Intro
Discover the causes of menopause spotting, including hormonal changes, thinning lining, and fibroids, and learn how to manage irregular bleeding during perimenopause and postmenopause.
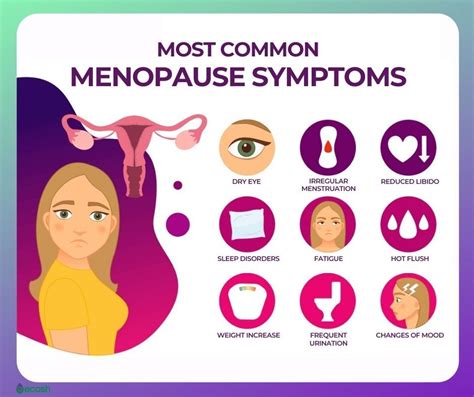
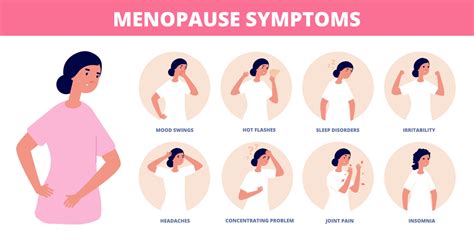
As women approach menopause, they may experience a range of symptoms, including hot flashes, mood swings, and changes in their menstrual cycle. One common symptom that can be particularly concerning is menopause spotting. This phenomenon refers to the light bleeding or spotting that occurs between periods or after menopause. Understanding the causes of menopause spotting is essential for women to navigate this transition with confidence and seek medical attention if necessary.
Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs when the ovaries stop producing eggs, and hormone levels decrease. During this time, the body undergoes significant changes, affecting the reproductive system and overall health. Menopause spotting can be a result of these hormonal fluctuations, as the body adjusts to the new balance of estrogen and progesterone. In some cases, spotting may be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. It is essential for women to be aware of the potential causes of menopause spotting to ensure their health and well-being.
The experience of menopause spotting can vary from woman to woman. Some may notice light bleeding or spotting between periods, while others may experience heavier bleeding or prolonged spotting. In some cases, menopause spotting can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as cramping, bloating, or mood changes. Understanding the potential causes of menopause spotting can help women identify when to seek medical attention and how to manage their symptoms effectively.
Introduction to Menopause Spotting

Menopause spotting is a common symptom experienced by many women during the menopausal transition. It is essential to understand that menopause spotting is not the same as a regular menstrual period. Menstrual periods occur when the uterus sheds its lining, whereas menopause spotting is often caused by hormonal fluctuations or other factors. Women who experience menopause spotting may notice light bleeding or spotting between periods, after sex, or after menopause.
Types of Menopause Spotting
Menopause spotting can be classified into different types, depending on the underlying cause. Some common types of menopause spotting include: * Irregular spotting: This type of spotting occurs when the menstrual cycle becomes irregular, leading to light bleeding or spotting between periods. * Postmenopausal spotting: This type of spotting occurs after menopause, when the ovaries have stopped producing eggs, and hormone levels have decreased. * Intermenstrual spotting: This type of spotting occurs between periods, often due to hormonal fluctuations or other factors.Causes of Menopause Spotting

Menopause spotting can be caused by a range of factors, including hormonal fluctuations, uterine fibroids, polyps, and other medical conditions. Some common causes of menopause spotting include:
- Hormonal fluctuations: The decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels during menopause can cause the uterine lining to become thinner, leading to light bleeding or spotting.
- Uterine fibroids: These non-cancerous growths can cause heavy bleeding, spotting, or prolonged menstrual periods.
- Polyps: These growths can occur on the cervix or in the uterus, causing irregular bleeding or spotting.
- Endometrial hyperplasia: This condition occurs when the uterine lining becomes too thick, leading to irregular bleeding or spotting.
Risk Factors for Menopause Spotting
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing menopause spotting. These include: * Age: Women over 45 years old are more likely to experience menopause spotting. * Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of hormonal imbalances, leading to menopause spotting. * Family history: Women with a family history of menopause spotting or other gynecological conditions may be more likely to experience spotting. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase the risk of menopause spotting.Diagnosing Menopause Spotting
Diagnosing menopause spotting requires a comprehensive medical evaluation. Women who experience menopause spotting should consult their healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical conditions. The diagnosis may involve:
- Medical history: The healthcare provider will ask questions about the woman's medical history, including her menstrual cycle, symptoms, and any previous gynecological conditions.
- Physical exam: A physical exam will be performed to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive system.
- Pelvic exam: A pelvic exam may be performed to check for any abnormalities in the cervix, uterus, or ovaries.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, may be performed to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive system.
Treatment Options for Menopause Spotting
Treatment options for menopause spotting depend on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include: * Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): HRT may be prescribed to regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce menopause spotting. * Birth control pills: Birth control pills may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce menopause spotting. * Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove any growths or abnormalities that are causing menopause spotting.Managing Menopause Spotting
Managing menopause spotting requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Women who experience menopause spotting can try the following:
- Keep a menstrual diary: Keeping track of the menstrual cycle and symptoms can help identify any patterns or changes.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques: Stress can exacerbate menopause symptoms, including spotting. Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help manage symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of hormonal imbalances, leading to menopause spotting. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of spotting.
Lifestyle Changes for Menopause Spotting
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing menopause spotting. Some lifestyle changes that may help include: * Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce menopause spotting. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances. * Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and regulate hormonal imbalances, reducing the risk of menopause spotting.Conclusion and Next Steps

Menopause spotting can be a concerning symptom for many women. Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options can help women navigate this transition with confidence. By making lifestyle changes and seeking medical attention when necessary, women can manage their symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. If you are experiencing menopause spotting, consult your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
We invite you to share your experiences and ask questions about menopause spotting in the comments below. Your input can help others who are going through similar situations. Please share this article with anyone who may benefit from this information, and let's work together to support women's health and well-being.
What is menopause spotting?
+Menopause spotting refers to the light bleeding or spotting that occurs between periods or after menopause.
What are the common causes of menopause spotting?
+Common causes of menopause spotting include hormonal fluctuations, uterine fibroids, polyps, and other medical conditions.
How is menopause spotting diagnosed?
+Diagnosing menopause spotting requires a comprehensive medical evaluation, including a medical history, physical exam, pelvic exam, and imaging tests.
