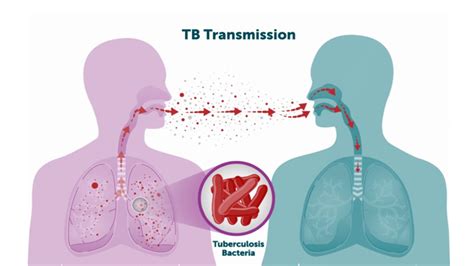
Intro
Discover 5 latent TB symptoms, including fatigue, cough, and chest pain. Learn about latent tuberculosis infection signs, diagnosis, and treatment options to manage TB symptoms and prevent active disease.
Latent tuberculosis (TB) is a condition where the bacteria that cause TB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, are present in the body but do not cause any symptoms. This condition is also known as dormant or inactive TB. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately one-third of the world's population is infected with latent TB. It is essential to identify and treat latent TB to prevent the development of active TB disease, which can be severe and even life-threatening. In this article, we will discuss the importance of recognizing latent TB symptoms and the steps to take if you suspect you have been infected.
Latent TB is often asymptomatic, meaning that people with the condition may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience subtle symptoms that can be easily overlooked. These symptoms can be similar to those of other illnesses, making it challenging to diagnose latent TB. If left untreated, latent TB can progress to active TB, which can cause severe symptoms, such as coughing up blood, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It is crucial to be aware of the potential symptoms of latent TB to seek medical attention early and prevent the development of active TB.
The importance of recognizing latent TB symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment of latent TB can prevent the development of active TB, reducing the risk of transmission to others and minimizing the risk of complications. Moreover, treating latent TB can also reduce the risk of developing drug-resistant TB, which is a significant concern in many parts of the world. By being aware of the potential symptoms of latent TB, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and the health of those around them.
Understanding Latent TB
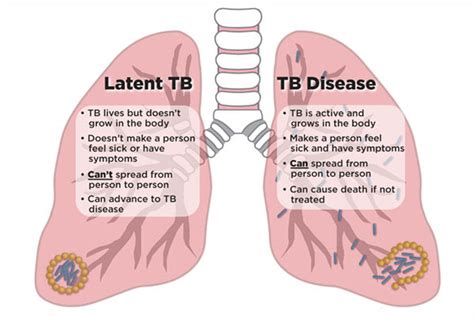
Risk Factors for Latent TB
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing latent TB, including: * People who have been in close contact with someone with active TB * Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or taking immunosuppressive medications * People who have been infected with TB in the past, but did not complete treatment * Individuals who have been born in or traveled to countries with high TB prevalence * People who work in healthcare or other settings where they may be exposed to TBCommon Symptoms of Latent TB
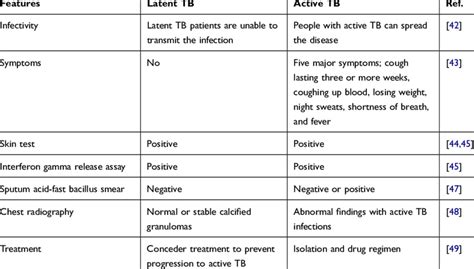
Diagnosing Latent TB
Diagnosing latent TB can be challenging, as the symptoms are often mild and nonspecific. A healthcare provider may use a combination of tests to diagnose latent TB, including: * Tuberculin skin test (TST): This test involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin to see if a reaction occurs. * Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA): This test measures the immune system's response to TB bacteria. * Chest X-ray: This test can help identify any abnormalities in the lungs that may be caused by TB. * Sputum test: This test involves collecting a sample of sputum to see if TB bacteria are present.Treatment Options for Latent TB
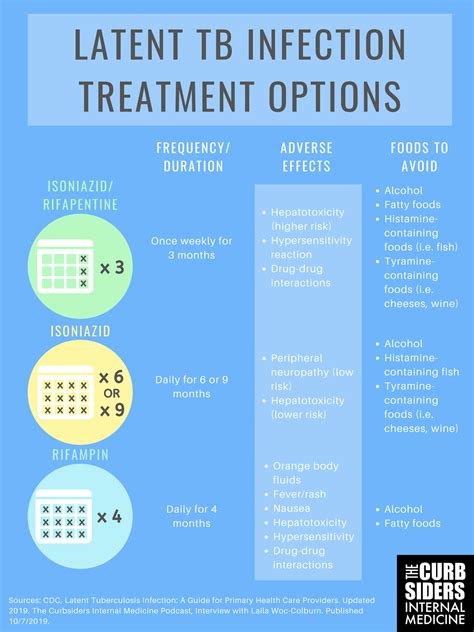
Benefits of Treating Latent TB
Treating latent TB can have several benefits, including: * Preventing the development of active TB * Reducing the risk of transmission to others * Minimizing the risk of complications, such as lung damage or meningitis * Reducing the risk of developing drug-resistant TBPreventing Latent TB

Public Health Efforts to Control Latent TB
Public health efforts to control latent TB include: * Screening high-risk individuals for latent TB * Providing treatment for latent TB to prevent the development of active TB * Implementing infection control measures in healthcare settings to prevent the transmission of TB * Educating the public about the risks of latent TB and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms occurLiving with Latent TB

Coping with the Emotional Impact of Latent TB
Coping with the emotional impact of latent TB can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help, including: * Seeking support from friends and family * Joining a support group for individuals with latent TB * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing * Focusing on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exerciseWhat is the difference between latent and active TB?
+Latent TB is a condition where the TB bacteria are present in the body, but the immune system is able to keep them under control. Active TB, on the other hand, occurs when the immune system is unable to control the bacteria, and they begin to multiply and cause symptoms.
How is latent TB diagnosed?
+Latent TB is typically diagnosed using a combination of tests, including the tuberculin skin test (TST), interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA), chest X-ray, and sputum test.
What are the treatment options for latent TB?
+Treatment for latent TB typically involves taking antibiotics, such as isoniazid (INH) or rifampin (RIF), to kill the TB bacteria. The most effective treatment regimen will depend on the individual's specific circumstances and medical history.
Can latent TB be prevented?
+Yes, latent TB can be prevented by taking steps to avoid exposure to TB bacteria, such as avoiding close contact with individuals who have active TB, wearing a mask when working in healthcare or other settings where TB may be present, and ensuring good ventilation in areas where TB may be present.
What are the benefits of treating latent TB?
+Treating latent TB can prevent the development of active TB, reduce the risk of transmission to others, minimize the risk of complications, and reduce the risk of developing drug-resistant TB.
In
Final Thoughts on Latent TB