Intro
Discover a comprehensive Low Fiber Foods List, featuring gentle digestive options like lean meats, low-fiber fruits, and refined grains, ideal for digestive health and low-fiber diets, including gut-friendly and easily digestible foods.
The importance of dietary fiber in maintaining a healthy digestive system and overall well-being cannot be overstated. However, there are instances where individuals may need to limit or avoid high-fiber foods, such as during certain medical procedures, digestive issues, or specific dietary requirements. Understanding which foods are low in fiber is crucial for these individuals to manage their diet effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of low-fiber foods, exploring their benefits, examples, and how they can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
For many, the concept of a low-fiber diet might seem counterintuitive, given the emphasis on the health benefits of high-fiber foods. Nonetheless, there are scenarios where reducing fiber intake is necessary, and knowing which foods to choose can make a significant difference. Whether you're looking to manage digestive issues, prepare for a medical procedure, or simply understand more about dietary fiber, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to low-fiber foods.
The need for a low-fiber diet can arise from various health conditions or requirements. For instance, individuals with gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis might find that high-fiber foods exacerbate their symptoms, necessitating a period of low-fiber intake to allow their digestive system to heal. Similarly, before certain surgeries or procedures, healthcare providers may recommend a low-fiber diet to minimize the risk of complications. Understanding the role of fiber in the diet and identifying low-fiber food options can help individuals navigate these dietary restrictions with ease.
Introduction to Low Fiber Foods

Low-fiber foods are typically those that have been processed or naturally contain lower amounts of dietary fiber. Dietary fiber refers to the parts of plant foods your body can't digest or absorb. Unlike other food components, such as fats, proteins, or carbohydrates, which your body breaks down and absorbs, fiber isn't digested by your body. Instead, it passes relatively intact through your stomach, small intestine, and colon and out of your body. Foods that are low in fiber include many types of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products, as well as refined or processed grains.
Benefits of Low Fiber Foods
The benefits of incorporating low-fiber foods into your diet, especially when medically advised, can be significant. For individuals with certain digestive conditions, reducing fiber intake can help alleviate symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel movements. Additionally, a low-fiber diet may be recommended before and after certain surgeries to reduce the risk of complications. However, it's essential to follow such dietary recommendations under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure you're getting all the necessary nutrients.Examples of Low Fiber Foods
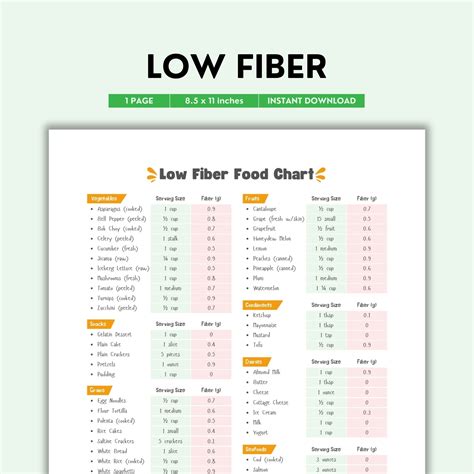
Examples of low-fiber foods include:
- Meat and Poultry: Beef, pork, lamb, chicken, turkey, and fish are all naturally low in fiber.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and eggs contain little to no fiber.
- Refined Grains: White bread, pasta, rice, and cereals that are not whole grain are low in fiber.
- Fruits and Vegetables: While many fruits and vegetables are high in fiber, some have lower amounts. Examples include bananas, avocados (in moderation), and well-cooked, skinless, seedless vegetables like carrots, green beans, and cucumbers.
- Processed Snacks: Many processed foods, such as crackers, chips, and cookies, are low in fiber due to their refined ingredients.
Working Mechanisms of Low Fiber Diets
A low-fiber diet works by reducing the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, thereby minimizing the risk of irritation or blockage in the digestive tract. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals undergoing certain medical procedures or those with specific gastrointestinal conditions. However, it's crucial to balance the reduction of fiber with the inclusion of other essential nutrients to prevent malnutrition.Steps to Incorporate Low Fiber Foods into Your Diet

Incorporating low-fiber foods into your diet, especially if you're used to consuming a lot of fiber, requires some planning. Here are steps you can follow:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before making any significant changes to your diet, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a dietitian. They can provide personalized advice based on your health needs and ensure that you're getting all the necessary nutrients.
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat can help identify high-fiber foods in your diet and find low-fiber alternatives.
- Choose Low-Fiber Alternatives: For example, choose white bread instead of whole wheat, or opt for well-cooked vegetables over raw ones.
- Gradually Adjust Your Diet: Sudden changes can be challenging for the digestive system. Gradually introducing low-fiber foods can help your body adjust.
Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that a low-fiber diet can significantly reduce symptoms in individuals with certain gastrointestinal conditions. For instance, a study on patients with Crohn's disease found that a low-fiber diet during flare-ups could help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Similarly, data from nutritional surveys indicate that many processed foods, which are often low in fiber, make up a significant portion of the average diet in many countries.Benefits and Risks of Low Fiber Diets
While a low-fiber diet can offer benefits for certain individuals, it's also important to consider the potential risks. A diet that is too low in fiber can lead to constipation, diverticulitis, and an increased risk of heart disease due to the lack of beneficial fiber. Therefore, it's crucial to balance the need for low-fiber intake with the inclusion of a variety of other nutrient-dense foods.
Key Information and Steps
Key to managing a low-fiber diet is understanding which foods are low in fiber and incorporating them into your meal plan in a balanced way. Here are some key points to consider: - **Stay Hydrated:** Drinking plenty of water can help prevent constipation, a common side effect of low-fiber diets. - **Choose Lean Proteins:** Lean meats, poultry, and fish are not only low in fiber but also rich in essential proteins. - **Incorporate Healthy Fats:** Foods like avocados (in moderation), nuts, and olive oil provide essential fats and can add flavor to low-fiber meals.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, while high-fiber foods are widely recognized for their health benefits, there are scenarios where a low-fiber diet is necessary. By understanding what constitutes low-fiber foods and how to incorporate them into your diet, individuals can better manage their health requirements. Whether you're looking to alleviate digestive symptoms, prepare for a medical procedure, or simply expand your knowledge of dietary fiber, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of low-fiber foods and their role in a balanced diet.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with low-fiber diets in the comments below. Have you found certain low-fiber foods to be particularly beneficial or challenging to incorporate into your diet? Your insights can help others navigate their own dietary needs. Additionally, consider sharing this article with anyone who might benefit from understanding more about low-fiber foods and their importance in certain health contexts.
What are low-fiber foods?
+Low-fiber foods are those that contain less than 2 grams of fiber per serving. Examples include meats, dairy products, refined grains, and certain fruits and vegetables.
Why might someone need a low-fiber diet?
+A low-fiber diet may be recommended for individuals with certain gastrointestinal conditions, before and after certain surgeries, or for those who need to minimize digestive discomfort.
How can I ensure I'm getting enough nutrients on a low-fiber diet?
+Consult with a healthcare provider or dietitian to plan a balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs while limiting fiber intake. Focus on a variety of lean proteins, healthy fats, and low-fiber fruits and vegetables.
