Intro
Discover the truth about Benzonatate, a non-antibiotic cough medicine, and learn how it works to relieve coughs without antibiotic properties, addressing respiratory issues with antitussive effects.
The world of medicine is vast and complex, with numerous treatments and medications available for various conditions. One such medication is benzonatate, which is often misunderstood as an antibiotic. However, this is not the case. Benzonatate is actually a cough suppressant, used to treat coughs associated with respiratory infections, such as the common cold, bronchitis, and pneumonia. In this article, we will delve into the world of benzonatate, exploring its uses, benefits, and working mechanisms, as well as highlighting the differences between benzonatate and antibiotics.
The importance of understanding the differences between various medications cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary. Benzonatate, being a non-antibiotic medication, plays a vital role in treating coughs without contributing to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, benzonatate has been shown to be effective in reducing cough severity and frequency, making it a valuable treatment option for individuals suffering from respiratory infections.
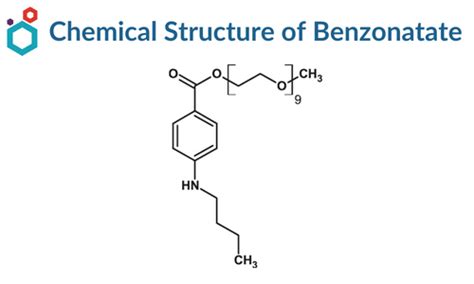
As we navigate the complexities of benzonatate, it is essential to recognize the significance of this medication in the medical world. Benzonatate is a topical anesthetic, which works by numbing the throat and lungs, thereby reducing the cough reflex. This mechanism of action is distinct from antibiotics, which work by targeting and killing bacteria. By understanding the differences between benzonatate and antibiotics, healthcare professionals and patients can make informed decisions about treatment options, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
What is Benzonatate?

How Does Benzonatate Work?
Benzonatate's mechanism of action is distinct from antibiotics. As a topical anesthetic, benzonatate numbs the throat and lungs, reducing the cough reflex. This is achieved through the inhibition of the nerve impulses that transmit cough signals to the brain. By reducing the frequency and severity of coughing, benzonatate provides relief from respiratory symptoms, allowing individuals to rest and recover more effectively. Unlike antibiotics, which target and kill bacteria, benzonatate does not have antibacterial properties and is not effective against bacterial infections.Benefits of Benzonatate
Common Uses of Benzonatate
Benzonatate is commonly used to treat coughs associated with respiratory infections, such as: * Common cold * Bronchitis * Pneumonia * Asthma * Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Benzonatate may also be used to treat coughs caused by other conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or postnasal drip.Side Effects of Benzonatate

Precautions and Interactions
Benzonatate can interact with other medications, such as sedatives, tranquilizers, and antidepressants. It is crucial to inform healthcare professionals about all medications being taken, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, as well as herbal supplements. Additionally, benzonatate should be used with caution in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, or in those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.Differences Between Benzonatate and Antibiotics

Importance of Antibiotic Stewardship
The rise of antibiotic resistance is a significant public health concern, highlighting the importance of antibiotic stewardship. By using antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary, healthcare professionals and patients can reduce the risk of contributing to antibiotic resistance. Benzonatate, as a non-antibiotic medication, plays a vital role in treating coughs without contributing to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with benzonatate in the comments below. Have you used benzonatate to treat a cough or respiratory infection? What were your experiences with this medication? Share your story and help others understand the benefits and uses of benzonatate.
What is benzonatate used for?
+Benzonatate is used to treat coughs associated with respiratory infections, such as the common cold, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Is benzonatate an antibiotic?
+No, benzonatate is not an antibiotic. It is a cough suppressant that works by numbing the throat and lungs, reducing the cough reflex.
What are the side effects of benzonatate?
+Common side effects of benzonatate include dizziness, drowsiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. Serious side effects, such as allergic reactions or seizures, are rare.
Can benzonatate be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, benzonatate can be used in combination with other medications, such as expectorants and decongestants, to provide comprehensive relief from respiratory symptoms.
Is benzonatate safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+Benzonatate should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using benzonatate during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
