Levofloxacin is a medication that belongs to the class of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones. It is widely used to treat various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. Despite its effectiveness, there are several important facts about levofloxacin that patients should be aware of to ensure safe and proper use. In this article, we will delve into the world of levofloxacin, exploring its benefits, potential side effects, and other crucial aspects that patients and healthcare professionals should consider.
The discovery of levofloxacin marked a significant milestone in the development of antibiotics, as it offered a broader spectrum of activity and improved pharmacokinetic properties compared to earlier fluoroquinolones. This advancement has led to the increased use of levofloxacin in clinical settings, making it essential to understand its mechanisms of action, indications, and potential risks. As we navigate the complexities of levofloxacin, it becomes clear that this medication plays a vital role in modern medicine, but its use must be guided by a thorough understanding of its properties and potential interactions.
The importance of levofloxacin in treating bacterial infections cannot be overstated, as it has been shown to be effective against a wide range of pathogens. However, the rise of antibiotic resistance has raised concerns about the long-term efficacy of levofloxacin and other antibiotics. As such, it is crucial to use levofloxacin judiciously, following established guidelines and dosing recommendations to minimize the risk of resistance and ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. By exploring the facts about levofloxacin, we can better appreciate the need for responsible antibiotic use and the importance of ongoing research into new and innovative treatments for bacterial infections.
Introduction to Levofloxacin
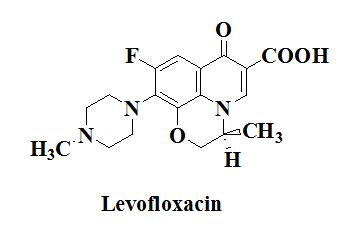
Levofloxacin is a synthetic antibacterial agent that belongs to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics. It is the L-isomer of the racemic compound, ofloxacin, and is known for its broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The medication works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for bacterial DNA replication and transcription. This mechanism of action allows levofloxacin to effectively target and eliminate bacterial pathogens, making it a valuable treatment option for various infections.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin are characterized by rapid absorption, extensive distribution, and moderate clearance. The medication is well absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1-2 hours. Levofloxacin is widely distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations achieved in tissues and fluids, including the lungs, liver, and kidneys. The elimination half-life of levofloxacin is approximately 6-8 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing in most cases. Understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin is essential for optimizing its use and minimizing potential side effects.
Indications and Usage
Levofloxacin is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including:
* Community-acquired pneumonia
* Skin and soft tissue infections
* Urinary tract infections
* Prostatitis
* Inhalational anthrax
The medication is available in oral and intravenous formulations, allowing for flexible dosing and administration. The recommended dose and duration of treatment vary depending on the specific infection being treated, and patients should follow the instructions provided by their healthcare provider to ensure optimal outcomes.
Side Effects and Warnings
While levofloxacin is generally well tolerated, it can cause a range of side effects, including:
* Nausea and vomiting
* Diarrhea
* Headache
* Dizziness
* Insomnia
* Rash
* Pruritus
In rare cases, levofloxacin can cause more serious side effects, such as:
* Tendinitis and tendon rupture
* Peripheral neuropathy
* Central nervous system effects (e.g., seizures, psychosis)
* Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
Patients should be aware of these potential side effects and seek medical attention if they experience any unusual or severe symptoms while taking levofloxacin.
Interactions and Contraindications
Levofloxacin can interact with various medications, including:
* Antacids and multivalent cations (e.g., calcium, magnesium, aluminum)
* Warfarin
* Theophylline
* Cyclosporine
* Digoxin
Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter products and supplements, to minimize the risk of interactions. Levofloxacin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the medication or other fluoroquinolones, as well as in patients with a history of myasthenia gravis.
Resistance and Stewardship
The emergence of antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, and levofloxacin is no exception. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have contributed to the development of resistant bacterial strains, making it essential to use levofloxacin judiciously and follow established guidelines. Healthcare providers should consider the following principles of antibiotic stewardship:
* Use antibiotics only when necessary
* Choose the most appropriate antibiotic for the specific infection
* Use the lowest effective dose and shortest duration of treatment
* Monitor for signs of resistance and adjust treatment accordingly
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, levofloxacin is a valuable antibiotic that plays a critical role in the treatment of various bacterial infections. However, its use must be guided by a thorough understanding of its properties, potential side effects, and interactions. As the threat of antibiotic resistance continues to grow, it is essential to use levofloxacin and other antibiotics responsibly, following established guidelines and principles of antibiotic stewardship. Ongoing research and development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments will be crucial in addressing the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance and ensuring the continued effectiveness of medications like levofloxacin.
What is levofloxacin used for?
+
Levofloxacin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and prostatitis.
What are the common side effects of levofloxacin?
+
Common side effects of levofloxacin include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, and insomnia. Rare but serious side effects can include tendinitis, peripheral neuropathy, and central nervous system effects.
Can I take levofloxacin with other medications?
+
Levofloxacin can interact with various medications, including antacids, warfarin, theophylline, cyclosporine, and digoxin. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to minimize the risk of interactions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with levofloxacin in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns about this medication, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to explore our other resources on antibiotic use and stewardship. By working together, we can promote responsible antibiotic use and ensure the continued effectiveness of medications like levofloxacin.