Intro
Discover the ultimate IUD birth control guide, covering types, insertion, and removal. Learn about hormonal and copper IUDs, benefits, and side effects for informed family planning decisions.
The world of birth control has evolved significantly over the years, offering women and couples a wide range of options to plan their families effectively. Among the various methods available, Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) have gained popularity due to their high efficacy, convenience, and minimal maintenance requirements. Understanding the intricacies of IUD birth control is crucial for making informed decisions about reproductive health. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the details of IUDs, exploring their types, benefits, potential side effects, and the process of insertion and removal.
IUDs are a form of long-term, reversible birth control that involves the insertion of a small device into the uterus. This device works by either releasing hormones or using copper to prevent pregnancy. The mechanism of action varies depending on the type of IUD. Hormonal IUDs, such as Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla, release a small amount of progestin, which thickens the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg and thins the uterine lining to prevent implantation. On the other hand, the copper IUD (ParaGard) works by causing a chemical reaction that is toxic to sperm, thereby preventing fertilization.
The decision to use an IUD as a birth control method is significant and should be based on thorough research and consultation with healthcare providers. It's essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks. One of the most significant advantages of IUDs is their high effectiveness rate, with some types being more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. Additionally, IUDs are a low-maintenance form of birth control, requiring no daily pills or patches, and they can be used for several years, depending on the type. For example, hormonal IUDs can last between 3 to 7 years, while the copper IUD can last up to 10 years.
Types of IUDs
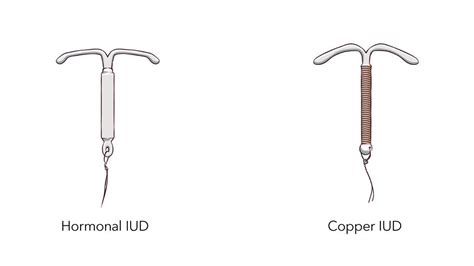
There are several types of IUDs available, each with its unique characteristics, benefits, and potential side effects. The primary distinction among IUDs is whether they are hormonal or non-hormonal (copper). Hormonal IUDs include Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla, which vary in their hormone release rates and durations of use. The copper IUD, ParaGard, is the only non-hormonal option available in the U.S. Understanding the differences among these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate IUD based on individual health needs and preferences.
Benefits of IUDs

The benefits of using an IUD for birth control are numerous and significant. They include:
- High effectiveness in preventing pregnancy
- Convenience and low maintenance
- Reversible, allowing for easy return to fertility
- Potential reduction in menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding (for hormonal IUDs)
- Long-acting, with durations ranging from 3 to 10 years
- Cost-effective over time, despite the initial higher cost of insertion
How IUDs Work
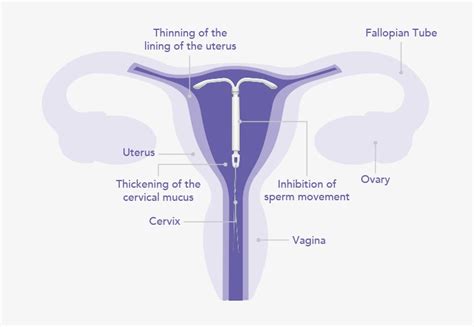
The working mechanism of IUDs is designed to prevent pregnancy through different methods depending on whether the IUD is hormonal or copper. Hormonal IUDs release progestin, which has several effects on the body to prevent pregnancy:
- Thickens cervical mucus to block sperm
- Thins the uterine lining to prevent implantation
- May stop ovulation, though this is less common
On the other hand, the copper IUD works by causing an inflammatory reaction in the uterus, which is toxic to sperm, thereby preventing them from fertilizing an egg. Copper also affects the uterine lining and cervical mucus, further enhancing its contraceptive effects.
Potential Side Effects

Like any medical device, IUDs can cause side effects, which vary in severity and frequency among users. Common side effects include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns (heavier or lighter periods)
- Cramping during and after insertion
- Spotting or irregular bleeding
- Mood changes
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
For hormonal IUDs, side effects can also include acne, weight gain, and mood swings due to the hormonal component. The copper IUD may cause heavier or more painful periods in some women.
Insertion and Removal Process

The process of inserting an IUD is relatively straightforward and typically performed in a healthcare provider's office. The procedure involves:
- Preparation: The healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to check the position and size of the uterus.
- Insertion: The IUD is inserted through the cervix into the uterus using a special instrument.
- Placement: The healthcare provider ensures the IUD is in the correct position.
- Follow-up: A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled to check the IUD's position and ensure there are no complications.
Removal of an IUD is also a simple procedure that can be performed in a healthcare provider's office. It involves the healthcare provider using a special instrument to gently pull on the IUD's strings, which are left in place after insertion, to remove the device from the uterus.
Cost and Accessibility
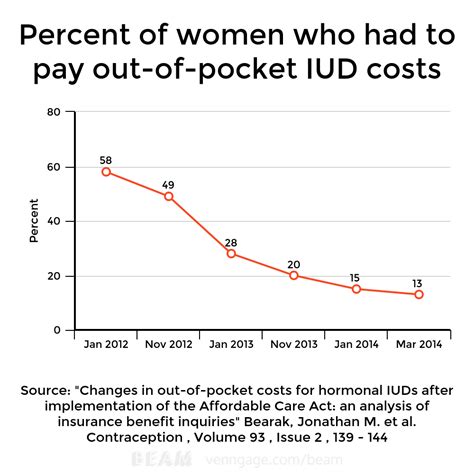
The cost of an IUD can vary significantly depending on the type, location, and insurance coverage. In the United States, for example, the cost of an IUD without insurance can range from $500 to over $1,000, including the cost of insertion. However, many insurance plans cover IUDs as a form of birth control, making them more accessible. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the specific costs and coverage.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, IUDs offer a highly effective and convenient form of birth control that can be tailored to individual needs and preferences. By understanding the different types of IUDs, their benefits, potential side effects, and the process of insertion and removal, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health. If you're considering an IUD, it's crucial to discuss your options with a healthcare provider to determine the best choice for you.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with IUDs in the comments section below. Whether you're a current user or considering this form of birth control, your insights can help others make informed decisions about their reproductive health. Additionally, if you found this guide helpful, please share it with others who might benefit from this comprehensive overview of IUD birth control.
What are the most common types of IUDs available?
+The most common types of IUDs include hormonal IUDs like Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla, and the non-hormonal copper IUD, ParaGard.
How long does an IUD last?
+The duration of an IUD varies by type, ranging from 3 to 10 years, depending on whether it's hormonal or copper.
Can I get pregnant after removing an IUD?
+Yes, fertility typically returns quickly after IUD removal, and most women can get pregnant within the first year after removal.
