Intro
The Lactate Dehydrogenase (LD) blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of lactate dehydrogenase, an enzyme found in nearly all living cells. This enzyme plays a vital role in the process of converting lactate to pyruvate, which is then used to produce energy for the body. Elevated levels of LD in the blood can indicate tissue damage or disease, making this test an essential component of modern medicine.
The importance of the LD blood test cannot be overstated, as it has far-reaching implications for the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions. For instance, high levels of LD can be indicative of liver disease, heart attack, or certain types of cancer. Moreover, this test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track the progression of disease. As such, it is essential to understand the intricacies of the LD blood test, its applications, and its limitations.
The LD blood test is typically performed in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient's condition. This test is often used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as liver disease, where elevated levels of LD can indicate liver damage or inflammation. Additionally, the LD blood test can be used to detect heart damage, such as that caused by a heart attack, and to monitor the progression of certain types of cancer, including lymphoma and leukemia.
What is the Lactate Dehydrogenase (LD) Blood Test?
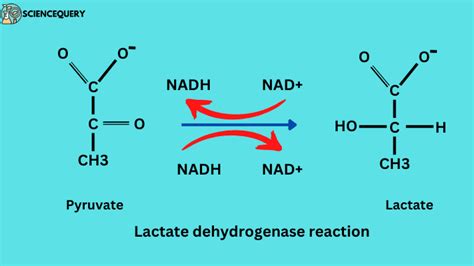
How is the LD Blood Test Performed?
The LD blood test is a relatively simple and straightforward procedure. A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in the arm, using a needle and syringe. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory, where it is analyzed for the presence and levels of lactate dehydrogenase. The test results are typically available within a few hours or days, depending on the laboratory and the specific testing procedures used.What are the Applications of the LD Blood Test?
- Diagnosing and monitoring liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Detecting heart damage, such as that caused by a heart attack
- Monitoring the progression of certain types of cancer, including lymphoma and leukemia
- Diagnosing and monitoring muscle damage or disease, such as muscular dystrophy
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for various medical conditions
What are the Benefits of the LD Blood Test?
The LD blood test offers several benefits, including:- Early detection and diagnosis of medical conditions, allowing for prompt treatment and improved outcomes
- Monitoring the progression of disease, allowing for adjustments to treatment and improved management
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatment, allowing for changes to be made as needed
- Providing valuable information for healthcare professionals, allowing for informed decision-making and improved patient care
What are the Limitations of the LD Blood Test?
- Elevated levels of LD can be caused by a variety of factors, making it difficult to determine the underlying cause of elevated levels
- The test is not specific to any particular disease or condition, making it necessary to use other diagnostic tests in conjunction with the LD blood test
- The test can be affected by certain medications or medical conditions, which can impact the accuracy of the results
What are the Risks and Side Effects of the LD Blood Test?
The LD blood test is a relatively safe and low-risk procedure. However, as with any blood test, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of, including:- Pain or discomfort at the needle site
- Bruising or swelling at the needle site
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Infection at the needle site
How to Prepare for the LD Blood Test
- Fasting for a certain period before the test, as instructed by your healthcare professional
- Avoiding certain medications or supplements that may impact the test results
- Wearing loose and comfortable clothing to the test
- Bringing any relevant medical records or test results to the test
What to Expect During the LD Blood Test
During the LD blood test, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm. The procedure typically takes only a few minutes and is relatively painless. You may feel a slight pinch or stinging sensation when the needle is inserted, but this should subside quickly.Understanding LD Blood Test Results

What are the Normal and Abnormal LD Blood Test Results?
The normal and abnormal results of the LD blood test can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing procedures used. In general, the following results are considered normal and abnormal:- Normal: 50-150 U/L
- Elevated: 150-300 U/L
- High: 300-500 U/L
- Very high: above 500 U/L
LD Blood Test and Disease Diagnosis
- Liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Heart disease, such as heart attack or cardiac arrest
- Cancer, such as lymphoma or leukemia
- Muscle disease, such as muscular dystrophy
- Neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease
What is the Role of LD Blood Test in Monitoring Disease Progression?
The LD blood test plays a crucial role in monitoring disease progression and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment. By measuring the levels of lactate dehydrogenase in the blood, healthcare professionals can:- Monitor the progression of disease
- Evaluate the effectiveness of treatment
- Make adjustments to treatment as needed
- Provide valuable information for informed decision-making and improved patient care
What is the normal range for LD blood test results?
+The normal range for LD blood test results can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing procedures used. In general, normal LD levels are typically considered to be between 50-150 U/L.
What are the risks and side effects of the LD blood test?
+The LD blood test is a relatively safe and low-risk procedure. However, as with any blood test, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of, including pain or discomfort at the needle site, bruising or swelling at the needle site, dizziness or lightheadedness, and infection at the needle site.
How is the LD blood test used in disease diagnosis?
+The LD blood test is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases. Some of the most common diseases diagnosed using the LD blood test include liver disease, heart disease, cancer, muscle disease, and neurological disorders.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the LD blood test, its applications, and its limitations. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare professional. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to leave a comment below with any thoughts or feedback you may have. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of the importance of the LD blood test in modern medicine.
