Intro
Dexamethasone is a potent steroid medication, used to treat inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and hormonal imbalances, with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties, commonly prescribed for conditions like asthma, arthritis, and adrenal insufficiency.
Dexamethasone is a type of steroid medication that has been widely used for its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It belongs to a class of corticosteroids, which are synthetic versions of the hormone cortisol that is naturally produced by the adrenal gland. Dexamethasone is used to treat a variety of conditions, including inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer. Its ability to reduce swelling, redness, and pain has made it a valuable treatment option for many patients. However, like all medications, dexamethasone can have side effects, and its use must be carefully monitored by a healthcare professional.
The importance of understanding dexamethasone and its effects cannot be overstated. With the rise of chronic diseases and the need for effective treatments, medications like dexamethasone play a critical role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Moreover, the ongoing research into the mechanisms of action of corticosteroids like dexamethasone continues to shed light on the complex interactions between the immune system, inflammation, and disease processes. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of how these drugs work but also informs the development of new therapeutic strategies. As such, exploring the benefits, risks, and applications of dexamethasone provides valuable insights into the broader landscape of healthcare and treatment options.
Dexamethasone, like other corticosteroids, mimics the effects of cortisol in the body, including its role in reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. This makes it particularly useful in treating conditions where inflammation is a significant component of the disease process. However, the use of dexamethasone must be balanced against its potential side effects, which can include weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infections, among others. The careful management of dexamethasone therapy, including the dose and duration of treatment, is crucial to maximizing its benefits while minimizing its risks.
Dexamethasone Mechanism of Action
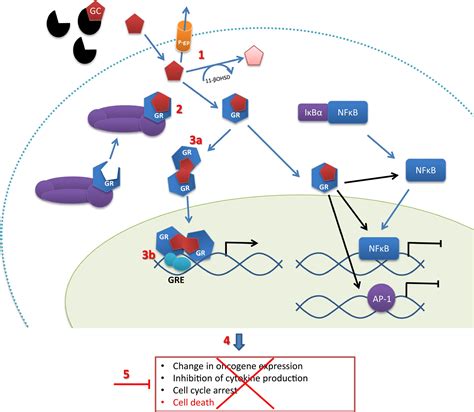
Dexamethasone works by binding to specific receptors in the body, which then influence the expression of various genes involved in the inflammatory response and immune function. This binding process triggers a cascade of downstream effects that ultimately lead to the reduction of inflammation and the suppression of immune activity. The drug's potent anti-inflammatory effects make it a valuable treatment for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and certain types of skin disorders. Furthermore, its immunosuppressive properties are utilized in the management of autoimmune diseases and in preventing the rejection of transplanted organs.
Benefits of Dexamethasone
The benefits of dexamethasone are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key advantages of using this medication include: - Rapid reduction of inflammation and swelling - Effective suppression of the immune system in autoimmune diseases - Ability to manage a wide range of conditions, from respiratory diseases to certain types of cancer - Availability in various forms, including oral tablets, injectables, and topical creams, allowing for tailored treatment approachesDexamethasone Uses and Applications
Dexamethasone is used in a variety of clinical settings due to its broad therapeutic effects. Some of the common uses of dexamethasone include:
- Treatment of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and gout
- Management of autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Prevention of organ rejection in transplant patients
- Treatment of certain types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma
- Reduction of inflammation and swelling in conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Risks and Side Effects of Dexamethasone
While dexamethasone is a valuable medication, it is not without risks and side effects. Some of the common side effects include: - Weight gain and changes in appetite - Mood changes, including anxiety, depression, and mood swings - Increased risk of infections due to immunosuppression - Osteoporosis and bone fractures with long-term use - Cushing's syndrome, characterized by high blood pressure, glucose intolerance, and other symptomsDexamethasone Administration and Dosage

The administration and dosage of dexamethasone depend on the specific condition being treated and the form of the medication being used. For oral dexamethasone, the dosage can range from a few milligrams to several dozen milligrams per day, divided into one or more doses. In cases where rapid effects are needed, intravenous administration may be used. The dosage must be carefully titrated to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Given the potential for side effects and the impact of dexamethasone on the body's immune response, regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial. This includes: - Regular blood tests to check for signs of infection or other complications - Monitoring of blood pressure and blood glucose levels - Assessment of bone density to prevent osteoporosis - Psychological evaluations to address any mood changes or other mental health concernsDexamethasone in Special Populations

The use of dexamethasone in special populations, such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly, requires careful consideration. In pregnancy, corticosteroids like dexamethasone are used with caution due to the potential for fetal harm. In children, the medication's effects on growth and development must be monitored. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to the side effects of dexamethasone, particularly osteoporosis and increased risk of infections.
Future Directions and Research
Research into the mechanisms of action of dexamethasone and other corticosteroids continues to evolve, offering insights into new therapeutic strategies. The development of drugs that can mimic the beneficial effects of corticosteroids while minimizing their side effects is an active area of investigation. Additionally, the exploration of corticosteroids in combination with other medications to enhance their efficacy and safety profiles is underway.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, dexamethasone is a powerful steroid medication with a wide range of applications in treating inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer. Its benefits are significant, but its use must be carefully managed to minimize the risk of side effects. As research continues to uncover the complexities of corticosteroid action and the development of new therapeutic agents, the role of dexamethasone in clinical practice is likely to evolve. For now, it remains a valuable tool in the management of various diseases, offering hope and improved outcomes for many patients.
What is dexamethasone used for?
+Dexamethasone is used to treat a variety of conditions, including inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer.
What are the common side effects of dexamethasone?
+Common side effects include weight gain, mood changes, increased risk of infections, osteoporosis, and Cushing's syndrome.
How is dexamethasone administered?
+Dexamethasone can be administered orally, intravenously, or topically, depending on the condition being treated and the desired therapeutic effect.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with dexamethasone in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand the complexities and benefits of this medication. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote a better understanding of healthcare and treatment options, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
