Intro
Discover Lisinopril uses and benefits, including blood pressure management, heart failure treatment, and kidney protection, with its ACE inhibitor properties and cardiovascular benefits.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing blood pressure. The importance of lisinopril lies in its ability to manage conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and to protect the kidneys from damage due to diabetes. Understanding the uses and benefits of lisinopril is crucial for patients who are prescribed this medication, as well as for healthcare providers who recommend it.
The mechanism of action of lisinopril involves the inhibition of the angiotensin-converting enzyme, a naturally occurring substance in the body that constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure. By blocking this enzyme, lisinopril causes the blood vessels to relax and widen, which lowers blood pressure and increases the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. This action not only helps in reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke but also alleviates the symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and swelling in the legs.
Lisinopril's benefits extend beyond its primary use in managing high blood pressure and heart failure. It has been shown to reduce the progression of diabetic nephropathy, a type of kidney damage that occurs in people with diabetes. The protective effects of lisinopril on the kidneys are particularly significant, as diabetic nephropathy can lead to end-stage renal disease, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Furthermore, lisinopril may be prescribed after a heart attack to improve survival and reduce the risk of further cardiovascular events.
Lisinopril Mechanism of Action

How Lisinopril Works
The process by which lisinopril works can be broken down into several key steps: - Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: Lisinopril binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme, preventing it from converting angiotensin I into angiotensin II. - Reduction in Angiotensin II Levels: Lower levels of angiotensin II result in decreased vasoconstriction and reduced stimulation of the adrenal glands to release aldosterone. - Decrease in Aldosterone Secretion: With less aldosterone, the body retains less water and sodium, leading to a decrease in blood volume. - Relaxation of Blood Vessels: The reduction in angiotensin II also leads to the relaxation of the smooth muscle in blood vessels, causing them to dilate.Lisinopril Uses

Lisinopril for High Blood Pressure
For patients with high blood pressure, lisinopril is often prescribed as a first-line treatment due to its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure and its protective effects on the kidneys and heart. It can be used alone or in combination with other medications, such as diuretics or calcium channel blockers, to achieve better blood pressure control.Lisinopril for Heart Failure
In the context of heart failure, lisinopril helps to reduce the workload on the heart by lowering blood pressure and reducing the amount of fluid in the lungs, making it easier to breathe. This can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with heart failure and reduce the risk of hospitalization due to worsening symptoms.Lisinopril Benefits

Long-Term Benefits
The long-term benefits of lisinopril include a reduced risk of end-stage renal disease in diabetic patients and a decrease in mortality rates among patients with heart failure. These benefits underscore the importance of adherence to treatment and regular monitoring by healthcare providers to adjust the dosage as necessary and to manage any potential side effects.Lisinopril Side Effects
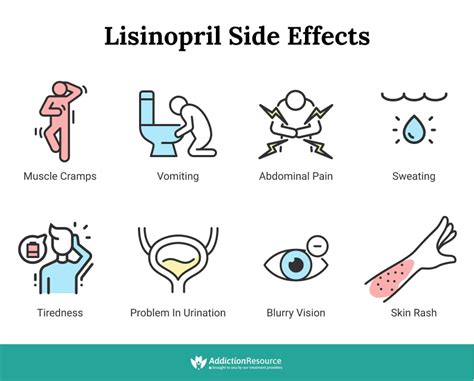
Managing Side Effects
Most side effects of lisinopril are mild and temporary, but in some cases, they can be more severe. Patients experiencing side effects should consult their healthcare provider, who may adjust the dosage or recommend alternative treatments.Lisinopril Interactions

Avoiding Drug Interactions
To avoid potential drug interactions, patients should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Regular monitoring of kidney function and blood potassium levels may be necessary for patients taking lisinopril, especially when combined with other medications.Lisinopril Dosage
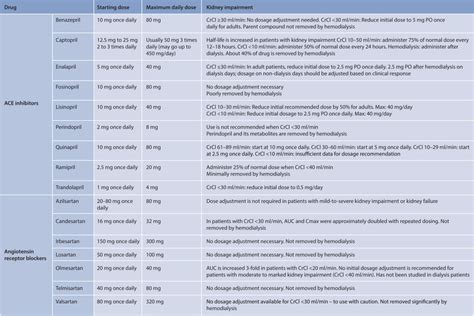
Adjusting the Dosage
The dosage of lisinopril may need to be adjusted based on the patient's blood pressure response and kidney function. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and to make any necessary adjustments to the dosage.Lisinopril and Pregnancy

Alternative Treatments During Pregnancy
For pregnant women with high blood pressure, other medications that are safer during pregnancy may be prescribed. Close monitoring of blood pressure and fetal development is crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.Lisinopril and Breastfeeding
Monitoring During Breastfeeding
Women who are breastfeeding and taking lisinopril should monitor their infant for any signs of side effects, such as drowsiness, lethargy, or changes in feeding patterns. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to identify any potential issues early.What is the primary use of lisinopril?
+Lisinopril is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and congestive heart failure.
How does lisinopril work?
+Lisinopril works by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, leading to the relaxation of blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure.
What are the common side effects of lisinopril?
+Common side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, fatigue, headache, and nausea.
Can lisinopril be used during pregnancy?
+Lisinopril is generally not recommended during pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters, due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus.
Is lisinopril safe for breastfeeding mothers?
+Lisinopril is excreted in breast milk, but the amount is generally considered to be low. However, nursing mothers should consult their healthcare provider before taking lisinopril.
In conclusion, lisinopril is a valuable medication for the management of high blood pressure, heart failure, and the protection of the kidneys in diabetic patients. Its benefits are well-documented, and when used appropriately, it can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. As with any medication, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage, monitor for side effects, and attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider. By understanding the uses, benefits, and potential side effects of lisinopril, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve the best possible outcomes. We invite readers to share their experiences with lisinopril, ask questions, or seek further information on this topic, and we encourage healthcare providers to continue educating their patients about the importance of adherence to treatment and regular monitoring.
