing pain and inflammation, its use is not without risks. Understanding the potential side effects, taking steps to minimize them, and exploring alternative pain management strategies can help individuals use ibuprofen safely and effectively. As research continues to uncover the complexities of ibuprofen's effects on the body, it is essential for healthcare providers and consumers to stay informed and adapt their practices to ensure the safe and responsible use of this medication.
Final Thoughts
The future of pain management likely involves a multifaceted approach that combines pharmacological treatments like ibuprofen with non-pharmacological therapies and lifestyle interventions. By embracing this holistic perspective, individuals can better navigate the complexities of pain management, reduce their reliance on medications with potential side effects, and improve their overall quality of life.What are the most common side effects of ibuprofen?
+The most common side effects of ibuprofen include gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, headache, and fatigue. These effects are usually mild and transient but can be more severe in some individuals.
Can ibuprofen increase the risk of heart attack and stroke?
+Yes, the use of ibuprofen, especially at high doses, has been associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. This risk is particularly concerning for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Are there any alternatives to ibuprofen for pain management?
+Yes, alternatives to ibuprofen include other NSAIDs like naproxen, acetaminophen, and non-pharmacological approaches such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications. The choice of alternative depends on the individual's specific condition and medical history.
Can pregnant women use ibuprofen?
+Pregnant women should avoid using ibuprofen during the third trimester due to the risk of premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. Use during the first and second trimesters is generally considered safe but should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
How can I minimize the risk of ibuprofen side effects?
+To minimize the risk of ibuprofen side effects, follow the recommended dosage, use the drug for the shortest duration necessary, avoid use in high-risk populations, and monitor for side effects. Regular communication with a healthcare provider is also crucial.
We hope this comprehensive overview of ibuprofen side effects has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or concerns about ibuprofen or pain management in general, please do not hesitate to reach out. Sharing this article with others who might benefit from this information is also appreciated. Together, we can promote safer and more effective pain management practices.
