Intro
Stay updated on the latest 5 flu updates, including influenza outbreaks, vaccine effectiveness, and prevention strategies, to protect against flu season and its complications, such as pneumonia and respiratory issues.
The flu season is a time of year that many people dread, and for good reason. The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that can cause mild to severe symptoms, and even lead to serious complications in some cases. With the constant evolution of the flu virus, it's essential to stay informed about the latest developments and updates to protect yourself and your loved ones. In this article, we'll delve into the world of flu updates, exploring the latest trends, vaccine information, and prevention strategies.
As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of flu season, it's crucial to understand the importance of staying up-to-date on the latest flu updates. The flu virus is constantly mutating, which means that last year's vaccine may not provide adequate protection against this year's strains. Furthermore, the flu can have a significant impact on public health, with millions of people affected each year, and thousands hospitalized due to flu-related complications. By staying informed, we can take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the flu and reduce the risk of severe illness.
The flu season typically runs from October to May, with peak activity usually occurring between December and February. During this time, it's essential to be vigilant and take steps to protect yourself and those around you. This includes getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. By taking these precautions, we can reduce the spread of the flu and minimize its impact on our communities.
Understanding the Flu Virus
Types of Flu Viruses
The different types of flu viruses can have a significant impact on the severity and spread of the illness. Type A flu viruses are typically the most severe and can cause widespread outbreaks. Type B flu viruses are usually milder and tend to affect children and young adults. Type C flu viruses are the mildest and typically cause mild symptoms. Understanding the different types of flu viruses can help us develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.Flu Vaccine Updates
Vaccine Effectiveness
The effectiveness of the flu vaccine can vary from year to year, depending on the match between the vaccine and the circulating flu viruses. In general, the flu vaccine is most effective in preventing severe illness and hospitalization, rather than mild symptoms. Studies have shown that the flu vaccine can reduce the risk of flu-related hospitalization by up to 40% in adults and up to 75% in children. While the flu vaccine is not 100% effective, it remains one of the best ways to protect yourself and your loved ones from the flu.Prevention Strategies

Additional Prevention Measures
Additional prevention measures, such as wearing a mask and using disinfectants, can also help reduce the spread of the flu. Wearing a mask can help prevent the spread of the flu when you're in close contact with others, such as in a healthcare setting or on public transportation. Using disinfectants can help kill the flu virus on surfaces, reducing the risk of transmission. By taking these additional precautions, we can further reduce the spread of the flu and protect ourselves and those around us.Flu Treatment Options
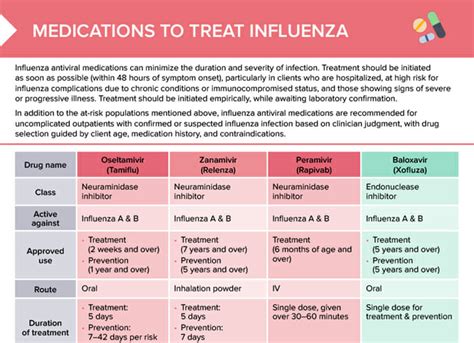
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are most effective when started within 48 hours of symptom onset. They can help reduce the severity and duration of the flu, as well as reduce the risk of complications. Oseltamivir and zanamivir are two of the most commonly prescribed antiviral medications for the flu. These medications can be prescribed by a healthcare provider and are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and inhalers.Complications and Risks
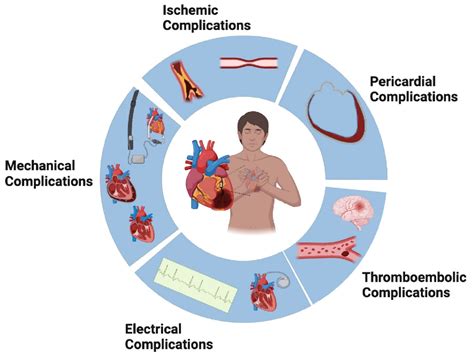
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups, such as young children, older adults, and people with chronic health conditions, are at higher risk for flu-related complications. Young children, particularly those under the age of 5, are at higher risk for flu-related hospitalization and death. Older adults, particularly those over the age of 65, are also at higher risk for flu-related complications, due to age-related declines in immune function. People with chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and asthma, are also at higher risk for flu-related complications, due to the potential for the flu to exacerbate underlying health conditions.Global Flu Updates

International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for preventing and responding to flu outbreaks. The WHO and the CDC work closely with health organizations and governments around the world to share information, coordinate responses, and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. By working together, we can reduce the spread of the flu and minimize its impact on global health.Future Directions

Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in flu research and development include the use of new technologies, such as mRNA vaccines and nanotechnology, to improve vaccine effectiveness and develop new treatment options. Additionally, there is a growing focus on global surveillance and cooperation, with the WHO and the CDC working closely with health organizations and governments around the world to share information and coordinate responses. By staying ahead of the curve and embracing emerging trends, we can stay one step ahead of the flu and protect ourselves and our communities.What is the best way to prevent the flu?
+Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent the flu. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, can help reduce the spread of the flu.
How long does the flu last?
+The flu typically lasts for 5-7 days, but some people may experience symptoms for up to 2 weeks. It's essential to stay home and rest when you're sick to avoid spreading the flu to others.
Can I get the flu from the vaccine?
+No, you cannot get the flu from the vaccine. The flu vaccine contains inactivated or weakened flu viruses, which cannot cause the flu. Some people may experience mild side effects, such as soreness or redness at the injection site, but these are typically mild and short-lived.
How often should I get the flu vaccine?
+The flu vaccine is typically updated annually to protect against the most common and severe flu viruses. It's recommended to get vaccinated every year to ensure you have the best protection against the flu.
Can I get the flu if I've already been vaccinated?
+Yes, it's possible to get the flu even if you've been vaccinated. However, the flu vaccine can help reduce the severity and duration of the flu, and reduce the risk of complications. If you do get the flu after being vaccinated, it's essential to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms or are at high risk for complications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the latest flu updates and prevention strategies. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones, you can reduce the risk of severe illness and stay healthy during the flu season. If you have any questions or concerns about the flu, please don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of flu prevention and stay up-to-date on the latest flu updates. Together, we can reduce the impact of the flu and create a healthier, happier community.
