Intro
Discover the versatile uses of Lisinopril, a popular ACE inhibitor, in managing hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy, while also exploring its benefits in stroke prevention and cardiovascular protection.
The importance of managing blood pressure and heart health cannot be overstated. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. One of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure is Lisinopril. This angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor has been a cornerstone in the management of cardiovascular health for decades. In this article, we will delve into the uses of Lisinopril, its benefits, and how it works to improve heart health.
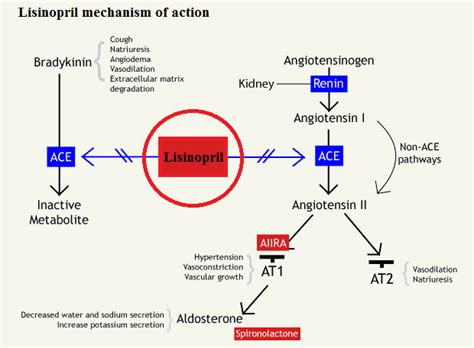
Lisinopril is a medication that has been extensively studied and proven to be effective in reducing the risk of major cardiovascular events. Its mechanism of action involves blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure. By inhibiting this conversion, Lisinopril helps to relax blood vessels, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the workload on the heart. This makes it an essential medication for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
The use of Lisinopril has been widely accepted due to its efficacy and safety profile. It is often prescribed as a first-line treatment for hypertension, especially in patients with diabetes or kidney disease. Lisinopril has also been shown to reduce the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular mortality in patients with heart failure. Additionally, it is used to treat conditions such as acute myocardial infarction, diabetic nephropathy, and renovascular hypertension. With its proven track record and numerous benefits, it is no wonder that Lisinopril remains a popular choice among healthcare professionals for the management of cardiovascular health.
What is Lisinopril Used For?

Benefits of Lisinopril
The benefits of Lisinopril are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using Lisinopril include: * Reduced blood pressure: Lisinopril helps to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. * Improved heart function: By decreasing the workload on the heart, Lisinopril can improve heart function and reduce the risk of heart failure. * Kidney protection: Lisinopril has been shown to slow the progression of kidney disease, especially in patients with diabetes. * Reduced risk of cardiovascular events: Lisinopril has been proven to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including heart attacks, strokes, and cardiovascular mortality.How Does Lisinopril Work?
Steps to Take Lisinopril
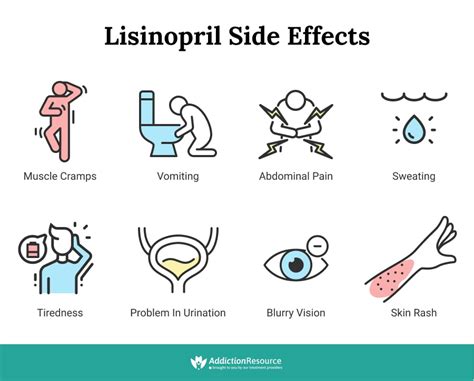
To get the most out of Lisinopril, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions. Here are some steps to take Lisinopril effectively: * Take Lisinopril exactly as prescribed: Follow the dosage and administration instructions provided by your healthcare professional. * Take Lisinopril at the same time every day: Consistency is key when taking Lisinopril. Take it at the same time every day to help maintain a consistent level of the medication in your system. * Monitor your blood pressure: Regularly monitor your blood pressure to ensure that Lisinopril is working effectively. * Report any side effects: If you experience any side effects, such as dizziness, coughing, or swelling, report them to your healthcare professional immediately.Lisinopril Side Effects
Lisinopril Interactions
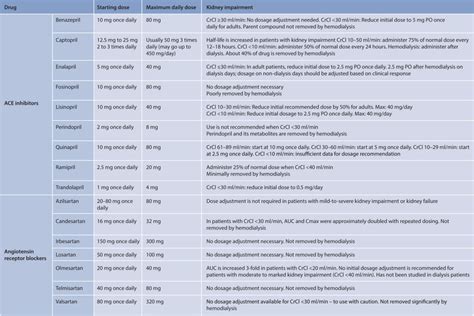
Lisinopril can interact with other medications, including: * Diuretics: Lisinopril can increase the risk of hypotension (low blood pressure) when taken with diuretics. * Potassium-sparing diuretics: Lisinopril can increase the risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) when taken with potassium-sparing diuretics. * Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Lisinopril can increase the risk of kidney damage when taken with NSAIDs. * Lithium: Lisinopril can increase the risk of lithium toxicity when taken with lithium.Lisinopril Dosage
Lisinopril Warnings
Lisinopril can cause serious side effects, including: * Angioedema: Lisinopril can cause angioedema, a severe swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat. * Hyperkalemia: Lisinopril can cause hyperkalemia, especially in patients with kidney disease. * Renal impairment: Lisinopril can cause renal impairment, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.What is the most common use of Lisinopril?
+The most common use of Lisinopril is to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and heart failure.
What are the benefits of taking Lisinopril?
+The benefits of taking Lisinopril include reduced blood pressure, improved heart function, and reduced risk of cardiovascular events.
Can Lisinopril be taken with other medications?
+Lisinopril can interact with other medications, including diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, NSAIDs, and lithium. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Lisinopril with other medications.
In conclusion, Lisinopril is a widely used and effective medication for the treatment of hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions. Its benefits, including reduced blood pressure, improved heart function, and reduced risk of cardiovascular events, make it an essential medication for patients with cardiovascular disease. By understanding the uses, benefits, and potential side effects of Lisinopril, patients can work with their healthcare professionals to develop an effective treatment plan. We invite you to share your experiences with Lisinopril, ask questions, or provide feedback on this article. Your input is valuable to us, and we look forward to hearing from you.
