Intro
Discover key facts about Lorazepam, a benzodiazepine medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in anxiety treatment and management, dosage, and potential risks.
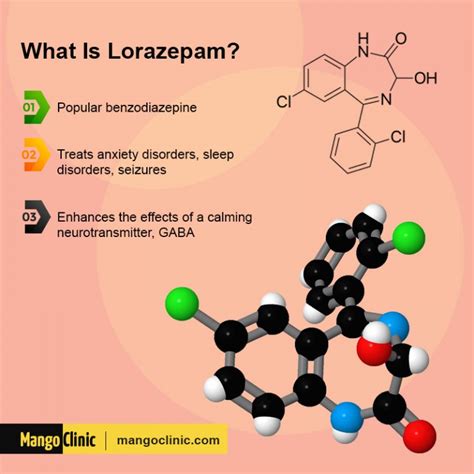
Lorazepam, commonly known by its brand name Ativan, is a medication that has been widely used for its therapeutic effects. It belongs to a class of drugs known as benzodiazepines, which are primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. Despite its popularity, there are several aspects of lorazepam that are not well understood by the general public. In this article, we will delve into the world of lorazepam, exploring its uses, side effects, and other essential facts that everyone should know.
The importance of understanding lorazepam and its effects cannot be overstated. With the rising prevalence of anxiety and stress-related disorders, the use of benzodiazepines like lorazepam has become more common. However, the potential for misuse and dependence on these drugs is a significant concern. By educating ourselves about lorazepam, we can better navigate the complexities of mental health treatment and make informed decisions about our well-being.
Lorazepam has been a staple in psychiatric and medical practice for decades, offering rapid relief from acute anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Its effectiveness in these areas has made it a popular choice among healthcare providers. Nevertheless, the long-term use of lorazepam can lead to dependence, tolerance, and a range of side effects that can negatively impact daily life. As we explore the world of lorazepam, it is crucial to consider both the benefits and the risks associated with this medication.
Introduction to Lorazepam
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of lorazepam involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. After oral administration, lorazepam is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 2 hours. It is then distributed throughout the body, with a high concentration in the brain, where it exerts its therapeutic effects. Lorazepam is metabolized by the liver and excreted in the urine, with a half-life of approximately 12-18 hours.Uses of Lorazepam
Anxiety Disorders
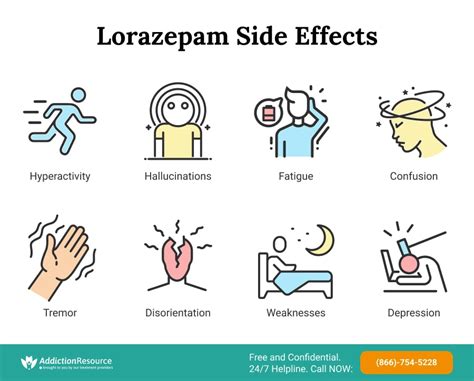
Lorazepam is commonly used to treat anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Its rapid onset of action makes it an effective treatment for acute anxiety, providing quick relief from symptoms. However, the long-term use of lorazepam for anxiety disorders is generally not recommended, as it can lead to dependence and tolerance.Side Effects of Lorazepam
Dependence and Withdrawal
One of the most significant concerns with lorazepam is its potential for dependence and withdrawal. Long-term use of lorazepam can lead to physical dependence, with the body adapting to the presence of the drug. When lorazepam is suddenly stopped or reduced in dose, withdrawal symptoms can occur, including anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. To minimize the risk of dependence and withdrawal, it is essential to use lorazepam only as directed and to gradually taper the dose when discontinuing treatment.Interactions with Other Medications
Cautions and Contraindications
Lorazepam is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines or any components of the formulation. It is also contraindicated in individuals with acute angle-closure glaucoma, as it can worsen this condition. Caution is advised when using lorazepam in individuals with a history of substance abuse, as it can increase the risk of dependence and misuse.Overdose and Emergency Treatment

Flumazenil
Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine antagonist that can be used to reverse the effects of lorazepam in the event of an overdose. It works by binding to the benzodiazepine receptor, displacing lorazepam and reversing its effects. Flumazenil is typically administered intravenously and can be effective in reversing respiratory depression, coma, and other symptoms of overdose.Dosage and Administration
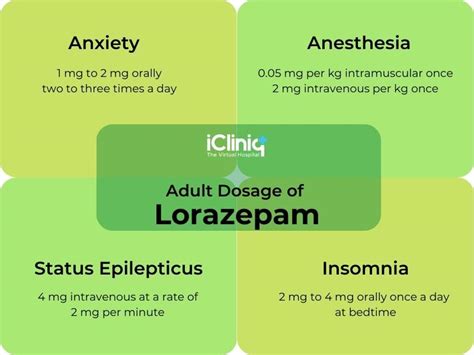
Special Populations
In special populations, such as the elderly, children, and individuals with renal or hepatic impairment, the dosage of lorazepam may need to be adjusted. The elderly may be more sensitive to the effects of lorazepam, and the dose may need to be reduced to minimize the risk of side effects. Children and individuals with renal or hepatic impairment may also require dose adjustments to minimize the risk of adverse effects.Conclusion and Future Directions
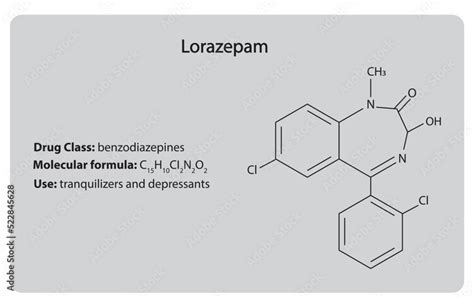
As we move forward, it is essential to consider the complex interplay between lorazepam and other medications, as well as its potential interactions with other substances. By working together, we can promote safe and responsible use of lorazepam and other benzodiazepines, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and maximizing their therapeutic potential.
What is lorazepam used for?
+Lorazepam is used to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. It is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain.
What are the common side effects of lorazepam?
+Common side effects of lorazepam include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, and nausea. More serious side effects can include respiratory depression, cognitive impairment, and increased risk of falls.
Can lorazepam be addictive?
+Yes, lorazepam can be addictive. Long-term use of lorazepam can lead to physical dependence, with the body adapting to the presence of the drug. When lorazepam is suddenly stopped or reduced in dose, withdrawal symptoms can occur.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of lorazepam, its uses, and its side effects. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and let's work together to promote safe and responsible use of lorazepam and other benzodiazepines.
